Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 26, 2025
Title: (0731–0764) Vasculitis – Non-ANCA-Associated & Related Disorders Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Giant cell arteritis (GCA) is the most common large-vessel vasculitis, and its cornerstone treatment is the use of corticosteroids (CS). Various therapies have been proposed as CS-sparing agents, with methotrexate (MTX) being the only conventional synthetic drug that has received favorable recommendations in clinical practice guidelines. However, results from clinical trials and observational studies have been inconsistent. The aim of this study was to evaluate the role of MTX added to standard CS therapy in facilitating CS withdrawal in real-world clinical practice, by analyzing data from the Spanish national ARTESER registry.
Methods: Descriptive, observational, multicenter study of patients diagnosed with GCA undergoing treatment with corticosteroids in real-life settings. Baseline characteristics and treatments were compared between patients on CS monotherapy and those receiving concomitant MTX (CS+MTX). A survival analysis was performed using the Kaplan-Meier method, and the groups were compared using the log-rank test. Additionally, a Cox regression analysis was conducted to identify factors associated with complete CS withdrawal and CS-free sustained remission for at least 6 months.
Results: A total of 885 patients with GCA were included (615 treated with CS monotherapy and 270 with CS+MTX). Compared to those receiving CS monotherapy, patients in the CS+MTX group were younger, predominantly female, had a higher prevalence of concomitant polymyalgia rheumatica, and experienced a longer symptom duration before diagnosis (Table 1). A higher relapse rate was observed in patients treated with CS+MTX compared to those on CS monotherapy (32.9% vs 12.5%, p< 0.001). Similarly, the cumulative dose of corticosteroids during follow-up was higher (8.87 g vs 7.56 g, p< 0.001). Time to reach doses of 5 mg, 7.5 mg, complete CS withdrawal, and CS-free remission for over 6 months was longer in the CS+MTX group. Survival analysis revealed statistically significant differences in time to CS withdrawal (p< 0.001) and CS-free remission sustained for more than 6 months (p< 0.001) (Figure 1). No significant differences were observed between the groups in time to reach 5 or 7.5 mg of prednisone. In the Cox regression models, the use of MTX (HR 0.563; 95% CI: 0.434–0.732; p< 0.001), female sex, and positive temporal artery biopsy were associated with a lower likelihood of achieving CS-free remission. Furthermore, MTX use was associated with a lower probability of achieving CS-free remission sustained for over 6 months (HR 0.724; 95% CI: 0.533–0.983; p< 0.001), along with female sex and headache (Table 2).
Conclusion: In the ARTESER registry, the use of MTX was not associated with a higher probability of achieving complete CS withdrawal or sustained CS-free remission compared to CS monotherapy. Additionally, patients did not show a lower cumulative dose of CS or a reduced relapse rate. Therefore, MTX use did not seem to be associated with better CS sparing outcomes in our real-life registry. Further research is needed to confirm our results and explore specific subgroups.
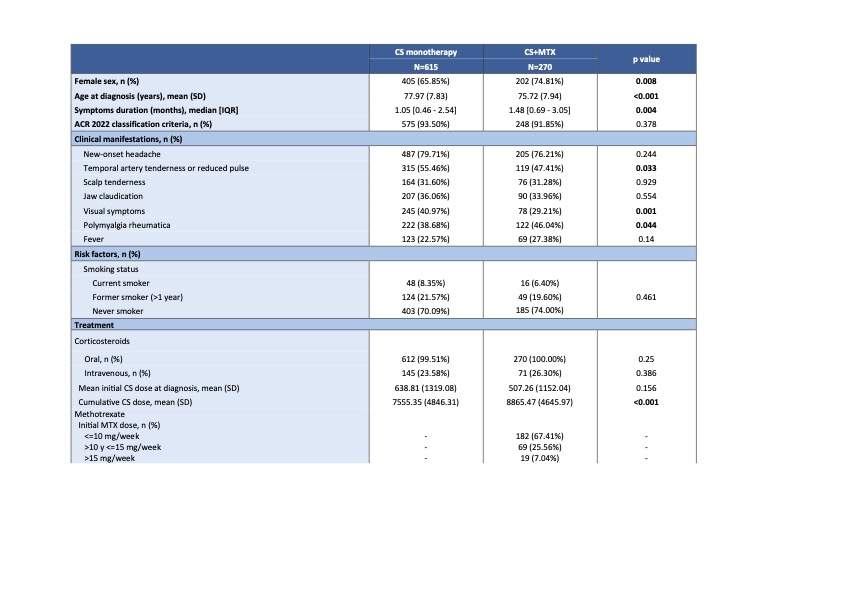 Table 1. Baseline clinical and treatment characteristics at the time of GCA diagnosis, stratified by MTX use (CS monotherapy vs CS+MTX).
Table 1. Baseline clinical and treatment characteristics at the time of GCA diagnosis, stratified by MTX use (CS monotherapy vs CS+MTX).
.jpg) Figure 1. Kaplan-Meier survival curves: a) CS discontinuation and b) CS-free sustained remission (last 6 months).
Figure 1. Kaplan-Meier survival curves: a) CS discontinuation and b) CS-free sustained remission (last 6 months).
.jpg) Table 2. Multivariable Cox regression models (parsimonious models).
Table 2. Multivariable Cox regression models (parsimonious models).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Muñoz-Martínez P, Domínguez-Álvaro M, Otero L, Moriano C, Sánchez Martín J, Narváez J, Galíndez Agirregoikoa E, Mendizábal J, Abasolo Alcazar l, Loricera J, Muñoz A, Castañeda S, Benito-Melero r, Larena C, Estrada-Alarcón P, Galisteo C, Riveros frutos A, Ortiz sanjuán F, Salman Montes T, Blanco R. The role of Methotrexate in the treatment of Giant Cell Arteritis: data from the ARTESER registry. [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-role-of-methotrexate-in-the-treatment-of-giant-cell-arteritis-data-from-the-arteser-registry/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-role-of-methotrexate-in-the-treatment-of-giant-cell-arteritis-data-from-the-arteser-registry/
