Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Drug exposure limitations of oral methotrexate (MTX) at doses >15mgs may be overcome by using a subcutaneous MTX auto-injector in pts with rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
Background/Purpose: MTX is the cornerstone of RA therapy but absorption saturability limitations compromise oral MTX bioavailability (BA). Parenteral MTX exhibits a dose-proportional increase in exposure throughout the dosing range, possibly leading to better efficacy. Parenteral MTX is used by < 5% of U.S. clinicians due to lack of familiarity and availability and the challenges of self-injection. To address these issues, an investigational, single-use, self-administered SC MTX auto-injector (MTXAI) was developed with 10-, 15-, 20-, and 25-mg fixed doses. This study compares the relative BA of MTXAI vs oral MTX to demonstrate safety and tolerability of MTXAI in RA pts.
Methods: In this 12-week, open-label, crossover study, 49 adults with RA already receiving MTX for ≥3 months were given 10, 15, 20, or 25 mg MTX, based on their current dose and disease control, via random assignment (1:1:1) to oral MTX, MTXAI (abdomen), or MTXAI (thigh). Blood samples for PK analysis were collected predose and at 13 timepoints from 0.25 to 12 hours postdose and were analyzed by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Mixed model analysis derived AUC, Cmax, and Tmax PK parameters. Dose-normalized parameter ratios were calculated. Safety was assessed by the incidence of treatment-emergent AEs (TEAEs), changes in safety laboratory parameters and vital signs, and administration site AEs.
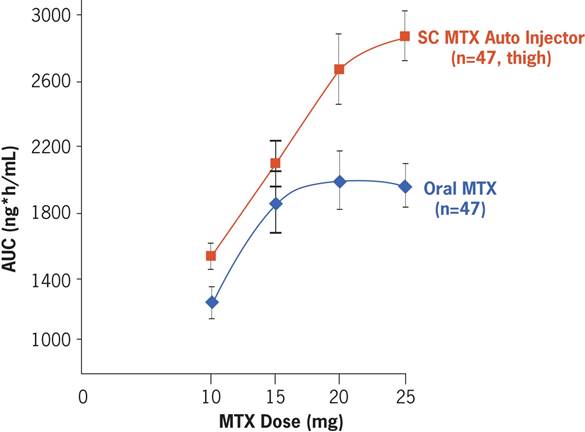
Results: Mean age was 61 years; mean body mass index, 30.7 kg/m2; and mean disease duration, 13 years; 63% of pts were female. PK analysis of MTXAI (thigh) vs. oral MTX showed that BA of MTXAI was consistently greater at all dose levels (Figure). MTXAI thigh and MTXAI abdomen PK measures were similar. Although oral MTX plateaued at 15 mg, MTXAI had no plateau, resulting in a higher exposure than comparable oral doses. Relative BA (AUC of MTXAI vs. oral MTX) at 10, 15, 20, and 25 mg were 121%, 114%, 131%, and 141%. Ratio of the dose-normalized AUC (0-24 h) and Cmax of MTXAI vs. oral MTX were 127.61 (90%CI: 122.30-133.15) and 94.88 (90%CI: 87.95-102.37). Few TEAEs were reported with MTXAI; observed AEs were transient, manageable, and required no medical treatment. Two serious AEs were considered unrelated to treatment, including a death from a myocardial infarction in a 79-year-old man with cardiac history that occurred several weeks after the study. MTX and MTXAI were otherwise safe and well tolerated.
Conclusion: SC MTX delivered by auto-injector has a linear absorption compared to oral MTX, which plateaued at doses >15 mg. Pts receiving oral MTX with an inadequate clinical response may benefit from higher drug exposure levels by switching to SC MTX via MTXAI. This study confirms existing findings that higher systemic exposure to MTX is not associated with increased rates of AEs.
Disclosure:
M. H. Schiff,
Antares Pharma,
5;
L. S. Simon,
Savient Pharma,
1,
See notes section for full list.,
5;
B. Freundlich,
Antares Pharma, Celgene, BMS,
5,
Pfizer Inc,
1;
J. Jaffe,
Antares Pharma,
3;
K. J. Dave,
Antares Pharma,
3.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/drug-exposure-limitations-of-oral-methotrexate-mtx-at-doses-15mgs-may-be-overcome-by-using-a-subcutaneous-mtx-auto-injector-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-ra/