Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Women with SLE are at an increased risk of developing cervical cancer, primarily by human papillomavirus (HPV) and immunosuppression. This elevated risk has been recognized by experts and updated guidelines recommend more frequent cervical cancer screening in women with SLE compared to the general population. This project aims to assess current cervical cancer screenings and HPV vaccination status in women with SLE compared to normal population at Houston Methodist Hospital (HMH).
Methods: We identified women aged 21-65 years who met the ACR/EULAR 2019 criteria for SLE diagnosis between 2015 and 2025 using electronic medical records, SlicerDicer software, and a retrospective chart review at HMH. Females with a history of hysterectomy or cervical cancer were excluded. A total of over 230 patients were initially identified, with 50 women confirmed through chart review. The SLE Disease Activity Index (SLEDAI) was obtained from their most recent visit. A healthy cohort of 50 women, matched by age and ethnicity, was also included. Individuals with diabetes, HIV, chronic immunosuppression, hysterectomy, cervical cancer, or tobacco use were excluded.
Results: Among the SLE group, 46% of the patients were Black, 32% were White, 16% were Hispanic, and 6% were Asian. The average age was 45, with a mean disease duration of 8 years. The mean SLEDAI score was 4, and most patients were on a combination of medications including Prednisone, Hydroxychloroquine, Azathioprine, Methotrexate, Mycophenolate, and Belimumab (Table 1). Our results indicated that 6% of the SLE group had received the HPV vaccine, compared to 20% in the healthy control (HC) group. Only 74% of SLE patients had undergone cervical screening and 64% had HPV testing within the past five years. However, the HC group had 100% cervical cancer screening and 72% had HPV testing within the same timeframe (Figure 1). Furthermore, only 30% of the SLE group had an annual PAP smear and 18% had annual HPV testing (Figure 2A). Among the SLE patients, 7 abnormal PAP smears were identified, including 2 low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (LSIL) and 5 cases of Atypical Squamous Cells of Undetermined Significance (ASCUS), compared to just one ASCUS in the HC group (Figure 2B). In the SLE group, 3% tested positive for HPV, including one patient with LSIL, while 8% of the HC group tested positive for HPV. The patients with LSIL were all Black and had notably higher SLEDAI scores (Figure 2C).
Conclusion: Our study confirms a significant gap in cervical cancer and HPV screening among women with SLE compared to healthy controls (HC). The findings underscore the importance of implementing annual screening for SLE patients. Additionally, the results suggest that a higher SLEDAI in Black patients may pose an increased risk for worse outcomes. The study also highlights the need for more HPV testing and greater education on vaccination to help prevent adverse outcomes in both groups. Collaborating with gynecologic experts could further raise awareness and improve screening practices. Larger studies are necessary to better understand the risks and long-term outcomes in this population.
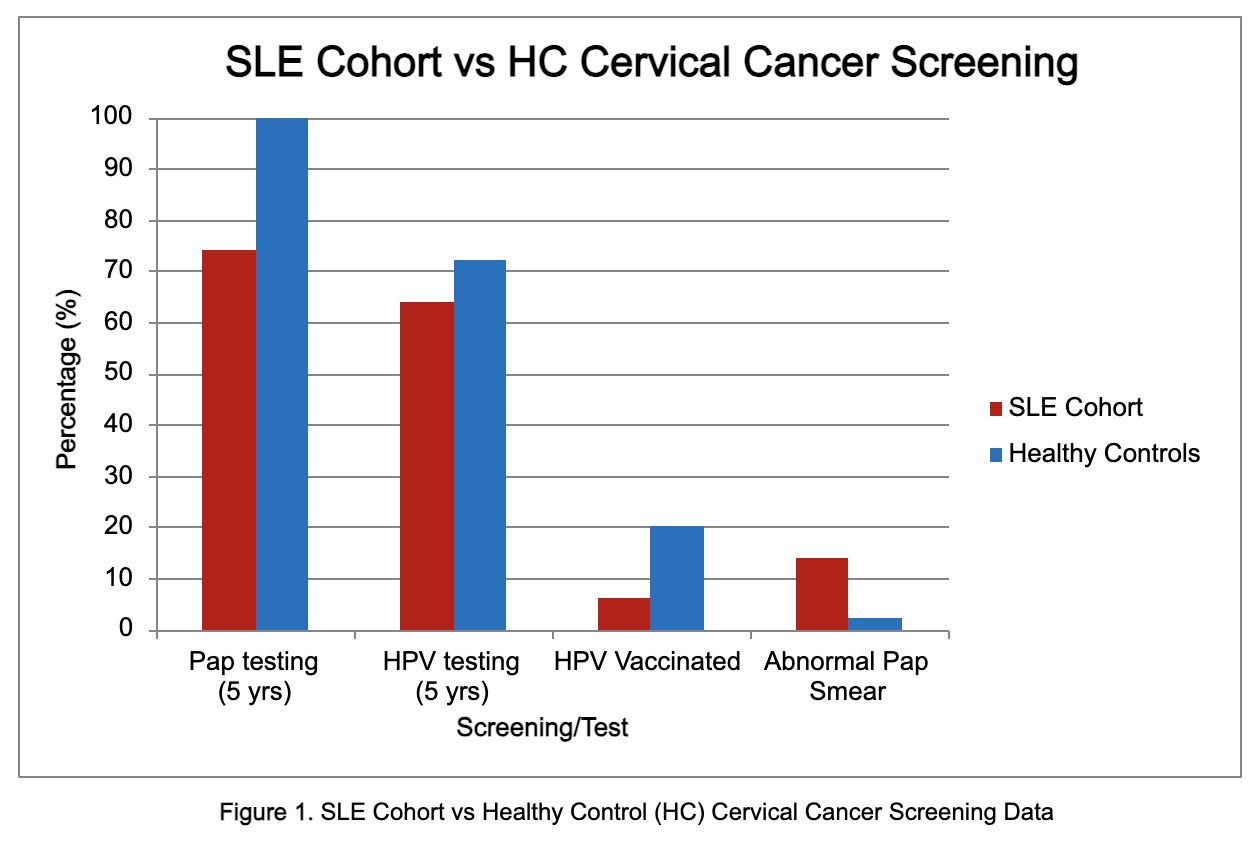 Table 1. SLE Cohort vs Healthy Control (HC) Characteristics
Table 1. SLE Cohort vs Healthy Control (HC) Characteristics
.jpg) Figure 1. SLE Cohort vs Healthy Control (HC) Cervical Cancer Screening Data
Figure 1. SLE Cohort vs Healthy Control (HC) Cervical Cancer Screening Data
.jpg) Figure 2. SLE Cohort Pap Smear Results by Frequency (2A), SLEDAI (2B) and Race (2C)
Figure 2. SLE Cohort Pap Smear Results by Frequency (2A), SLEDAI (2B) and Race (2C)
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Javed M, Jagannath D, Aveytia Camacho A, Mathew A, Harms K, Daliri S, Guevara M. Cervical Cancer and HPV Screening in Women with Lupus vs Healthy Control Group: A Retrospective Study at a Tertiary Referral Center [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cervical-cancer-and-hpv-screening-in-women-with-lupus-vs-healthy-control-group-a-retrospective-study-at-a-tertiary-referral-center/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cervical-cancer-and-hpv-screening-in-women-with-lupus-vs-healthy-control-group-a-retrospective-study-at-a-tertiary-referral-center/
