Background/Purpose
Significant advances have been made in the diagnosis and treatment of patients with ANCA-associated vasculitis (AAV). However, little is known about how these advances have changed long-term outcomes especially among patients with renal involvement. The objective of this study was to examine temporal changes of long-term outcomes, including the impact of early diagnosis and duration of cyclophosphamide use in AAV.
Methods
An inception cohort of patients with AAV from the Glomerular Disease Collaborative Network diagnosed from 1985 and 2009 was evaluated. All patients had a positive test for ANCA and a renal biopsy consistent with AAV. Patients were categorized into 5-year time periods based on year of diagnosis. The primary outcome was occurrence of end-stage renal disease (ESRD) or death in 5 years; secondary outcome was occurrence of relapse in 5 years. Kaplan-Meier estimates, Cox proportional hazard models, and linear contrasts were used for analysis. Models were adjusted for age, sex, race, diagnosis (granulomatosis with polyangiitis, microscopic polyangiitis, or renal-limited vasculitis), ANCA type (C/PR3 or P/MPO), site (tertiary care or community practice), duration of disease before biopsy, extra-renal organ involvement, and serum creatinine (SCr) at time of diagnosis. In a subgroup of patients with no event by 12 months, duration on cyclophosphamide (CYCdur, months) up to 12 months was also included.
Results
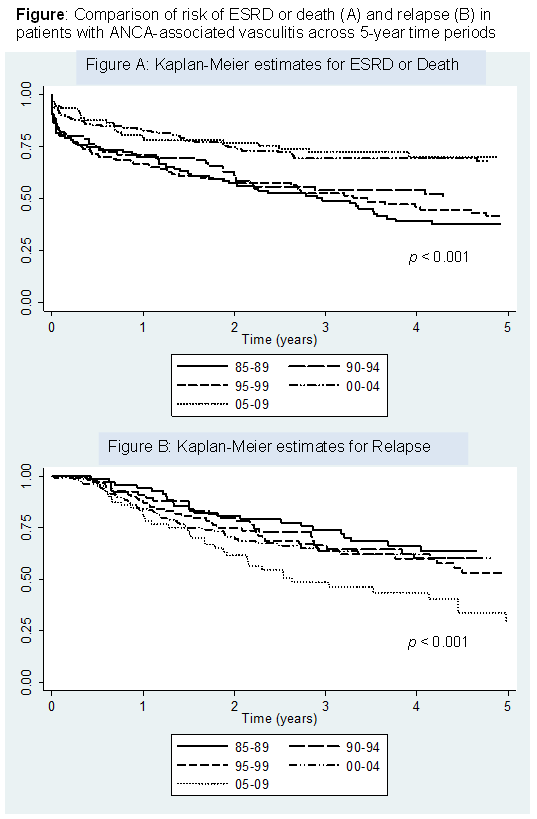
Data was available on 568 patients who met the inclusion criteria. Across the 5 time periods, there were no significant differences in baseline characteristics or duration of follow-up; however, over time increasing proportions of patients were managed in a tertiary care center and baseline SCr decreased (Table). There was a decreasing 5-year risk of ESRD or death across the time periods and an increasing 5-year risk of relapse, p for trend < 0.001 (Figure). After adjustment for baseline characteristics, the risk of relapse was similar between the time periods (p for trend = 0.698) but the risk of ESRD or death continued to decrease over time (p for trend = 0.008). SCr was the only significant predictor of decreasing risk of ESRD or death (HR 1.14, 95% CI 1.08-1.21, P<0.001) while CYCdur was not associated with risk of ESRD or death.
Conclusion
In patients with AAV, over 25 years, the risk of ESRD or death decreased and the risk of relapse has not changed. A lower SCr at diagnosis, a potential marker of earlier disease detection, is the strongest predictor of improvement in risk of ESRD or death.
|
Table: Patient characteristics at diagnosis |
|||||||
|
Characteristic |
All |
Time Period |
p-value |
||||
|
85-89 |
90-94 |
95-99 |
00-04 |
05-09 |
for trend |
||
|
N |
568 |
88 |
81 |
136 |
172 |
91 |
— |
|
Median age, years (IQR) |
60 (46-71) |
61 (18-70) |
61 (42-68) |
64 (49-72) |
58 (47-71) |
58 (46-68) |
0.32 |
|
Female, % |
47% |
47% |
52% |
46% |
49% |
42% |
0.80 |
|
Race, % White Black Other |
85% 9% 6% |
85% 14% 1% |
84% 10% 6% |
91% 7% 1% |
84% 8% 8% |
79% 9% 12% |
0.17 0.61 0.01 |
|
Diagnosis, % GPA MPA RLV |
20% 55% 24% |
15% 60% 25% |
21% 49% 30% |
20% 54% 26% |
20% 56% 24% |
25% 57% 18% |
0.62 0.68 0.48 |
|
ANCA ELISA, % PR3/P MPO/C |
41% 59% |
44% 56% |
35% 65% |
44% 56% |
41% 59% |
36% 64% |
0.58 |
|
Organ Involvement, % Lung Joint Upper respiratory Skin GI Neurologic Muscle |
50% 41% 35% 22% 11% 10% 3% |
50% 35% 35% 22% 15% 14% 6% |
41% 35% 28% 26% 16% 9% 7% |
50% 40% 35% 25% 12% 15% 2% |
52% 44% 33% 19% 8% 8% 3% |
53% 47% 43% 18% 4% 7% 0% |
0.49 0.39 0.43 0.52 0.08 0.25 0.18 |
|
Mean serum creatinine, mg/dl (SD) |
4.5 (3.5) |
5.9 (4.1) |
4.9 (3.7) |
4.7 (3.4) |
3.9 (3.2) |
3.5 (2.6) |
<0.001 |
|
Duration of follow-up, median months (IQR) |
31 (11-66) |
33 (5-68) |
31 (7-72) |
25 (7-48) |
29 (14-91) |
38 (11-55) |
0.33 |
|
Tertiary care, % (vs community practice) |
48% |
31% |
27% |
41% |
54% |
82% |
< 0.001 |
|
*Test of significance for linear contrast of 5 time periods. GPA: granulomatosis with polyangiitis; MPA: microscopic polyangiitis; RLV: renal-limited vasculitis. |
|||||||
Disclosure:
R. L. Rhee,
None;
S. L. Hogan,
None;
C. J. Poulton,
None;
J. A. G. McGregor,
None;
J. R. Landis,
None;
R. Falk,
None;
P. A. Merkel,
Genentech and Biogen IDEC Inc.,
2,
Bristol-Myers Squibb,
2,
GlaxoSmithKline,
2,
Actelion Pharmaceuticals US,
2,
Actelion Pharmaceuticals US,
5,
Sanofi-Aventis Pharmaceutical,
5,
Chemocentryx,
5.
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/long-term-outcomes-among-patients-with-renal-disease-secondary-to-anca-associated-vasculitis-temporal-trends-over-25-years/