Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 28, 2025
Title: (1830–1854) Systemic Lupus Erythematosus – Etiology and Pathogenesis Poster
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) encompasses a subset of patients who exhibit resistance to standard treatments, posing a significant challenge to achieving remission. Our study aimed to elucidate the molecular mechanisms underlying treatment resistance in clinical practice. To address this, we conducted RNA sequencing analysis using longitudinal peripheral blood samples.
Methods: 42 peripheral blood samples from naïve or flare 14 SLE patients were collected before treatment and 4 and 12 weeks after treatment who received standard induction therapy except for belimumab, anifrolumab, and rituximab. Patients were divided into two groups based on their response to treatment. 1) Treatment responder group; those who achieved a SLEDAI-2K score of less than 4 after 12 weeks, and 2) Treatment-resistant group; those who did not achieve less than 4. RNA sequencing was performed using NovaSeq 6000 (Illumina) with a paired-end read of 100 base pairs. FASTQ format data were mapped to the UCSC human genome 38 as the reference sequence. Sequence read count data was analyzed using R (4.3.2). Basic analysis were performed using edgeR. Time-course expression analysis was performed using maSigPro. We identified differentially expressed genes (DEGs) by comparing samples obtained before treatment and at 12 weeks post-treatment.
Results: Patients with a SLEDAI score of 4 or less at 12 weeks were classified as responders (n=8), and those with a score of more than 4 were classified as the resistant group (n=6). In PCA plot of RNA-seq of peripheral blood, there was no clear distinction between responders and resistant. No clear group discrimination was found after treatment.In DEG analysis, 19 DEGs were detected in responder comparing 0w and 12 weeks after treatment, and 85 in resistant. Enrichment analysis showed that adequately suppressed immune response in resistant group. We thought that information of the time series sample of the same person was not utilized, and planned to take advantage of the sequential sampling information.We performed time-course analysis using samples before treatment and 4 and 12 weeks after treatment to identify critical factors that are involved in treatment resistance over time. maSigPro is a software to identify genes that show different gene expression profiles across analytical groups in time-course experiments. maSigPro can also perform time-series clustering to identify genes with significant intergroup differential expression.The responder and resistant group were compared, and the differentially expressed genes in the time series were extracted. TNFRSF17 (P = 1.144 x 10-21) and MZB1 (P = 3.547 x 10-16) were identified in addition to immunoglobulin-related genes. TNFRSF17 (BCMA), a receptor for BAFF/BLyS, has been investigated as a therapeutic target for SLE. MZB1 is a B-cell-specific endoplasmic reticulum chaperone complex that plays a key role in antibody secretion and is increased in SLE lymph nodes. These molecules are supposed to be critical for treatment resistance.
Conclusion: Time-course analysis using longitudinal peripheral blood samples of SLE suggested that the expression levels and trends of TNFRSF17 and MZB1 are important for treatment resistance in SLE.
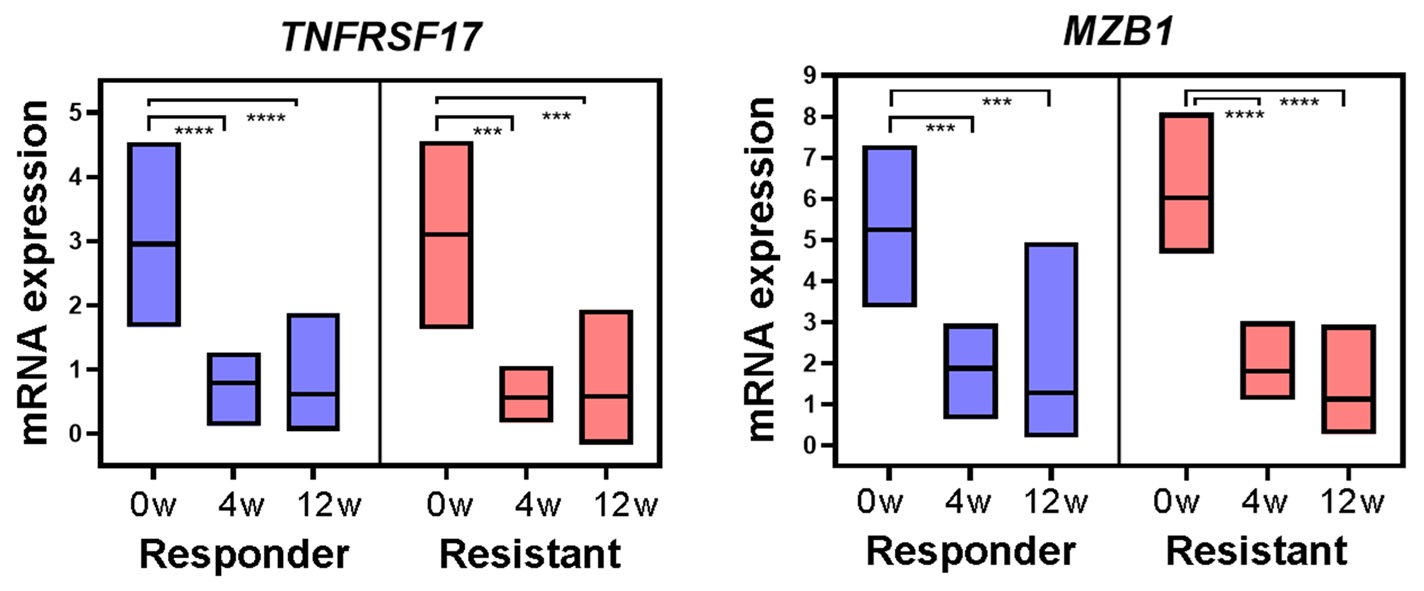 Figure 1. DEG-based analysis; 85 DEGs were detected in treatment-resistant group comparing 0w and 12 weeks after treatment (left, volcano plot). Enrichment analysis (right) showed that immune response process is suppressed in treatment-resistant group.
Figure 1. DEG-based analysis; 85 DEGs were detected in treatment-resistant group comparing 0w and 12 weeks after treatment (left, volcano plot). Enrichment analysis (right) showed that immune response process is suppressed in treatment-resistant group.
.jpg) Figure 2. Time course expression of TNFRSF17 and MZB1; The time course expression patterns of TNFRSF17 and MZB1, being sufficiently suppressed from the week 4 and further decreasing at week 12. ***: p < 0.001, ****: p < 0.0001.
Figure 2. Time course expression of TNFRSF17 and MZB1; The time course expression patterns of TNFRSF17 and MZB1, being sufficiently suppressed from the week 4 and further decreasing at week 12. ***: p < 0.001, ****: p < 0.0001.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sumitomo S, Oka H, Iwasaki T, Ohmura K. Time-course RNA sequencing analysis of longitudinal peripheral blood samples to elucidate the factors determining treatment resistance in systemic lupus erythematosus [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/time-course-rna-sequencing-analysis-of-longitudinal-peripheral-blood-samples-to-elucidate-the-factors-determining-treatment-resistance-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/time-course-rna-sequencing-analysis-of-longitudinal-peripheral-blood-samples-to-elucidate-the-factors-determining-treatment-resistance-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/
