Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 26, 2025
Title: Abstracts: Systemic Lupus Erythematosus – Treatment I (0801–0806)
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 1:00PM-1:15PM
Background/Purpose: Ianalumab, a fully human monoclonal antibody against the B cell–activating factor receptor (BAFF-R), has a dual mechanism of action of B cell depletion through antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity and BAFF-R blockade. A treat-to-target approach, targeting Definition of Remission in SLE (DORIS) and Lupus Low Disease Activity State (LLDAS), has demonstrated potential in reducing organ damage progression and improving quality of life.1 Here, we investigated the 52-week impact of ianalumab on attainment of LLDAS, DORIS, and glucocorticoid (GC) taper in patients with active SLE enrolled in a phase IIa study (NCT03656562).
Methods: Patients with SLE were randomized 1:1 to subcutaneous ianalumab 300 mg or placebo every 4 weeks (W). The study included two treatment periods consisting of a double-blind period with a comparison between ianalumab and placebo for 28W followed by a 24W open-label (OL) period with continued ianalumab 300 mg in the active arm (ianalumab/OL-ianalumab) and switch from placebo to ianalumab 300 mg (placebo/OL-ianalumab). Following 52W treatment, patients entered a post-treatment (PT) period up to W68. Patients on stable GC were required to undergo GC tapering from W4 to W16 and remain on the dose achieved through Week 28. Endpoints evaluated include: proportion of patients achieving LLDAS, DORIS, and tapered GC ≤5 mg at each visit; time-to-first LLDAS; cumulative time (defined as 20%/50% of time) spent in LLDAS and DORIS during the placebo-controlled period (28W) and the overall 52W treatment period; and cumulative time with GC taper (≤5 mg and ≤ baseline dose). All efficacy outcomes are summarized descriptively. Time-to-event endpoints were assessed using Kaplan-Meier analysis.
Results: This analysis included 67 patients: 34 in ianalumab/OL-ianalumab and 33 in placebo/OL-ianalumab. Although LLDAS/DORIS attainment increased after switching, at W52, more patients in the ianalumab/OL-ianalumab group had achieved LLDAS and DORIS (38.2% and 26.5%) than those in placebo/OL-ianalumab (21.2% and 12.1%); this trend was maintained in the PT period (ianalumab/OL-ianalumab: 41.2% and 29.4%; placebo/OL-ianalumab: 21.2% and 12.1%; Fig. 1a,1b). Median time to first LLDAS was 40W in the ianalumab/OL-ianalumab group (Fig. 2). At W52, more patients in ianalumab/OL-ianalumab (85.3%) achieved GC taper than in placebo/OL-ianalumab (72.7%). During the 52W treatment period, cumulative time spent on LLDAS, DORIS, and tapered GC ≤5 mg was higher in ianalumab/OL-ianalumab than in placebo/OL-ianalumab (Table 1).
Conclusion: A 52W week of ianalumab treatment was associated with more time in LLDAS and DORIS, as well as higher attainment of GC taper goals compared to 28W placebo followed by 24W ianalumab exposure. This suggests that earlier ianalumab exposure led to cumulative clinical benefit in patients with SLE. Larger studies are required to confirm these findings. ReferenceParra Sánchez AR et al. Rheumatol Ther 2023;10:1459-77.
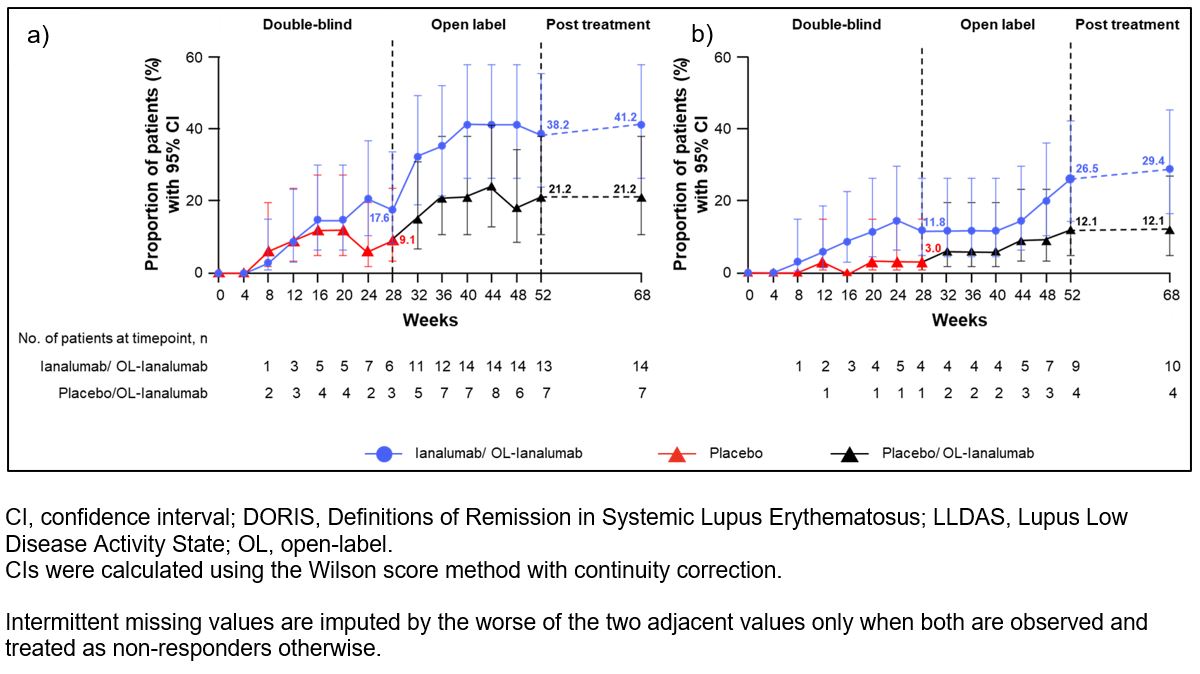 Fig. 1. Proportion of patients who achieved a) LLDAS and b) DORIS by treatment and visit over the 52-week treatment period
Fig. 1. Proportion of patients who achieved a) LLDAS and b) DORIS by treatment and visit over the 52-week treatment period
.jpg) Fig. 2: Time to first LLDAS over the 52-week treatment period
Fig. 2: Time to first LLDAS over the 52-week treatment period
.jpg) Table 1: Cumulative time spent on LLDAS, DORIS, and tapered GC ≤5 mg during the 28-week double-blind period and during the 52-week study period
Table 1: Cumulative time spent on LLDAS, DORIS, and tapered GC ≤5 mg during the 28-week double-blind period and during the 52-week study period
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Morand E, Gaillez C, Oliver S, Ghanshani S, Pozzobon M, Bao W, Vital E. Achieving Sustained Lupus Low Disease Activity State and Remission With Ianalumab (VAY736) in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A post hoc Analysis From a Phase II Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/achieving-sustained-lupus-low-disease-activity-state-and-remission-with-ianalumab-vay736-in-patients-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-a-post-hoc-analysis-from-a-phase-ii-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/achieving-sustained-lupus-low-disease-activity-state-and-remission-with-ianalumab-vay736-in-patients-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-a-post-hoc-analysis-from-a-phase-ii-study/
