Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) is initially treated with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. In case of inadequate response, ACR/EULAR recommend biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARDs). Up to 2015, TNF inhibitors (TNFi) were the only available option. Since then, IL-17A inhibitors (IL-17Ai) have also demonstrated efficacy. The 2022 ASAS-EULAR guidance proposes switching an alternative bDMARD after TNF inhibitors failure without mandating a change of mechanism of action. Therefore, we designed a randomized multicenter clinical trial to identify the most effective treatment after a first TNFi failure in axSpA, comparing an IL-17Ai to a second TNFi.
Methods: The ROC-SpA (Rotation Or Change of biologics after first TNFi treatment failure in axSpA patients) study is a prospective, randomized, multicenter, open-label, superiority, phase IV trial. Patients with active axSpA (BASDAI >4 or ASDAS >3.5), an inadequate 3-month response to a first TNFi, and stable doses of conventional synthetic (cs)DMARDs, oral corticosteroids, and/or NSAIDs for at least one month were enrolled across 31 centers in France and Monaco. Patients were randomized to receive either an IL-17Ai or a second TNFi. The primary outcome was the ASAS40 response at week 24. Secondary outcomes were ASAS 40 at weeks 12 and 52, other clinical assessments (ASAS20, partial remission rate, ASDAS major improvement rate) at weeks 12, 24, and 52. The primary analysis was performed at the end of the study according to the intent-to-treat principle.
Results: Baseline characteristics of the enrolled patients are shown in Table 1. Both drug options led to similar rates of response ASAS40 at week 24 (15.2% for IL-17Ai and 14.5% for TNFi (14.5%), thus the primary outcome assessing the superiority of IL-17Ai was not achieved (Figure 1). No statistically significant difference was observed between groups for other secondary endpoints. ASDAS declined similarly in both groups to 2.6 (1.0) at week 12, 2.5 (0.9) at week 24, and 2.3 (1.0) at the end of follow-up. On-treatment maintenance at week 54 was 62.8% with IL-17Ai and 54.9% with TNFi. No new safety signals were identified, and adverse-event rates were comparable between groups. Exploratory, non-significant trends favored an IL-17Ai after primary nonresponse and in patients with cutaneous psoriasis, HLA-B27 negativity, or CRP < 5 mg/L. Conversely, when the first TNFi was discontinued for an adverse event, cycling to another TNFi appeared more favorable.
Conclusion: In this randomized trial of axSpA patients with inadequate response to a first TNFi, switching to an IL-17Ai was not superior to cycling to a second TNFi for the primary endpoint. These findings directly inform treatment sequencing after TNFi failure and support individualized, shared decision-making in axSpA. They also align with current recommendations that, for the axial symptom control, the choice among available bDMARDs should not be based on anticipated efficacy differences.
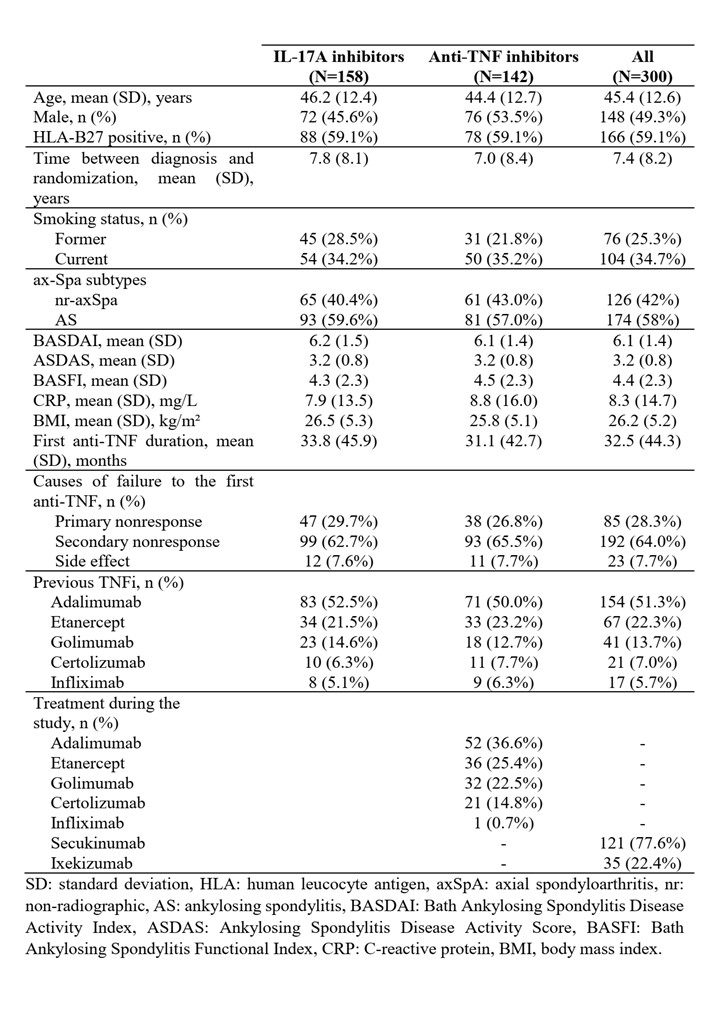 Table 1. Main characteristics of the patients at baseline
Table 1. Main characteristics of the patients at baseline
.jpg) Figure 1. Clinical responses with adjusted odds ratio in IL-17i and TNFi groups at weeks 12, 24, and 52
Figure 1. Clinical responses with adjusted odds ratio in IL-17i and TNFi groups at weeks 12, 24, and 52
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Dalix E, Goupille P, Wendling D, Roux C, Samon J, Brocq O, Tournadre A, Constantin A, Breban M, Cormier G, Pascart T, Lequerre T, Claudepierre P, Lespessailles E, Legoff B, Sellam J, Baillet A, Schaeverbeke T, Pavy S, Devauchelle-Pensec V, Gervais E, Gossec L, Miceli C, Pers Y, Lukas C, Felten R, Bouvard B, Denis A, Dernis E, Presles E, Rancon F, Marotte H. Rotation or Change of Biologic After TNF blocker treatment failure for axial Spondyloarthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/rotation-or-change-of-biologic-after-tnf-blocker-treatment-failure-for-axial-spondyloarthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/rotation-or-change-of-biologic-after-tnf-blocker-treatment-failure-for-axial-spondyloarthritis/
