Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Title: (1221–1247) Pain in Rheumatic Disease Including Fibromyalgia Poster
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Oxytocin, also known as love hormone, is important in contextual memory. Oxytocin secreting parvocellular neurons suppress pain through projections to brain and spinal cord besides endocrine action. Optogenetic activation of Oxytocin neurons relieved pain in a rodent model of Fibromyalgia. We had previously shown association of rs6754031 (GG) promoter polymorphism in SCN9A with Fibromyalgia. This hypothalamic expressed voltage sodium channel Nav1.7 is upregulated in stress and its activity is linked to Oxytocin secretion. Hence, we studied SNPs rs4273468, rs3796863 and rs1556314 in genes BST1 (CD157), CD38 and TRPM2 genes involved in hypothalamic Oxytocin secretion. BST1 and CD38 catalyze the formation of cyclic ADP Ribose from NAD+ while TRPM2 is involved in Calcium secretion triggered by cyclic ADP Ribose. The minor alleles of the chosen SNPs are sufficiently common in our population and previously found to be associated with diseases such as Post Traumatic Stress Disorder and Restless Leg Syndrome that are themselves associated with Fibromyalgia
Methods: Patients diagnosed as Fibromyalgia using ACR1990 and/or ACR2016 criteria and consenting to genetic study were included. Healthy subjects with no widespread pain or connective tissue disease or medical comorbidity were taken as controls. Subjects were the same as our prior SCN9A study. DNA was extracted by phenol-chloroform method. Genotyping was done by TaqMan real time PCR. All continuous variables among baseline characteristics are expressed in mean (SD) and comparison by one way ANOVA while Fisher’s exact test was used for frequency tables. Odds Ratios and confidence intervals were estimated using Logistic Regression using a recessive minor allele (G) model using STATA14
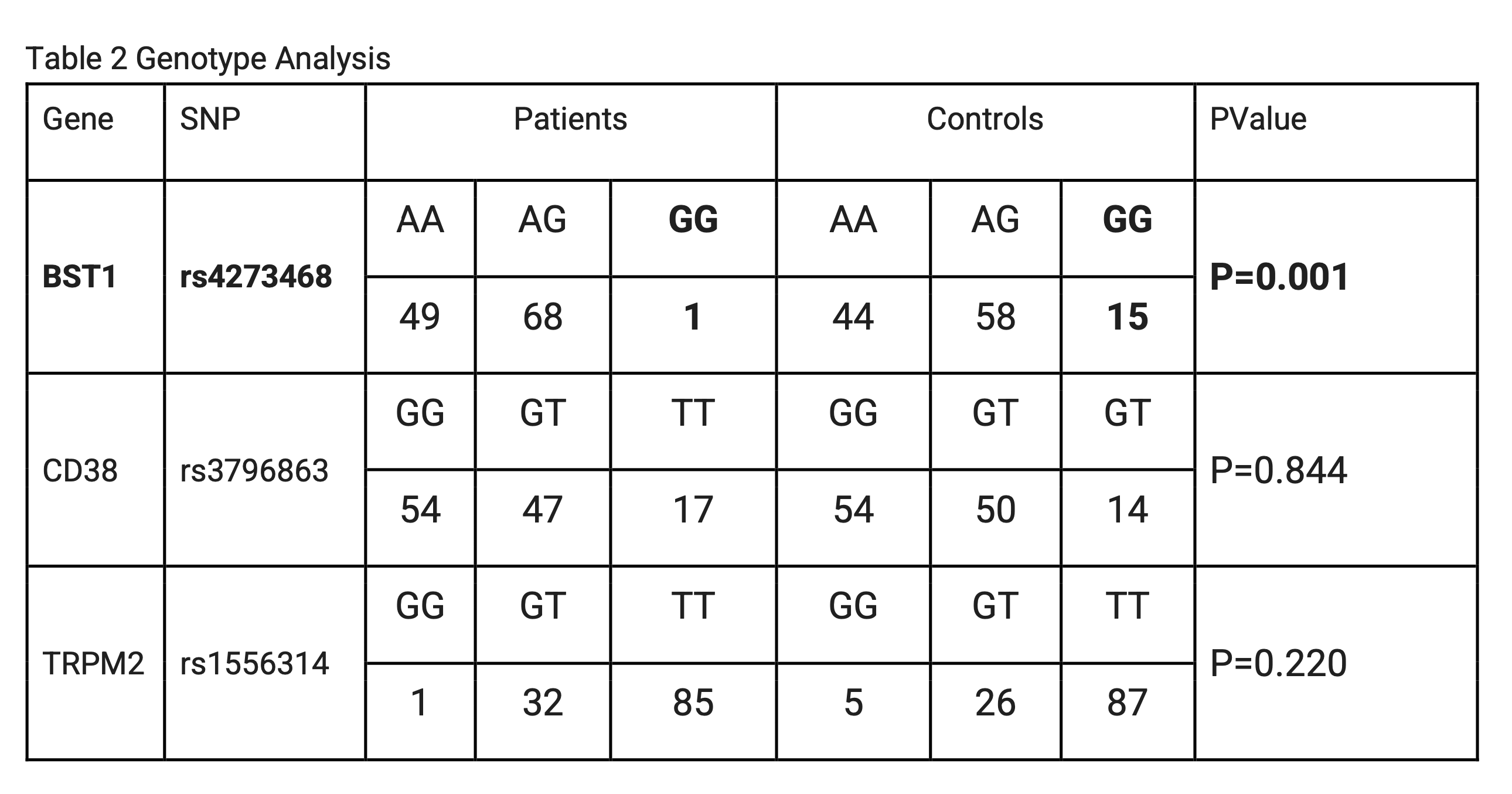
Results: A total of 118 FMS patients (88% female) of mean age of onset 35 (±9.6) years and 118 healthy controls (78% female) of age 34.7 (±10.9) years were included. Clinical features and comorbidities of patients are given in Table 1. Of the 118 patients, 74 were classified Fibromyalgia by both ACR2016 and ACR1990 criteria while 33 and 11 subjects were classified by ACR2016 and ACR1990 alone respectively. All three SNPs were in Hardy Weinberg equilibrium. Homozygous GG allele of BST1 rs4273468 polymorphism was protective with an Odds Ratio of 0.058 (0.0075-0.44, P < 0.001). The rs3796863 polymorphism of CD38 and rs1556314 of TRPM2 did not show any association with Fibromyalgia.
Conclusion: This is the first study showing association of BST1/CD157 with Fibromyalgia. This SNP rs4273468 in BST1 has previously been associated with Idiopathic Restless Leg Syndrome. Genes in the Oxytocin secretion pathway names BST1, CD38, TRPM2 and Oxytocin Receptor gene require further study.
 Clinical Characteristics of Fibromyalgia subjects
Clinical Characteristics of Fibromyalgia subjects
.gif) Genotype Analysis of BST1 CD38 and TRPM2
Genotype Analysis of BST1 CD38 and TRPM2
.gif) BST1 polymorphism rs4273468 genotype homozygous GG protects from Fibromyalgia
BST1 polymorphism rs4273468 genotype homozygous GG protects from Fibromyalgia
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ahmed Z, Thomas K, Guleria S, Aggarwal A, Lawrence A. Oxytocin pathway gene BST1 polymorphism rs4273468 genotype GG is negatively associated with Fibromyalgia [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/oxytocin-pathway-gene-bst1-polymorphism-rs4273468-genotype-gg-is-negatively-associated-with-fibromyalgia/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/oxytocin-pathway-gene-bst1-polymorphism-rs4273468-genotype-gg-is-negatively-associated-with-fibromyalgia/
