Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose
Biologics such as etanercept (ETN), adalimumab (ADA), infliximab (IFX) and tocilizumab (TCZ) have led dramatic improvement in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA), but the impact of their high drug costs on medical expenditure remains a concern. The aim of this study is to characterize the treatment patterns of patients with RA treated with biologics and evaluate the direct biologics cost and medical cost using Japanese claims data provided by Japan Medical Data Center Co., Ltd.
Methods
Patients with RA (defined by ICD10 code) treated with ETN, IFX, ADA, and TCZ between Jan, 2005 and Mar, 2013 were included. Annual costs of the biologics per patient, based on average daily dose and NHI drug price, were calculated from 2009 to 2012 for ETN, IFX, ADA, and TCZ. Patients were grouped based upon their initial prescription for either ETN, IFX, ADA, or TCZ. One year biologics cost including all biologics (including second or more, e.g. golimumab) and total medical cost following initial prescription were compared between ETN and the other treatment groups. Discontinuation and switching event rates to other biologics in each group were estimated using Kaplan-Meier survival analysis. Dose changes, based on +/-50% change in average dose per administration, at 3 month intervals were also evaluated up to 4 years following initial prescription.
Results
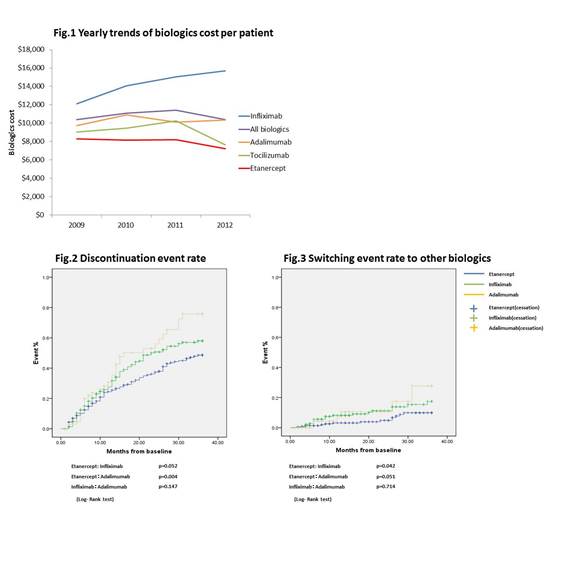
A total of 524 patients were identified for longitudinal analysis, with 45% (n=238) initiating ETN, 41% (n=217) initiating TFX, and 13% (n=69) initiating. The cross-sectional annual biologics cost was $8,000 in 2009 and $7,200 in 2012 in patients with ETN, $10,000 both in 2009 and in 2012 in patients with ADA, $12,000 in 2009 and $16,000 in 2012 in patients with IFX, $9,000 in 2009 and $8,000 in 2012 in patients with TCZ (Fig.1). The one year total medical costs from the initial prescription in ETN, IFX and ADA groups were approximately $19,000, $26,000 and $23,000, respectively (ETN: IFX p<0.001, ETN: ADA p<0.001). A similar trend was also observed in the biologics cost. The discontinuation event rates at 36 months was 48.6%, 58.0% and 75.8% in ETN, IFX and ADA group, respectively (ETN: IFX p=0.052, ETN: ADA p=0.004) (Fig.2). The switching event rate to other biologics at 36 months was 9.9%, 17.4% and 27.7% in ETN, IFX and ADA group, respectively (ETN: IFX p=0.042 , ETN: ADA p=0.052) (Fig.3). The longitudinal dose changing trend in IFX was different from ETN and ADA group.
Conclusion
The biologic and total medical costs, along with discontinuation and switching event rates were lowest in ETN group. Although there are limitations such as channeling bias, these findings might imply the clinical cost reductive benefits in ETN first line treated group.
Disclosure:
N. Sugiyama M.D., Ph.D,
Pfizer Inc,
3;
T. Murata, M.S.,
Pfizer Inc,
5;
Y. Morishima,
Pfizer Inc,
3;
Y. Fukuma,
Pfizer Inc,
3;
Y. Shibasaki,
Pfizer Inc,
3;
L. Marshall,
Pfizer Inc,
3.
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/treatment-pattern-and-direct-cost-of-biologics-for-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-a-real-world-analysis-of-nationwide-japanese-claims-data/