Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Title: (1191–1220) Muscle Biology, Myositis & Myopathies – Basic & Clinical Science Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Although herpes zoster vaccination has been evaluated in immunocompromised populations, studies assessing vaccine immunogenicity and safety in idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIM) are restricted to H1N1 and SARS-CoV-2 and no data are available for the recombinant zoster vaccine (RZV). Thus, the objectives are to compare immune response of RZV in IIM patients and healthy control group (CG), and evaluate the vaccine safety profile, the influence on IIM disease activity and factors associated with vaccine responsiveness.
Methods: This prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled study included 70 immunosuppressed IIM patients ( >18y) and 280 healthy controls (≥50y), all receiving two RZV doses (6 weeks apart). IIM patients were randomized 1:1 to receive vaccine (P1) or placebo (P2), with P2 subsequently vaccinated after unblinding at D84. Serum anti-glycoprotein E (anti-gE) antibody levels were measured by in-house GSK ELISA at baseline and 6 weeks post-second dose. Humoral response was defined as an anti-gE concentration ≥4-fold the pre-vaccination level. Geometric mean titers (GMTs) and Factor Increase (FI), as the ratio of post-vaccination to pre-vaccination titers were calculated. Adverse events were recorded using a standardized questionnaire. Disease activity was evaluated at baseline and 6 weeks after each RZV and placebo doses through clinical scores [Myositis Disease Activity Assessment Visual Analogue (MYOACT), Manual Muscle Test (MMT), Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ) and Modified Medical Research Council (mMRC) Dyspnea Scale] and serum muscle enzymes (ALT, AST, LDH, CK).
Results: Seventy IIM patients (54 dermatomyositis, 16 antisynthetase syndrome) and 280 individuals in control group (CG) were analyzed. Groups were balanced for sex (p >0.05), although IIM were slightly younger (54 vs. 55y; p=0.022). At D84, the humoral response rate was significantly lower in IIM compared to CG (78.8% vs. 99.3%, p < 0.001%). IIM patients exhibited markedly lower post-vaccine GMT (5.1 vs 11.8 mUI/mL, p < 0.001) and factor increase (FI) (18.5 vs. 53.0, p < 0.001) (Table 1). A trend toward reduced response with mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) was observed (30.8% vs. 57.1%, p=0.069) but not confirmed in multivariate analysis. Adverse events were less frequent in IIM vs CG (71.4 vs 88.9%, p=0.001), including local (65.7 vs. 83.9%, p < 0.001) and systemic reactions (38.6 vs. 61.4%, p=0.001). Disease activity metrics were comparable between groups (p >0.05), [patients VAS (p=0.308), physicians VAS (p=0,285, MMT (p=0.711), MYOACT (0,510), CPK (p=0,403) and DHL (p=0.065) (Table 2).
Conclusion: In immunosuppressed IIM patients, RZV showed good short-term immunogenicity and safety, with no disease worsening. However, reduced post-vaccination antibody titers suggest a potential risk for diminished long-term protection, highlighting the need for continued monitoring. (ClinicalTrials NCT05879419).
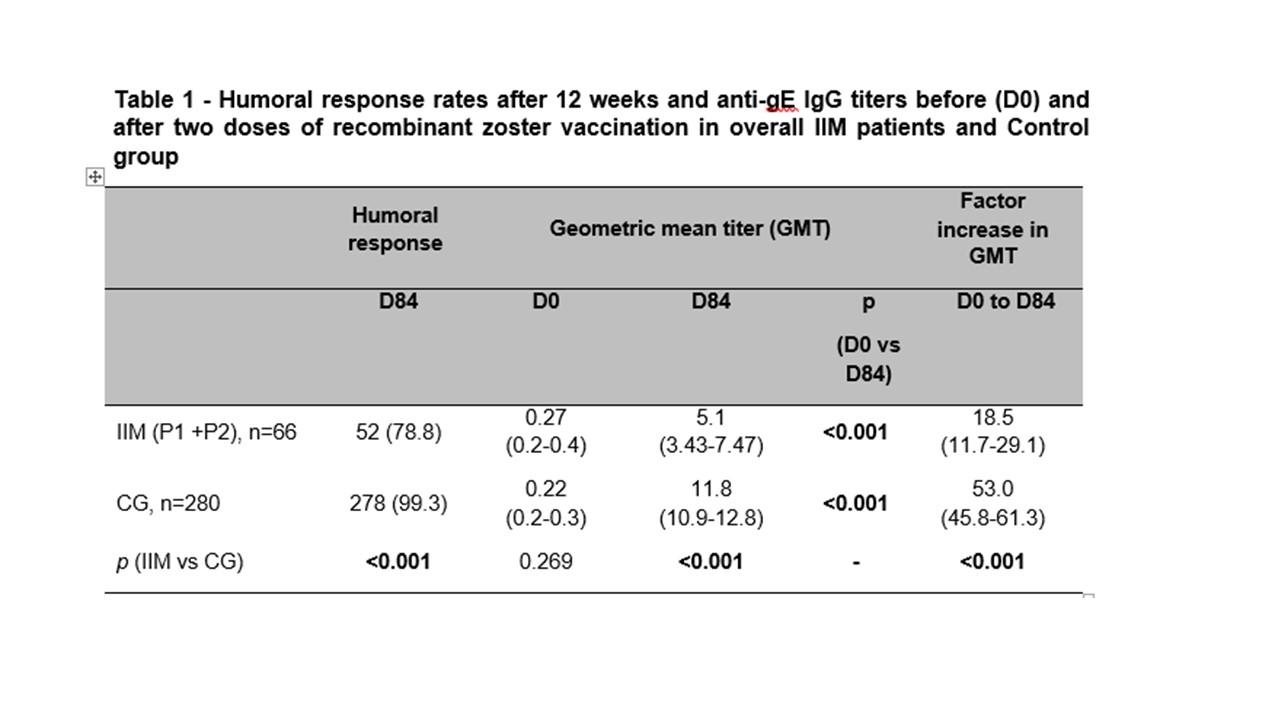 IIM – idiopathic inflammatory myopathies; CG – control group
IIM – idiopathic inflammatory myopathies; CG – control group
GMT – Geometric mean titers (AU/mL); Frequencies of humoral response are presented as number (%) and they were compared using two-sided chi-square test between ARD and CG at D84. Ig-gE IgG titers and factor increase in GMT are expressed as geometric means with 95% confidence interval (95%CI). Data regarding anti-gE titers were analyzed using ANOVA with repeated measures and 2 factors [2 groups (ARD vs. CG), at 2 time points (D0 and D84)], followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons at neperian logarithm (ln)-transformed data. GMT and factor increase in GMT were compared using Mann-Whitney test for intergroup comparisons in ln-transformed data at pre-specified time points (D0 and D84). All analyses were two-sided.
P1 – IIM patients who received the RZV on the day of randomization (D0) and after 6 weeks (D42) P2 – IIM patients who initially received placebo and were vaccinated 12 weeks after randomization, on D84 and after 6 weeks (D126)
.jpg) MYOACT-Myositis Disease Activity Assessment Visual Analogue, pPGA Patient global assessment, phPGA- Physician Global Assessment MMT-Manual Muscle Test, HAQ- Health Assessment Questionnaire, mMRC Modified Medical Research Council (mMRC) Dyspnea Scale
MYOACT-Myositis Disease Activity Assessment Visual Analogue, pPGA Patient global assessment, phPGA- Physician Global Assessment MMT-Manual Muscle Test, HAQ- Health Assessment Questionnaire, mMRC Modified Medical Research Council (mMRC) Dyspnea Scale
Results are expressed in medians (interquartile range) and n (%). Continuous data were compared using Mann-Whitney test, and categorical variables with the chi-square or Fisher’s exact tests, as appropriate, always as two-sided analyses.
P1 – IIM patients who received the RZV on the day of randomization (D0) and after 6 weeks (D42)
P2 – IIM patients who initially received placebo and were vaccinated 12 weeks after randomization, on D84 and after 6 weeks (D126)
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Pasoto S, Gorayeb T, Luppino-Assad A, Aikawa N, Medeiros-Ribeiro A, Kupa L, Borges B, Shinjo S, De Souza F, Miossi R, Bonfa E, Silva C. Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies: A Prospective Phase 4 Controlled Trial Of Recombinant Herpes Zoster Vaccine [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/idiopathic-inflammatory-myopathies-a-prospective-phase-4-controlled-trial-of-recombinant-herpes-zoster-vaccine/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/idiopathic-inflammatory-myopathies-a-prospective-phase-4-controlled-trial-of-recombinant-herpes-zoster-vaccine/
