Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose
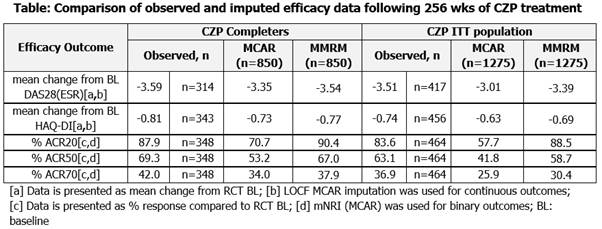
Use of imputed or observed data, as well as the patient (pt) population evaluated (eg. intention-to-treat [ITT], completer), affects the interpretation of long-term efficacy data. Statistical analysis of data from long-term studies must consider the impact of missing values, which result from pt drop-out due to various reasons. Imputation methods should link such reasons with assumptions made for missingness. Missing completely at random (MCAR) approaches (eg. last observation carried forward [LOCF], non-responder imputation [NRI]), assume that missingness is independent of observed and unobserved outcomes. In contrast, missing at random (MAR) methods (eg. mixed models with repeated measures [MMRM]) assume that missingness is dependent on observed outcome.
Data from pooled analysis of Rheumatoid Arthritis Prevention of Structural Damage (RAPID) 1 and 2 RCTs and open-label extensions (OLE) (NCT001523861, NCT001758772, NCT001606023 and NCT001606414) were used. RAPID11 and 23 evaluated safety and efficacy of certolizumab pegol (CZP) with methotrexate. Efficacy data were collected up to 256 weeks (wks) of CZP exposure for clinical measures, including DAS28(ESR) (LOCF), HAQ-DI (LOCF) and ACR20/50/70 (modified NRI [mNRI]). Observed and imputed (MCAR, MAR) data are presented for CZP ITT (all pts randomized to CZP in RCT) and CZP Completer (CZP ITT pts who completed RCT and reconsented into OLE) populations. Results Improvements from baseline in DAS28(ESR) and HAQ-DI were evident in CZP Completer and ITT populations at 256 wks. The use of LOCF and MMRM imputation gave results consistent with observed data (Table). Long-term CZP exposure resulted in sustained ACR response. mNRI determined rates were, per definition, lower than observed data (Table), but were in line with data observed in blinded periods.1,3 MMRM imputation followed long-term mean treatment response more closely and was more homogeneous between patient populations compared to LOCF/mNRI. Different reasons for discontinuation lead to distinct differences in imputed results. Imputed mean response was more homogeneous in the completer population. Conclusion Considering multiple populations and imputation approaches enables more reliable long-term efficacy data interpretation. Pooled RAPID1 and 2 results revealed similar patterns between observed and imputed data, although differences were observed between different imputation methods and reasons for withdrawal. Analysis of the ITT population gives a less biased estimate of efficacy compared with CZP Completers. Nonetheless, results were consistent with maintained improvements in RA signs and symptoms following 256 wks of exposure to CZP. References 1. Keystone E. Arthritis Rheum 2008;58:3319-3329 2. Keystone E. Ann Rheum Dis 2013;epub 3. Smolen J.S. Ann Rheum Dis 2009;68:797-804 4. Smolen J.S. Arthritis Rheum 2013;65:S988
Disclosure:
E. C. Keystone,
Abbott, AstraZeneca, Biotest, BMS, F. Hoffmann-La Roche, Genentech, Janssen, Lilly, Merck, Nycomed, Pfizer, UCB Pharma,
2,
Abbott, Amgen, AstraZeneca, BMS Canada, F. Hoffmann-La Roche, Janssen, Pfizer, UCB Pharma,
8;
J. Smolen,
UCB Pharma,
2,
UCB Pharma,
5;
V. Strand,
AbbVie, Afferent, Amgen, Biogen Idec, Bioventus, BMS, Carbylan, Celgene, Celltrion, CORRONA, Crescendo, Genentech/Roche, GSK, Hospira, Iroko, Janssen, Lilly, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi, SKK, Takeda, UCB, Vertex,
5;
T. Kumke,
UCB Pharma,
3;
I. Mountian,
UCB Pharma,
3;
S. Walker,
UCB Pharma,
3;
R. B. M. Landewé,
Abbott, Ablynx, Amgen, Astra-Zeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Centocor, Glaxo-Smith-Kline, Novartis, Merck, Pfizer, Roche, Schering-Plough, UCB Pharma, Wyeth,
5,
Abbott, Amgen, Centocor, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, Schering-Plough, UCB Pharma, Wyeth,
2,
Abbott, Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Centocor, Merck, Pfizer, Roche, Schering-Plough, UCB Pharma, Wyeth,
8.
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/multiple-approaches-for-implementation-of-long-term-efficacy-interpretation-of-certolizumab-pegol-data-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-case-study/