Session Information
Title: Imaging of Rheumatic Diseases I: Imaging in Gout, Pediatric, Soft and Connective Tissue Diseases
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Abstract
Background/Purpose: The aim of this study was to assess the usefulness of 18F-fluoro-dexoxyglucose positron emission tomography/Computed tomography (18F-FDG PET/CT) for the diagnosis or the evaluation of Adult-onset Still’s disease (AOSD) visually.
Methods: 7 consecutive AOSD patients who had undergone PET at our department between 2007 and 2012 were included in the study. In addition, the literature review was performed about 6 previously reported AOSD patients who had undergone PET. We evaluate FDG uptake for characteristic findings in patients with AOSD.
Results: FDG accumulation was positive mainly in the bone marrow (70%), spleen (80%), lymph nodes (77.8%), and joints (50%). In addition, FDG uptake was positive in the pericardium, pleura, salivary glands, eyelids, muscle, and major blood vessels. 8 patients underwent FDG PET/CT for evaluating the efficacy of treatment. The follow-up PET showed diminished FDG accumulation in the bone marrow, spleen, lymph nodes , with SUVmax being significantly reduced from 4.03±0.95 to 2.20±0.75 (P=0.04), from 4.15±1.10 to 2.55±1.13(P=0.04), and from 5.47±5.19 to 2.10±1.91 (P=0.11), respectively. No significant correlation was found between max SUVs in each site and the laboratory data; the only significant correlation was between LDH and the spleen SUV.
Conclusion: Our study suggests that 18F-FDG PET may play a potential role in diagnosing or monitoring of disease activity marker in patients with AOSD. Additionally,we suspect that future PET/CT imaging will reveal that AOSD is a disease involving lesions with a little clinical description.
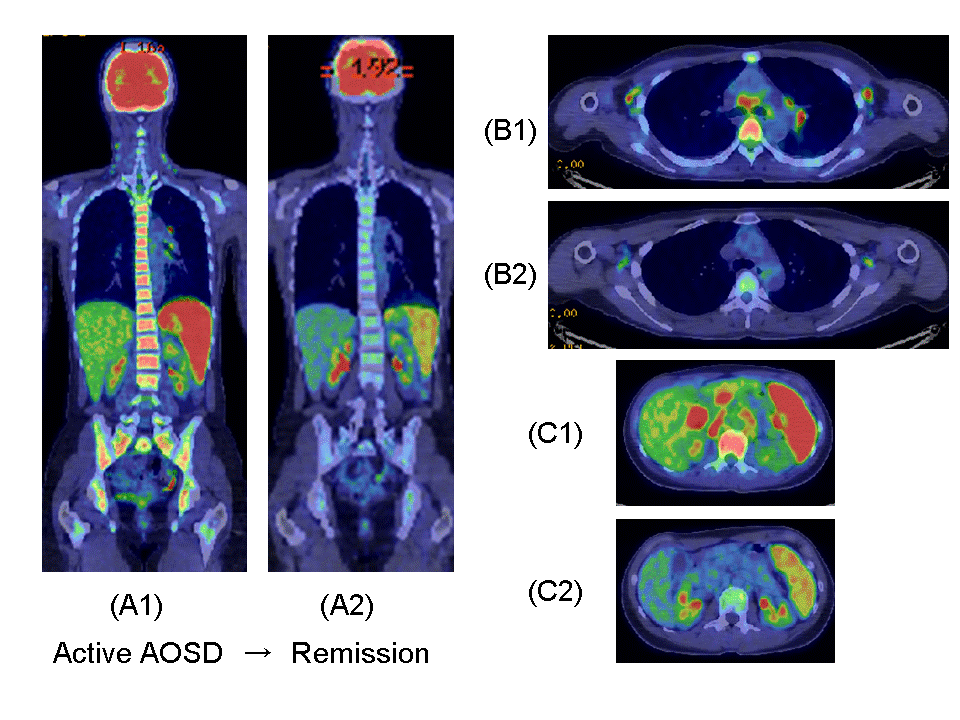
Fig.1FDG-PET/CT images at diagnosis (A1,B1,C1) and after steroid and Tocilizmab treatment (A2,B2,C2) in a 32-year-old woman (Patient 4) with AOSD.
Marked FDG accumulation was observed in the bone marrow, spleen and multiple lymph nodes at the time of diagnosis before treatment. After treatment, bone marrow FDG uptake improved from SUVmax��4.02 (A1) to 2.50 (A2) and spleen FDG uptake decreased from SUVmax��6.05(A1,C1) to 4.38(A2,C2). In addition, multiple lymph node FDG uptake observed in the axilla, mediastinum, hilar region of the lung, hilar region of the liver and para-aortic region declined or disappeared (B1/C1→B2/C2).
Disclosure:
H. Yamashita,
None;
K. Kubota,
None;
Y. Takahashi,
None;
H. Kaneko,
None;
T. Kano,
None;
A. Mimori,
None.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-value-of-18f-fluoro-dexoxyglucose-positron-emission-tomography-in-patients-with-adult-onset-stills-disease/