Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) patients with prior failure or intolerance to TNFα inhibitors (TNFi) represent a clinically challenging population with limited therapeutic options. The AgAIN study (CAIN457FDE04; NCT04632927) is the first randomized, double-blind, active-controlled, multicenter trial directly comparing secukinumab (SEC) and ustekinumab (UST) in this population.
Methods: A total of 119 patients (pts) were randomized (SEC: 56, UST: 63; see Fig. 1 for Study Design) at 28 clinical centers in Germany. The mean age was 53.5 ± 11.0 years, with 15.1% of pts aged over 65. Female pts comprised 69.6% in the SEC group and 65.1% in the UST group. Body weight over 100 kg was observed in 30.4% of SEC pts and 22.2% of UST pts. All pts met the CASPAR criteria for PsA diagnosis (score ≥3). Key CASPAR features included current psoriasis (91.1% SEC, 82.5% UST), negative rheumatoid factor (100.0% SEC, 96.8% UST), and juxta-articular new bone formation (37.5% SEC, 31.7% UST). All pts had prior TNFi exposure and failed TNFi, with adalimumab (68.9%) being the most commonly used. Treatment discontinuation rates were notably higher in the UST group (25.4% vs. 3.6% SEC), primarily due to lack/loss of efficacy, with a mean ± SD duration of exposure of 24.3 ± 2.0 weeks for SEC vs. 21.5 ± 6.8 weeks for UST. Despite recruitment issues resulting in early recruitment termination, the study was successfully completed, offering descriptive analysis of comparative efficacy and safety.
Results: For the primary endpoint, HAQ-DI© response increased continuously over time in SEC group and was numerically higher than in UST group at all analyzed time points (see Figure 1), with a notably greater response rate of 57.1% (32/56 pts) for SEC vs. 27.0% (17/63 pts) for UST at week 28 [ OR=3.647, 95% CI: 1.601–8.311; p=0.002;]. Further, SEC showed qualitatively better outcomes across all secondary and exploratory endpoints, see Table 1 for details. No new safety signals of secukinumab were identified. Treatment emergent adverse events (TEAEs) occurred in 76.8% (SEC; 43/56 pts) vs. 81.0% (UST; 51/63 pts); SAEs in 8.9% (SEC; 5/56 pts) vs. 3.2% (UST; 2/63 pts). TEAEs leading to discontinuation were seen in 3.6% in SEC arm (2/56 pts) and 12.7% in UST arm (8/63 pts).
Conclusion: AgAIN is the first study to provide head-to-head data comparing SEC and UST in TNFi-experienced PsA patients. SEC showed qualitatively better efficacy across all clinical and patient-reported outcomes (PRO), and safety signals in line with known safety profile. Notably, improvements in key clinical endpoints and PROS—including HAQ-DI, joint counts, pain, and skin outcomes—were observed as early as Week 2 and sustained through Week 28. In conclusion, the results of this randomized controlled study highlight the benefit that secukinumab can offer for management of PsA in the described population.
Acknowledgement: We gratefully acknowledge the invaluable contributions of all of the study participants as well as all investigators & study personnel involved whose dedication and expertise made this clinical trial possible
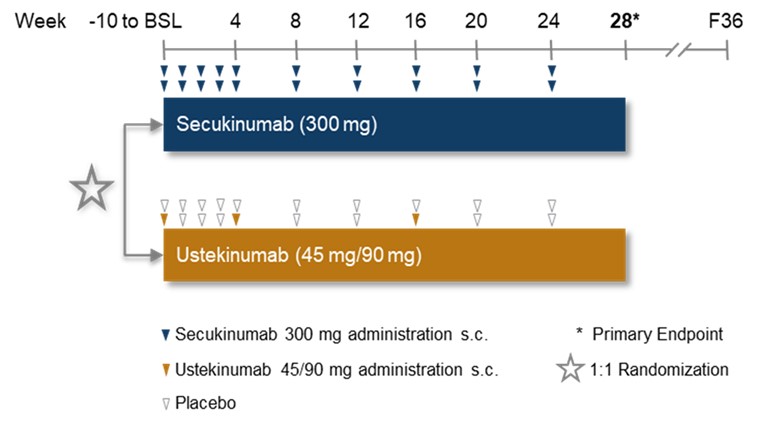 Figure 1: Study Design of AgAIN
Figure 1: Study Design of AgAIN
.jpg) Figure 2: HAQ-DI© response over time
Figure 2: HAQ-DI© response over time
.jpg) Table 1: Results of primary, secondary and some exploratory Endpoints at Week 28
Table 1: Results of primary, secondary and some exploratory Endpoints at Week 28
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Behrens F, Sternad P, Krueger K, App C, Lefevre S, Schiedel C. AgAIN Study: First Head-to-Head Trial of Secukinumab vs. Ustekinumab in TNFα Inhibitor-Experienced Psoriatic Arthritis Patients Reveals Better Efficacy Across Multiple Domains [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/again-study-first-head-to-head-trial-of-secukinumab-vs-ustekinumab-in-tnf%ce%b1-inhibitor-experienced-psoriatic-arthritis-patients-reveals-better-efficacy-across-multiple-domains/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/again-study-first-head-to-head-trial-of-secukinumab-vs-ustekinumab-in-tnf%ce%b1-inhibitor-experienced-psoriatic-arthritis-patients-reveals-better-efficacy-across-multiple-domains/
