Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Lung disease in systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis and adult-onset Still’s disease (Still’s-LD) is a severe manifestation that strongly associates with features of drug hypersensitivity reactions (fDHR), including eosinophilia, non-Still’s rashes, and elevated liver function tests. In patients with Still’s disease, both LD and fDHR are strongly associated with HLA-DRB1*15 alleles; however, the pathogenesis of these phenomena remain unknown. This study investigates whether Still’s-LD and fDHR are associated with pathogenic antigens through hypersensitivity reactions to Aspergillus fumigatus, for which HLA-DRB1*15 is a known risk allele, or drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS), which is frequently associated with human herpesvirus reactivation.
Methods: Pediatric and adult subjects were drawn from the NIH Still’s disease cohort, subjects with Still’s-LD and/or fDHR were identified by chart review. Serum samples were analyzed for anti-Aspergillus fumigatus IgE via ImmunoCap assay. Subjects were screened for EBV, CMV, and HHV-6 by PCR assay for viral nucleic acids and/or Viral Transcript Usage Sensor (VIRTUS) analysis of whole blood RNAseq data for viral transcripts. The prevalence of anti-Aspergillus fumigatus IgE antibodies and viral nucleic acids were compared between groups using two-tailed Fisher’s exact tests with a significance level set at 0.05.
Results: Fifty-five subjects were included in the study, 11 had LD and fDHR and 8 had fDHR alone. Thirty-three subjects were tested for anti-Aspergillus antibodies and all were negative. Fifty subjects were tested for EBV, CMV, and HHV-6, 23 by PCR only, 17 by VIRTUS only, and 10 by both PCR and VIRTUS. All subjects were negative for CMV and HHV-6 by PCR and VIRTUS. Two subjects without LD or fDHR had detectable EBV nucleic acids by PCR and no subjects with LD or fDHR had detectable EBV by PCR or VIRTUS, a difference which was not statistically significant (p = 0.52). Of those tested for viral nucleic acids, 11/19 (58%) had testing performed within 1 year of active LD or fDHR.
Conclusion: The absence of anti-Aspergillus IgE antibodies and detectable herpesvirus nucleic acids in subjects with Still’s-LD and fDHR does not support a mechanistic association with hypersensitivity to Aspergillus fumigatus or with human herpesvirus reactivation. Additional work is needed to improve the mechanistic understanding of Still’s-LD and fDHR.
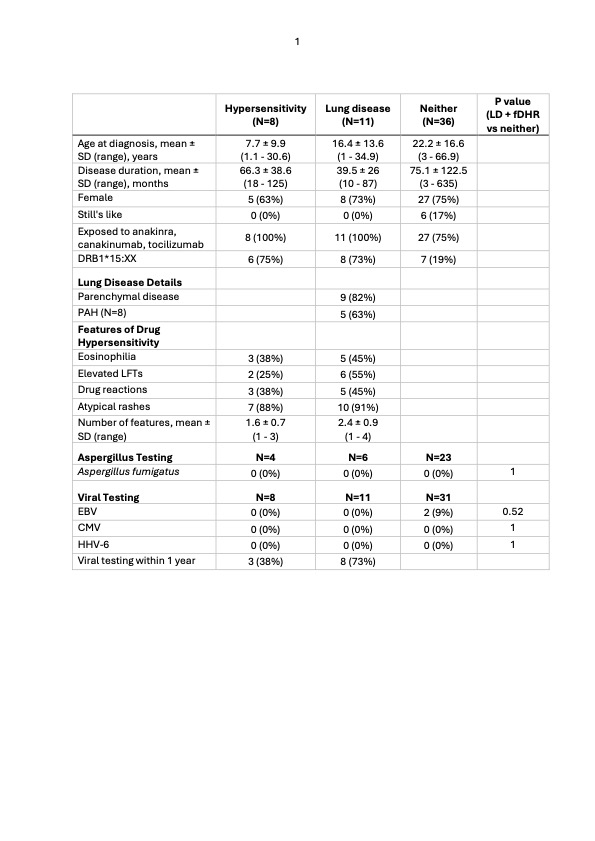 Table 1: Clinical characteristics and results of testing for Aspergillus fumigatus antibodies and viral nucleic acids
Table 1: Clinical characteristics and results of testing for Aspergillus fumigatus antibodies and viral nucleic acids
Continuous variables are presented as mean ± standard deviation (range), categorical variables are presented as N (% of non-missing values). LD: lung disease, fDHR: features of drug hypersensitivity reactions, PAH: pulmonary arterial hypertension, TTE: transthoracic echocardiography, RHC: right heart catheterization, LFT: liver function test, EBV: Epstein-Barr virus, CMV: cytomegalovirus, HHV-6: human herpesvirus 6. Anti-Aspergillus fumigatus IgE via ImmunoCap Allergen m3 assay. EBV, CMV, and HHV-6 nucleic acids by PCR and/or VIRTUS.
.jpg) Figure 1: Subjects tested for EBV, CMV, and HHV-6 by PCR and VIRTUS
Figure 1: Subjects tested for EBV, CMV, and HHV-6 by PCR and VIRTUS
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kobrin D, Brown G, Correia Marques M, Lake C, Millwood M, Workman L, Lawrence M, Deng Z, Das S, Ombrello M. Examination of HLA-DRB1*15-linked Candidate Antigens in Still’s Disease with and without Lung Disease and Features of Drug Hypersensitivity [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/examination-of-hla-drb115-linked-candidate-antigens-in-stills-disease-with-and-without-lung-disease-and-features-of-drug-hypersensitivity/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/examination-of-hla-drb115-linked-candidate-antigens-in-stills-disease-with-and-without-lung-disease-and-features-of-drug-hypersensitivity/
