Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: : Early adherence data for newly approved drugs guide clinical management, yet small cohorts hamper conventional analyses. Romosozumab (Romo), licensed April 2019 for high-risk postmenopausal osteoporosis, is an ideal example. This study is to identify determinants of Romo adherence using Bayesian logistic regression.
Methods: Medicare fee-for-service claims (2006–2022) were used to identify women ≥65 who began Romo in 2019 and maintained ≥4 years of continuous enrollment (≥3 baseline). Exclusion criteria include metastatic cancer, Paget’s disease. A priori predictors – guided by literature and expert input – age groups (younger [≤75] vs older [ >75]), race, regions, metropolitan residence (MR), Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI), CKD, COPD, antidepressants (anti-DP), antidiabetics (anti-DM), hormone therapy (HT), steroids, and ER visits—were entered into frequentist and Bayesian logistic models. High adherence was proportional days covered (PDC) ≥80% in the first 3 months. Results are odds ratios (OR) with 95% confidence or credible intervals(CI/CrI).
Results: Among 1,777 initiators (younger: n = 752; older: n = 1,025), 77.8 % were indicated as high adherence. Frequentist analysis linked White race to higher adherence in younger women (OR 2.42, 95%CI [1.35–4.36]) and COPD to lower adherence in older women (0.64, [0.44–0.91]). Bayesian analysis revealed additional associations. In younger patients (Figure 1), anti-DP (OR=0.81, 95% CrI: [0.74–0.89]), CKD (0.88 [0.81–0.97]), COPD (0.79 [0.74–0.83]), anti-DM (0.95 [0.91–0.99]), ER visits (0.90 [0.84–0.96]), and higher CCI (0.78 [0.70–0.88]) were associated with decreased adherence, while White race (2.83 [2.37–3.26]) , MR (1.29 [1.13–1.47]) and HT (1.05 [1.01–1.09]) were associated with high adherence. In older patients (Figure 2), CKD (0.89 [0.84–0.96]), COPD (0.81 [0.77–0.86]), steroids (0.78 [0.73–0.85]), and higher CCI (0.83 [0.77–0.90]) were associated with decreased adherence, while White race (2.05 [1.82–2.28]) and MR (1.34 [1.22–1.48]) were associated with high adherence.
Conclusion: Bayesian analysis identified additional adherence factors among early Romo adopters compared with frequentist models, including anti-DP and HT. Future research should consider Bayesian modeling when studying medication adherence, particularly when sample size may be limited.
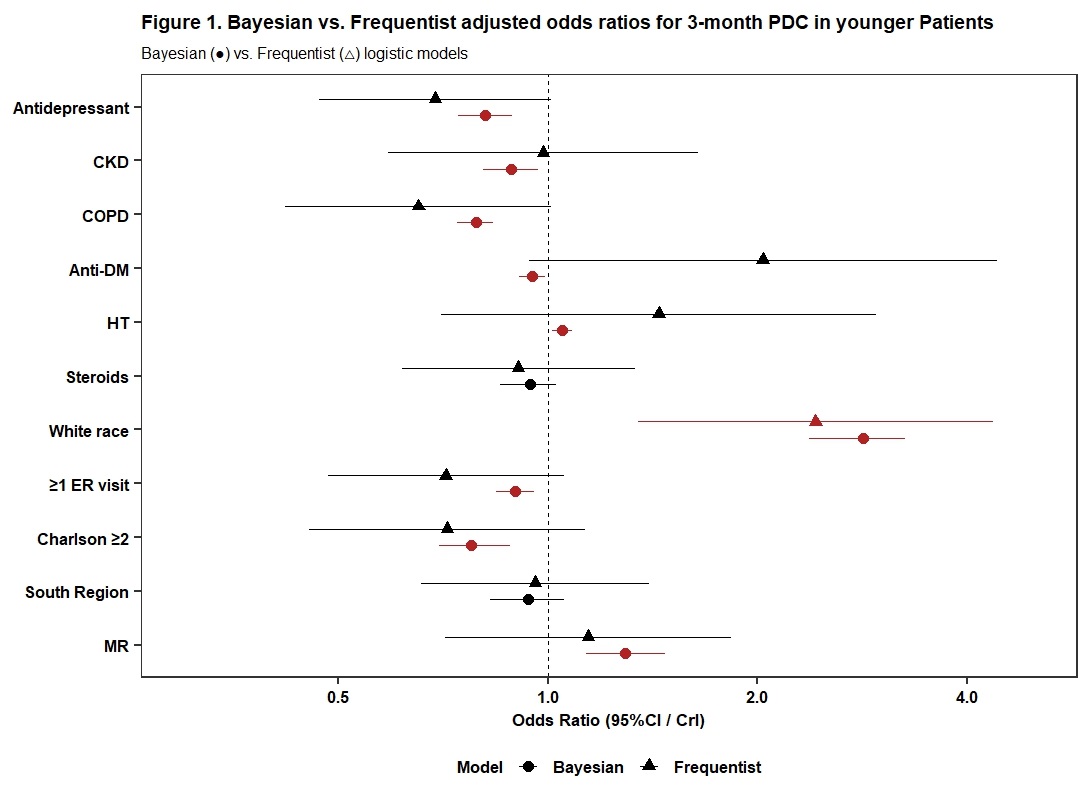 Notes: PDC: proportion of days covered; CKD: chronic kidney disease; COPD: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; DM: diabetes mellitus; HT: hormone therapy; ER: emergency room; MR: metropolitan region; CI: confidence interval; CrL: credit interval
Notes: PDC: proportion of days covered; CKD: chronic kidney disease; COPD: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; DM: diabetes mellitus; HT: hormone therapy; ER: emergency room; MR: metropolitan region; CI: confidence interval; CrL: credit interval
.jpg) Notes: PDC: proportion of days covered; CKD: chronic kidney disease; COPD: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; DM: diabetes mellitus; HT: hormone therapy; ER: emergency room; MR: metropolitan region; CI: confidence interval; CrL: credit interval
Notes: PDC: proportion of days covered; CKD: chronic kidney disease; COPD: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; DM: diabetes mellitus; HT: hormone therapy; ER: emergency room; MR: metropolitan region; CI: confidence interval; CrL: credit interval
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Wu H, Liu Y, Arora T, Curtis J. Bayesian Analysis of Factors Associated with Romosozumab Adherence Among Early Adopters in Medicare Beneficiaries [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/bayesian-analysis-of-factors-associated-with-romosozumab-adherence-among-early-adopters-in-medicare-beneficiaries/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/bayesian-analysis-of-factors-associated-with-romosozumab-adherence-among-early-adopters-in-medicare-beneficiaries/
