Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: T helper cell(Th17), the third lineage of CD4+T cells, has been determined its important role in pathogenesis of AS, and its main effector, IL-17, has a critical effect on mediating AS inflammation. Survival and function of Th17 is dependent on induction of IL-23. And JAK2/STAT3 signal pathway works on IL-23 signal transduction essentially. Here we investigate the role of JAK2/STAT3 signal pathway and IL-23/Th17 in pathogenesis of AS.
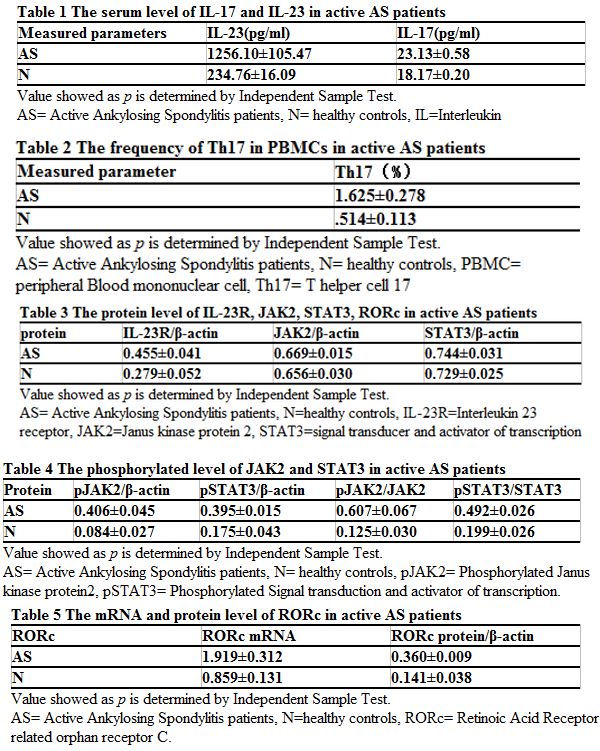
Methods: A total of 30 AS patients( average age, 27.6±9.5years) in active stage and 30 healthy controls(average age, 23.5±3.6 years) without any tissue diseases participated in the experiments. All patients were diagnosed with AS by experienced rheumatologists and met with the modified New York criteria(Bath Disease Activity Score ≥4). The serum level of IL-17 and IL-23 in peripheral serum were detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay(ELISA), the percentage of Th17 were detected by flow cytometry, the protein levels of JAK2/STAT3 signal pathway mainly involved in IL-23R, JAK2, pJAK2, STAT3, pSTAT3 and RORc(the lineage-specific transcription factor of Th17) were detected by Western blotting, and the mRNA level of RORc was detected by real-time quantitative PCR(qPCR).
Results: The serum IL-23 and IL-17 levels were significantly higher of active AS patients than that of the healthy controls(IL-23:p<0.001; IL-17:p<0.001). The frequency of Th17 in PBMCs were also elevated(p<0.001). About the proteins of JAK2/STAT3 signal pathway, the level of IL-23R was higher in PBMCs of AS patients than that of the healthy controls (p<0.05), and though we found no differences of JAK2 and STAT3 in PBMCs between AS patients and healthy controls(JAK2:p=0.538; STAT3_p=0.0.554), the phosphorylated levels of JAK2 and STAT3 were critically higher(pJAK2:p<0.001; pSTAT3:p<0.001). Besides, the protein level and mRNA level of RORc were both significantly higher in PBMCs of AS patients than that of the healthy controls(protein level: p<0.001; mRNA level: p<0.001).
Conclusion: Our findings showed the exist of high serum IL-23 level, high activity degree of JAK2/STAT3 signal pathway and high protein and mRNA level of RORc in active AS patients. Important as IL-23 for Th17’s differentiation and function, STAT3 phosphorylated by IL-23 signal can not only promote the expression of RORc, acting on differentiation of Th17, but bind to IL-17’s promoter, being a direct regulator of IL-17. That’s to say, high serum IL-23 level and its active JAK2/STAT3 signal pathway play a critical role in resulting in high serum IL-17 level and high frequency of Th17 existed in active AS patients. In this way, our results suggest the possible role of JAK2/STAT3 signal pathway and IL-23/Th17 axis in pathogenesis of AS.
Disclosure:
H. Liu,
None;
P. Chen,
None;
Y. Zhou,
None;
J. Song,
None;
B. Liu,
None;
X. Feng,
None;
X. Feng,
None.
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/highly-activated-il-23th17-axis-and-jak2stat3-signal-pathway-in-pbmc-of-active-as-patients-involve-in-pathogenesis/
