Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Title: (1517–1552) Systemic Lupus Erythematosus – Treatment Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
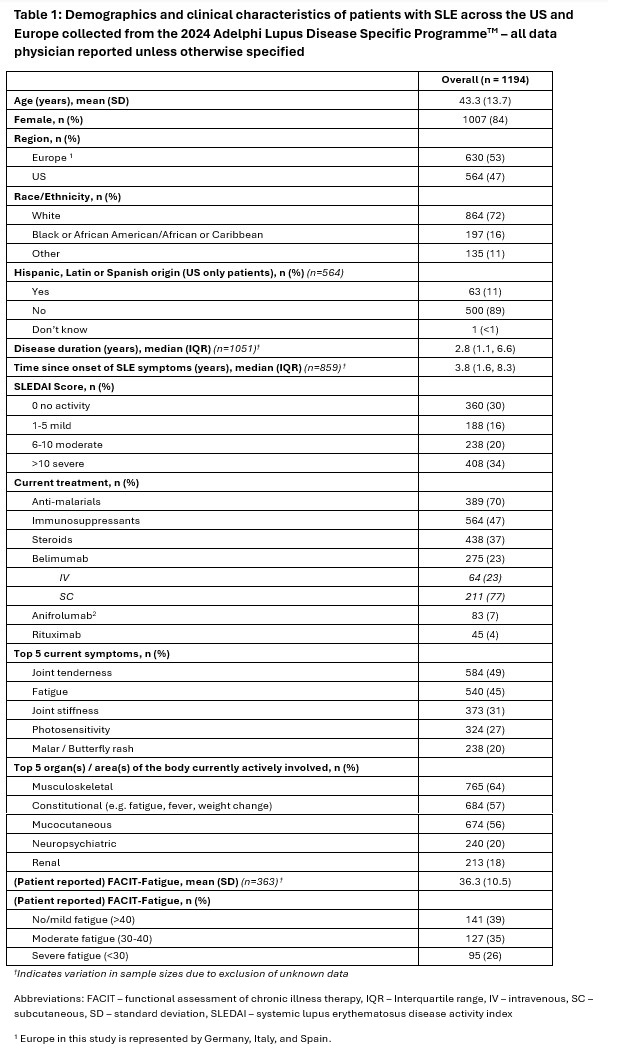
Background/Purpose: As new treatment options for systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) become available, understanding patient burden and preferences is key to optimizing shared decision-making. This study evaluated patient burden and physician/patient treatment preferences through a global real-world survey.
Methods: Data were drawn from the 2024 Adelphi Lupus Disease Specific Programme™, a cross-sectional survey with retrospective data collection of rheumatologists and their patients with SLE in Germany, Italy, Spain and the US from Jul 2024 – Jan 2025; physicians provided data for their next 6 consulting patients with SLE. Physicians reported patient demographics, clinical characteristics (including SLE Disease Activity Index [SLEDAI]), and treatment preferences. Patients self-reported treatment preferences for their SLE and quality of life via the Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy – Fatigue Scale (FACIT-Fatigue). Patients and physicians rated their preference for four treatment modes including an oral pill once or twice per day, self-administered subcutaneous (SC) injection every week, or intravenous [IV] injection every 4 weeks. All analyses were descriptive.
Results: Overall, 176 physicians across the US (n=71) and Europe (n=105) reported data for 1,194 patients of which 47% were from the US and 53% from Europe. Patients’ mean (SD) age was 43.3 (13.7), 72% were White, 84% female, with a median (IQR) disease duration of 2.8 (1.1, 6.6) years (Table 1). Most patients (54%) had moderate/severe disease activity as defined by a SLEDAI score >6. The most reported organs affected were musculoskeletal (64%), constitutional (57%) and mucocutaneous (56%). Joint tenderness (49%), fatigue (45%), and joint stiffness (31%) were the most prevalent symptoms; 61% of patients reported moderate or severe fatigue via FACIT-Fatigue. Current treatment with injectable biologics at data collection included 23% on belimumab, 7% on anifrolumab, and 4% on rituximab. Physician-reported reasons for initiation of patient’s current treatment were overall efficacy (99%), safety (55%), treatment administration (39%), quality of life (38%), and cost (23%) (Figure 1a). When asked to choose among the four administration modes, a once daily oral pill was most preferred by both patients and physicians: 60% of patients and 77% of physicians respectively (Figure 1b, Figure 1c). An oral pill twice daily was the least preferred option by both patients and physicians, but following this option there was some discordance with patients more likely to choose the every-4-week IV injection where physicians chose the weekly SC injection. There were 62% of patients who indicated they would ask their doctor to switch to an oral pill if one was available as an alternative to their biologic injection (Figure 1d).
Conclusion: Despite the availability of injectable advanced treatments, patients with SLE continue to have a high disease burden. Overall efficacy, safety, and treatment administration were reported as key reasons for treatment choice by SLE treating physicians. A once-daily oral pill was the preferred route and frequency of administration by both physicians and patients. These findings may help optimize shared decision-making in SLE.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Touma Z, Saffore C, Masri K, Clewell J, Goddard E, O'Neill G, Foxall M, Costenbader K. Disease Burden and Treatment Preferences for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Results from a Global Real-World Survey [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/disease-burden-and-treatment-preferences-for-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-results-from-a-global-real-world-survey/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/disease-burden-and-treatment-preferences-for-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-results-from-a-global-real-world-survey/

.jpg)