Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: The prevalence of depression in patients who have rheumatic diseases is high and has been shown to be associated with poorer outcomes. Additionally, certain medications for rheumatologic conditions have been associated with an increased risk of depression, depressed mood, and suicidal ideation, namely apremilast and belimumab. Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ9) screening is a well-established tool in screening for depression at medical appointments, including those with rheumatic diseases. A score of 10 or higher is a standard cut point to diagnose depression. This study assessed PHQ9 scores for patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) on apremilast and belimumab, respectively.
Methods: The study population included patients with PsA and SLE seen within Allegheny Health Network rheumatology clinics between November 2021 through November 2024 with at least one PHQ9 score documented. Demographic and clinical variables were collected. Descriptive statistics were used to describe the patient population. PHQ9 scores for persons with PsA were compared based on apremilast usage, and scores for patients with SLE were compared based on belimumab usage. The Kruskal-Wallis test was conducted to compare the PHQ9 score amongst the two patient populations. Fisher’s exact test was performed to examine the association between PHQ9 category with medications.
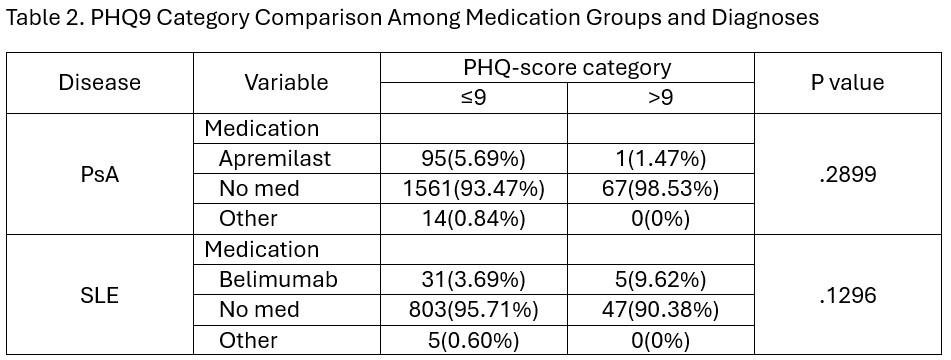
Results: At least one PHQ9 score was documented for 1738 patients with PsA, and 892 patients with SLE (Table 1). Of the patients with PsA, 96 (5.52%) were treated with apremilast. There was no significant difference in median PHQ9 scores between patients that were on apremilast compared to those that were not (median 0 [IQR 0-0], median 0 [IQR 0-0]; p=0.2076). In addition, when stratified by apremilast usage, there was no significant difference found in patients with PsA who had PHQ9 scores of ≤9 compared to those with a score of ≥10 (p=0.2899; Table 2).Of the patients with SLE, 36 (4.04%) were treated with belimumab. There was no significant difference in median PHQ9 scores between those treated with belimumab compared to those that were not (median 0 [IQR 0-1.5], median 0 [IQR 0-0]; p=0.0995). And when stratified by belimumab usage, there was no significant difference in the SLE patients with PHQ9 scores of ≤9 compared to those with a score of ≥10 (p=0.1296; Table 2).
Conclusion: In this single center observational cohort, we found that PHQ9 scores were no different between patients with PsA treated with apremilast compared to those not; and no difference between patients with SLE treated with belimumab compared to those who were not. The overall positive depression screening was low in all patients. This provides real world assurance of the safety of apremilast and belimumab, but should not underscore the importance of monitoring depression in rheumatologic diseases.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Dolecki C, Hajizadeh S, Yin Y, Dore A. Prevalence of Depression Associated with Rheumatologic Medications with Labeled Warnings: Real World Evidence from a Tertiary Care Center [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/prevalence-of-depression-associated-with-rheumatologic-medications-with-labeled-warnings-real-world-evidence-from-a-tertiary-care-center/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/prevalence-of-depression-associated-with-rheumatologic-medications-with-labeled-warnings-real-world-evidence-from-a-tertiary-care-center/

.jpg)