Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Title: (1434–1466) Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: The aim of this study was to compare the effectiveness of switching from a first-line TNFi to upadacitinib (UPA), an oral JAKi, versus cycling to another TNFi or switching from a TNFi to an IL-17 inhibitor (IL-17i) on tender and swollen joint involvement in patients with PsA.
Methods: Data were drawn from the Adelphi Real World Spondylarthritis (SpA) V and VI Disease Specific Programmes™, cross-sectional surveys administered to physicians (rheumatologists, dermatologists, and internal medicine specialists) and their consulting patients in routine clinical practice in Germany, France, Italy, Spain, the United Kingdom, and the United States (SpA VI only), with respective data collection periods from March 2021 to November 2021 for SpA V and from June 2023 to June 2024 for SpA VI. Adult patients with PsA who switched treatment from a TNFi in the first line of advanced therapy to another advanced therapy were stratified by the second-line therapy of interest: TNFi to UPA, TNFi to TNFi, or TNFi to IL-17i. The outcome of physician-reported assessment of both TJC ≤ 1 and SJC ≤ 1 was evaluated ≥ 3 months from treatment switch. Patient demographics and clinical characteristics were balanced using inverse-probability-weighted regression adjustment (IPWRA).The covariates balanced within the IPWRA were age, sex, Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI), and severity at initiation of second-line therapy as reported by their physician for the weighting and regression adjustment stage, and additionally second-line treatment duration was used for the regression adjustment stage. The regression analyses were conducted separately for comparisons between TNFi to UPA and TNFi to TNFi as well as between TNFi to UPA and TNFi to IL-17i.
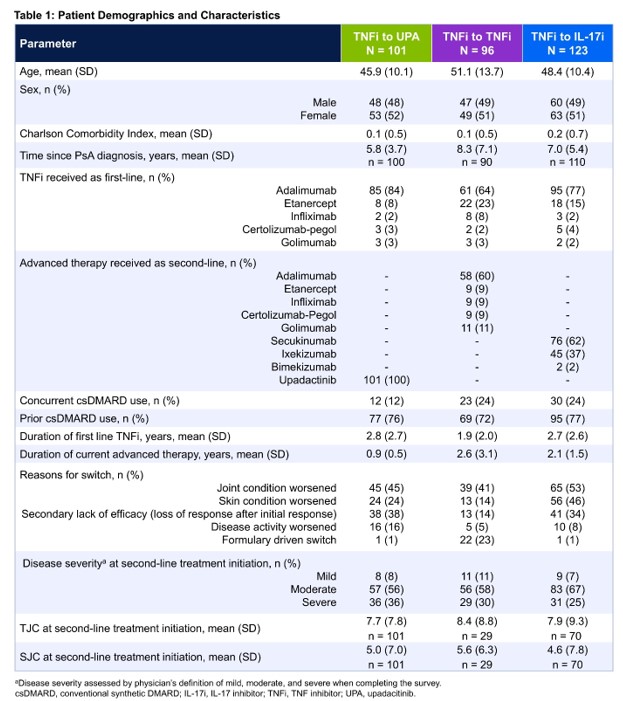
Results: Of the 320 patients included in the analysis who switched from a first-line TNFi, 101 switched to UPA, 96 switched to a second TNFi, and 123 switched to an IL-17i. Patient demographics are presented in Table 1. The most commonly used first-line TNFi in each group was adalimumab. The most commonly used second-line therapy in the TNFi to TNFi group was adalimumab while secukinumab was the most used second-line therapy in the TNFi to IL-17i group. The most frequent reason for switching reported by the physician was a worsening of the joints. At the time of switch, most patients had a physician-reported assessment of moderate/severe disease severity (TNFi to UPA: 92%; TNFi to TNFi: 89%; TNFi to IL-17i: 93%). After adjustment via IPWRA, significantly more patients in the TNFi to UPA group had physician-reported assessment of both TJC and SJC ≤ 1 at the time of data collection compared with patients in the TNFi to TNFi group (94% vs. 76%; P = .0342) and the TNFi to IL-17i group (91% vs. 72%; P = .0123) (Figure 1).
Conclusion: In this real-world study, a higher proportion of patients who switched from their first TNFi advanced therapy to UPA as their second-line advanced therapy had both TJC ≤ 1 AND SJC ≤1 than cycling to a second TNFi or switching to an IL-17i. The results demonstrate that switching to UPA after a TNFi may benefit patients with PsA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mease P, Tillett W, Ye X, Saffore C, Edwards M, Truman I, Barlow S, Stigler J, Parikh B, Aletaha D. Real-World Comparative Effectiveness of Upadacitinib in Psoriatic Arthritis: Evaluation of Switching to Upadacitinib Versus Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitors or Interleukin-17 Inhibitors After First-Line Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitors [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/real-world-comparative-effectiveness-of-upadacitinib-in-psoriatic-arthritis-evaluation-of-switching-to-upadacitinib-versus-tumor-necrosis-factor-inhibitors-or-interleukin-17-inhibitors-after-first-li/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/real-world-comparative-effectiveness-of-upadacitinib-in-psoriatic-arthritis-evaluation-of-switching-to-upadacitinib-versus-tumor-necrosis-factor-inhibitors-or-interleukin-17-inhibitors-after-first-li/

.jpg)