Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: Iguratimod (IGU), known as T-614, is a small-molecule antirheumatic drug developed in Japan and used in Japanese clinical practice since June in 2012. IGU is known to inhibit nuclear factor-kappa B activation in cultured human synovial cells. Although biological agents (BIO) have good efficacy to treat rheumatoid arthritis (RA), they costs very much. IGU is not comparatively expensive and used as monotherapy or combination therapy with methotrexate (MTX). Data in clinical practice is lacking and necessary for the best use of IGU.This retrospective study investigated efficacy of IGU in RA patients with focus on disease activity at initiation of IGU using data from the Japanese multicenter registry.
Methods: 78 cases (62 female and 16 male) with RA from 9 institutes in Japan were included. These patients were divided into two groups (high disease activity group; HG and moderate and low disease activity group; MLG) using DAS28-CRP at initiation of IGU. 42 cases were included in HG and 36 cases were included in MLG. Patients’ characteristics, time course of disease activity, drug retention rate at 24 weeks and change value in disease activity parameters from 0w to 24w were compared with each other.
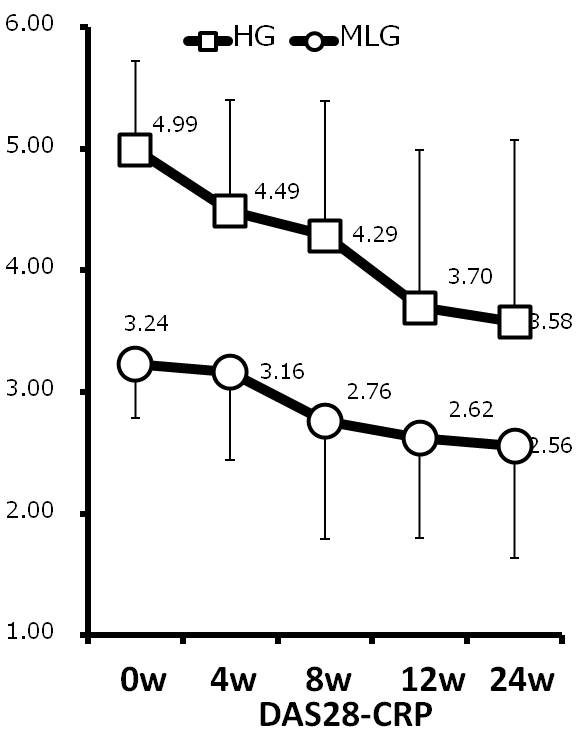
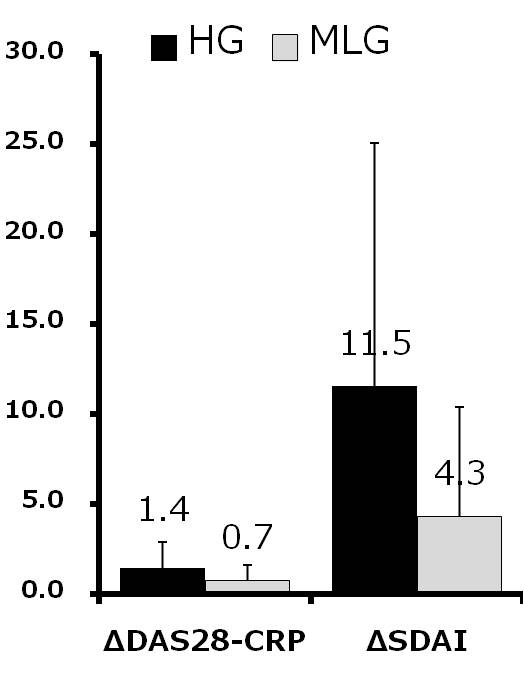
Results and Conclusion: Mean age was 68.3 years old in HG and 65.7 years old in MLG. Mean RA duration was 147 months in HG and 94 months in MLG. Although MTX use rate was low in HG compared with in MLG (52.4% vs. 63.9%), there was no significant difference between groups. The mean dose of MTX used was 4.7 mg/w in HG and 5.2 mg/w in MLG. The mean DAS28-CRP at 0, 4, 8, 12 and 24w was 4.99, 4.49, 4.29, 3.70 and 3.58 in HG and 3.24, 3.16, 2.76, 2.62 and 2.56 in MLG. DAS28-CRP was significantly decreased after 4w in HG and after 8w in MLG. Similar findings were observed in SDAI. Drug retention rates at 24w were 81.0% in HG and 86.1% in MLG (not significant). Delta DAS28-CRP from 0w to 24w was 1.4 in HG and 0.7 in MLG (p=0.04). Delta SDAI were 11.5 in HG and 4.3 in MLG (p=0.02). There were significant differences in delta tender joints counts, delta ESR between two groups and better improvement was seen in HG than MLG. More treatment options other than sufficient MTX and BIO are needed in RA patients with concomitant disease such as lung disease or renal dysfunction. High cost of BIO is another issue to inhibit improvement of signs and symptoms in RA patients. This study suggests that IGU is one of the options not only in RA patients with high disease activity treated with insufficient MTX.
Disclosure:
Y. Hirano,
Abbott Immunology Pharmaceuticals,
8,
Mitsbishi-Tanabe Pharma,
8,
Pfizer Inc,
8,
Eisai,
8,
Chugai,
8,
Bristol-Myers Squibb,
8,
Astellas Pharma,
8;
T. Kojima,
Takeda Pharma Corporation, Janssen Pharmaceutical, and Astellas Pharma Corporation.,
2,
Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation, Takeda Pharma Corporation, Eisai Pharma Corporation, Abbvie, Bristol-Myers Squibb、Pfizer and Chugai Pharma Corporation,
8;
Y. Kanayama,
Astellas Pharma,
8,
Eisai,
8;
S. Hirabara,
None;
N. Takahashi,
Abbott Japan Co. Ltd., Eisai Co. Ltd., Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation, Pfizer Co. Ltd, Chugai Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., and Bristol-Myers Squibb Co. Ltd. ,
8;
A. Kaneko,
Janssen Pharmaceutica Product, L.P.,
8,
Astellas Pharma,
8,
Mitsubishi-Tanabe Pharma,
8,
Chugai,
8,
Eisai,
8,
Abbott Immunology Pharmaceuticals,
8,
Bristol-Myers Squibb,
8;
N. Ishiguro,
AbbVie, Chugai, Daiichi-Sankyo, Eisai, Mitsubishi Tanabe, Pfizer and Takeda.,
5,
AbbVie, Chugai, Daiichi-Sankyo, Eisai, Mitsubishi Tanabe, Pfizer and Takeda.,
8.
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/influences-of-disease-activity-at-the-initiation-of-iguratimod-a-small-molecule-antirheumatic-drug-on-efficacy-of-iguratimod-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-multicenter-registr/