Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: Fibromyalgia has both idiopathic and post traumatic forms. The idiopathic type is insidious in onset, becoming established without a known triggering event. The post-traumatic form is defined by the presence of a triggering event such as a significant illness, an injury or an accident. The purpose of this study is to examine the age distribution of the two forms of onset in order to determine if either form is age-linked
Methods: Age of onset and the presence of a triggering event were investigated in 169 female patients who met ACR criteria for fibromyalgia. In response to the question “Did a specific event or condition trigger your symptoms of fibromyalgia”, 97 (57.4%) recorded yes and formed the post-traumatic group. Forty two percent (42.6%) recorded no and formed the idiopathic group
Results: The mean age of post-traumatic FMS patients was 47.1±11.6 years and for idiopathic FMS patients was 49.7± 12.8 years. The mean age of symptom onset was 35.3 ±11.7 years in the post-traumatic group and 37.1±12.3 years in the idiopathic group. Differences between groups on the two variables were non-significant.
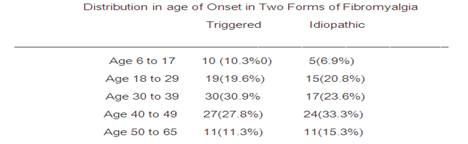
Table 1: illustrates that the age distribution in both forms of fibromyalgia is similar. The two forms of FMS occurred in people of all ages, and ranged from 8 to 65 in the post-traumatic group and 6 to 63 in the idiopathic group. The frequency of onset in both forms is highest between the ages of 30 and 49.
Conclusion: It is curious that the mean age of onset in the group with post-traumatic FMS (35.3 y.o.) was similar to the mean age of onset in patients with idiopathic FMS (37.1 y.o.). Neither the idiopathic nor the post-traumatic form of FMS appears age dependent. Onset can be encountered both early and late in life with approximately 10% of each form occurring before the age of 18 and after the age of 50. FMS onset peaks in the 3rd, 4th and 5thdecades in women.
The similar pattern of onset is puzzling since one is presumably an internally generated process and the other occurs on an apparently chance basis, such as after car accidents. One theory is that the idiopathic form of fibromyalgia is also stress driven but on a more subtle basis. Like the post-traumatic form, it also occurs because cumulative stress builds, in an unnoticed manner, and exceeds a critical threshold dependent on life circumstances.
Disclosure:
R. S. Katz,
None;
F. Leavitt,
None.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/age-distribution-of-women-with-idiopathic-and-traumatic-fibromyalgia/