Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: Galectin-3 has been suggested as a pro-inflammatory mediator in Rheumatoid Arthritis(1). Thus, Galectin-3 is over-expressed in RA-synovitis and bone erosions were significantly decreased in GAL-3 -/- mice compared with wild type animals (2,3). Furthermore, in long-standing RA, Galectin-3 was increased in synovial fluid and serum compared with osteoarthritis and controls (2). These findings indicate that Galectin-3 may serve as biomarker for synovitis pathology in RA.
The objectives of this study were to investigate whether serum Galectin-3 exhibits circadian variation and/or is influenced by physical exercise in patients with RA at different stages and controls.
Methods: The study on circadian patterns comprised eleven patients with newly diagnosed RA, disease duration less than 6 months (ERA), 10 patients with long-standing RA (5-15 years (LRA)) and 16 self-reportedly healthy control subjects. During 24 hours 7 blood samples were drawn at 3-hour intervals starting at 10 a.m. through 10 p.m. and at 7 and 10 a.m. on the following day. The study on the effect of physical activity included 10 patients with ERA, 10 with LRA and 14 controls. The participants underwent a standardized exercise program and four blood samples were drawn before, during and after exercise. Serum Galectin-3 was quantified by ELISA (R&D systems). An age and sex adjusted mixed model analysis was applied in both substudies.
Results: Circadian variation substudy: Galectin-3 was borderline increased at baseline in ERA and LRA, 6.03 ug/l (95% CI 4.44;7.61) and 5.95 ug/l (4.44;7.47) vs. 4.51 ug/l (3.48;5.53) in control subjects (p = 0.08). There was no association between time of blood sampling and Galectin-3 in serum (p = 0.85).
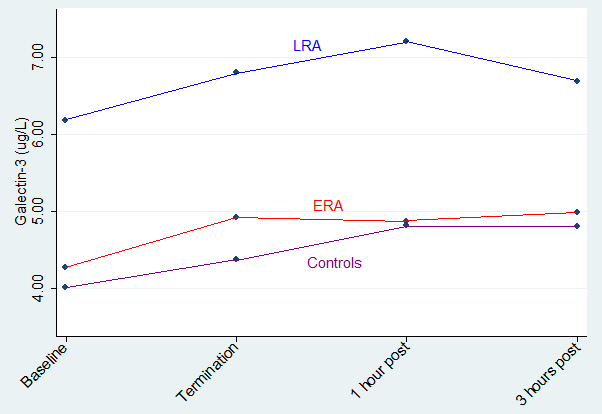
Physical exercise substudy: Baseline mean Galectin-3 in both subsets was also elevated, however without reaching statistical significance in the ERA group; LRA 6.18 ug/l (95% CI 4.46;7.89; p = 0.01), ERA 4.27 ug/l (3.23;5.30; p = 0.68) vs controls 4.01 ug/l (3.10;4.91). A submaximal physical challenge elicited comparable Gal-3 increments at 10-15% above baseline with peak values 1-3 hours post exercise in RA patients and controls (p-value < 0.001), fig. 1.
Figure 1. Galectin-3 increments in healthy controls, and in patients with early (ERA) and longstanding rheumatoid arthritis (LRA) before and after termination of exercise.
Conclusion: Circulating Galectin-3 was increased in early and longstanding RA. Galectin-3 did not exhibit circadian variation. Galectin-3 increased comparably in RA patients and healthy controls following submaximal exercise, which should be avoided before bloodsampling for Galectin-3 determination.
Acknowledgements: We would like to thank The Danish Rheumatism Association for financial support.
References:
1) Filer A et al. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;60:1604-14.
2) Ohshima S et al. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;48:2788-95.
3) Forsman H et al. Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63:445-54.
Disclosure:
S. F. Issa,
None;
A. F. Christensen,
None;
T. Lottenburger,
None;
K. Junker,
None;
H. M. Lindegaard,
None;
K. Hoerslev-Petersen,
None;
P. Junker,
None.
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/within-day-variation-and-influence-of-physical-exercise-on-circulating-galectin-3-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-and-healthy-individuals/