Session Information
Date: Wednesday, October 29, 2025
Title: Abstracts: Pediatric Rheumatology – Clinical III (2675–2680)
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 11:45AM-12:00PM
Background/Purpose: Tofacitinib is a JAK inhibitor that has been approved for treatment of polyarticular Juvenile idiopathic arthritis. However, data on its use in juvenile spondyloarthropathy including Enthesitis related arthritis is limited. MRP8/14 and MMP3 are good biomarkers of activity in Juvenile spondyloarthropathy1,2. Thus, we studied the effect of Tofacitinib on disease activity, biomarkers and compared that with treatment with adalimumab.
Methods: Patients with juvenile spondyloarthropathy (onset < 18 years), and having poor response to NSAIDs and/or methotrexate/Sulphasalazine were included in the study. Patients were given a choice of tofacitinib(tofa) or Adalimumab (ADA) and based on preference, the availability of cold chain to store ADA patients were treated with either ADA or tofacitinib. Drugs were provided free of cost and were supported by a foundation. The disease activity was assessed using JSpADA, BASDAI, BASFI, BASMI and ASDAS at baseline, 4 weeks, 16 weeks and 24 weeks. ESR, CRP, MMP3, MRP 8/14, were measured at 0 and 4 weeks. The study was approved by institutional ethics committee and consent was taken from patient/guardian.
Results: The study included 53 patients with JSpA (29 on Tofacitinib and 24 on ADA). The clinical features of the two groups showed that the mean age of onset, duration of disease and clinical features were similar in both the groups however disease activity was higher in ADA group. (Table 1). In ADA group 1 patient had transaminitis at 12 weeks, 1 had flare after 16 weeks, 1 had anemia and GI infection and one each was lost to follow up at 16 and 24 weeks. In Tofa group 1 patient each was lost to follow up at 4, 12 and 24 weeks thus 26 complete the 24 week follow up.Both JSpADA score and BASDAI reduced after 4 weeks and over the next 24 weeks there was further reduction of the score (figure 1). Both groups had a similar reduction in scores. BASDAI remission (< 2) was seen in 14/19 (73.7%) in ADA group and 20/26 (76.9%) patients in Tofa group. ASDAS based low disease activity was achieved by 73.6% in ADA group and in 88.4% in tofa group (p< 0.05) (figure 1). The blood biomarkers i.e. ESR, CRP, MMP and MRP8/14 showed a significant fall at 4 weeks, however the degree of fall was similar between ADA and Tofa.(Figure 2)
Conclusion: Tofacitinib shows similar efficacy, reduction in markers of inflammation as adalimumab in JSpA. It has a good safety profile and also has rapid onset of action.1.. J Rheumatol. 2011 Nov;38(11):2482-7. 2. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2014 Feb;53(2):270-4.The study was funded by an intramural grant to AA
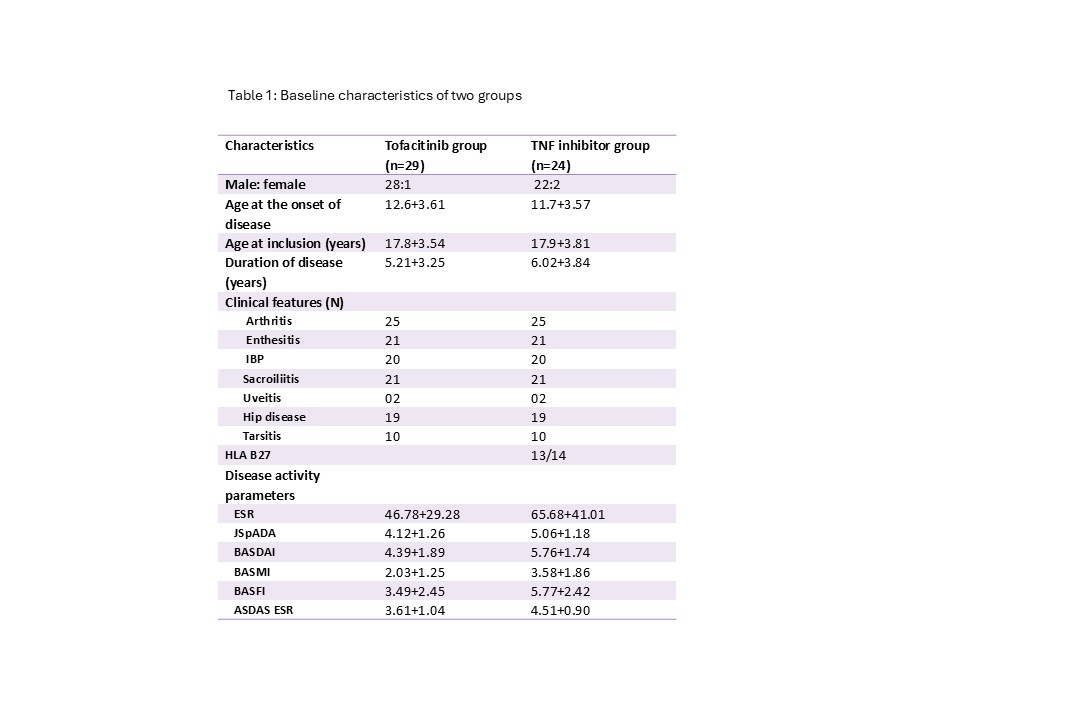 Table 1: Clinical features of patients
Table 1: Clinical features of patients
.jpg) Figure 1: Effect of ADA and Tofa on JSpADA, BASDAI, ASDAS at different time points
Figure 1: Effect of ADA and Tofa on JSpADA, BASDAI, ASDAS at different time points
.jpg) Figure 2: Effect of ADA and Tofa on ESR, CRP, MMP3 and MRP8/14
Figure 2: Effect of ADA and Tofa on ESR, CRP, MMP3 and MRP8/14
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Balakrishnan A, Khan A, Guleria S, Umam F, R N, Jain P, Minikumari Rahulan L, Chatterjee R, Aggarwal A. Tofacitinib in Juvenile spondyloarthropathy: clinical efficacy, impact on biomarkers and comparison with Adalimumab [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/tofacitinib-in-juvenile-spondyloarthropathy-clinical-efficacy-impact-on-biomarkers-and-comparison-with-adalimumab/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/tofacitinib-in-juvenile-spondyloarthropathy-clinical-efficacy-impact-on-biomarkers-and-comparison-with-adalimumab/
