Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 26, 2025
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: In reactive arthritis (ReA) approximately a half of patients achieve drug-free remission (DFR), while others develop chronic disease. To identify predictive biomarkers for DFR, we performed a baseline transcriptomic analysis of whole blood and synovial fluid in ReA and undifferentiated peripheral spondyloarthritis (pSpA) and followed them up for 3 months each. Key differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were validated.
Methods: Fifty-seven patients meeting Braun criteria for ReA or ASAS criteria for pSpA (excluding IBD-related or psoriatic arthritis) were recruited. Baseline whole blood and synovial fluid (SF) samples from inflamed joints were collected. Drug free remission (DFR) was defined as being completely symptom-free at three months while off all medications. Patients were grouped as chronic ReA or DFR. Transcriptomics was performed on whole blood (n=14) and paired SF (n=10) using Illumina NovaSeq for RNAseq, X Plus and DRAGEN for demultiplexing/alignment, DESeq2 for DEG analysis, and cluster Profiler for KEGG pathway enrichment in R.Amongst the top differentially expressed genes, Complement factor D (CFD) and Cytochrome enzyme CYP1B1, were validated internally in the RNAseq cohort (n=14) along with another external validation (n=5) using a SYBRGreen- TaqMan system. Mann-Whitney U test compared ΔCT values between DFR and chronic groups.
Results: Out of total 57 patients [75% males; median age 32 (IQR12-40) years], 37 were ReA and 20 were undifferentiated pSpA. Fifty-two percent (n=30) of patients achieved DFR. We selected baseline whole blood (n=14) and paired synovial fluid (SF, n=10) samples based on RNA quality for RNAseq. Of these, 6 had attained DFR (SF available for 3). There was no difference in the transcriptome profiles of ReA versus undifferentiated pSpA.Whole blood transcriptomics identified four differentially expressed genes associated with DFR (Upregulated: CFD, MYOM2, CYP1B1. Down-regulated: CACNA1l) [Figure 1A]. KEGG enrichment analysis revealed pathways related to Endocytosis, Shigellosis, Salmonellosis and certain viral-related pathways were enriched in patients who ultimately attained DFR [Figure 1B]. Differentially expressed genes in the synovial fluid were not statistically significant (not shown). However, the KEGG analysis also showed the enrichment of pathways associated with Salmonellosis, Shigellosis, Endocytosis and different viruses [Figure 2A]. Figure 2B shows the concept maps of the top 8 upregulated pathways in the KEGG analysis.In the preliminary validation, CFD [median ΔCT DFR: 6.48 (IQR 4.63-12.87), chronic: 9.20 (IQR 7.27-12.65); p=0.2] and CYP1B1 [median ΔCT DFR: 6.95 (IQR 6.63-8.76), chronic: 10.25 (IQR 7.98-11.69); p=0.055] did not reach statistical significance in DFR patients compared to chronic ReA.
Conclusion: Baseline whole blood gene expression profiles predict DFR in ReA. Enrichment of bacterial and viral pathways in DFR patients, despite the absence of live bacteria in SF, suggests a potential role for bacterial exosomes or other pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) in the resolution of ReA. The role of CFD and CYP1B1 needs to be elucidated.
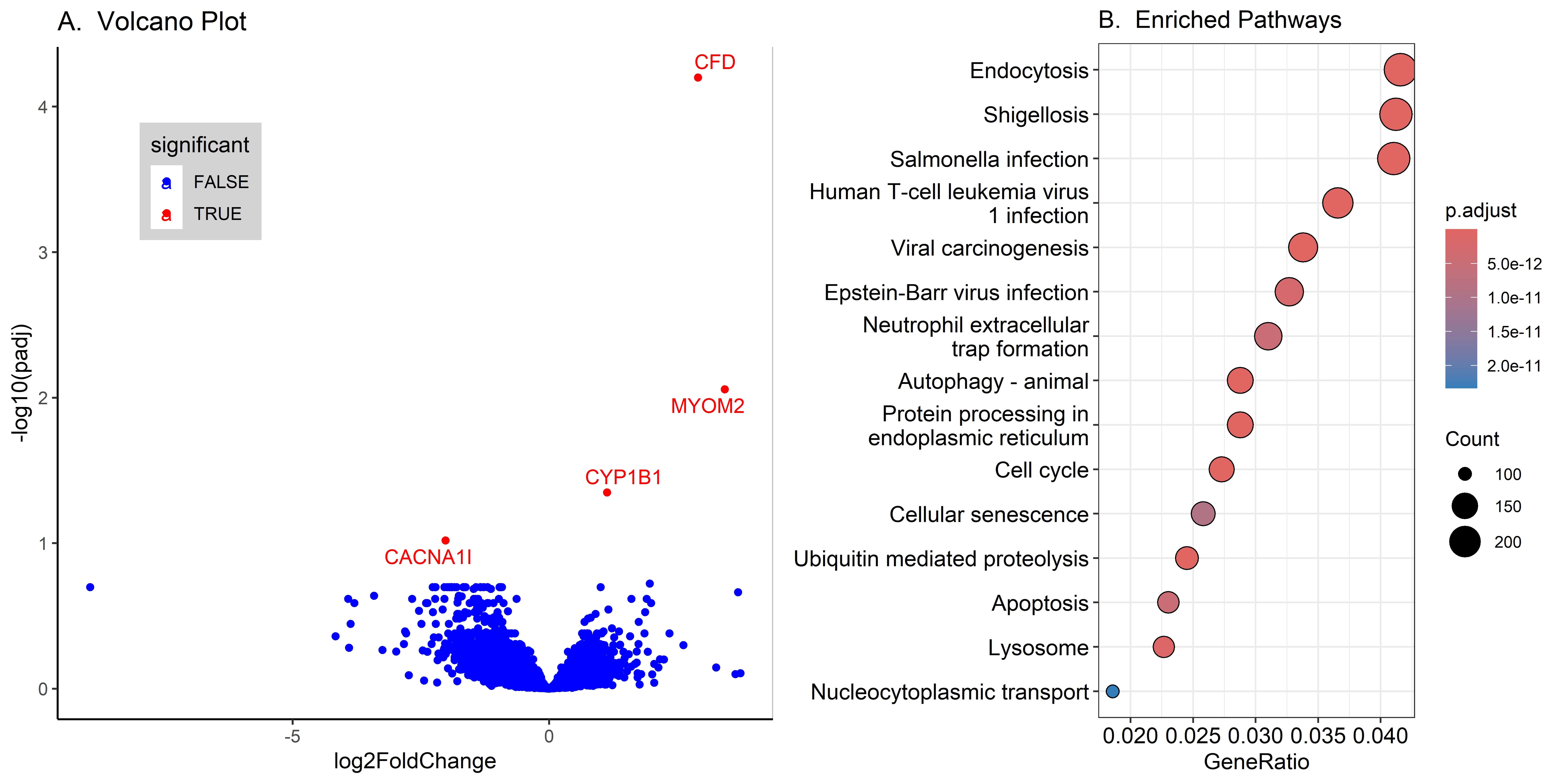 Figure 1: Comparison between whole blood transcriptome profiles of patients with chronic reactive arthritis and those with drug-free remission. (A) Volcano plot showing differentially expressed genes and (B) Showing the top 15 enriched pathways (KEGG)
Figure 1: Comparison between whole blood transcriptome profiles of patients with chronic reactive arthritis and those with drug-free remission. (A) Volcano plot showing differentially expressed genes and (B) Showing the top 15 enriched pathways (KEGG)
.jpg) Figure 2: Comparison between synovial fluid transcriptome profiles of patients with chronic reactive arthritis and those with drug-free remission. (A) Dot plot of the top 15 enriched pathways (KEGG) and (B) showing a Concept network map between the top 8 enriched pathways.
Figure 2: Comparison between synovial fluid transcriptome profiles of patients with chronic reactive arthritis and those with drug-free remission. (A) Dot plot of the top 15 enriched pathways (KEGG) and (B) showing a Concept network map between the top 8 enriched pathways.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Agarwal A, Dhanekula P, Verma S, ravi Nayak S, Mruthyanjaya P, Padhan P, Patro A, Misra R, Ahmed S. Reactive Arthritis Transcriptomics: Enriched Enterobacteriaceae-related Pathways in Synovial Fluid and in Blood is Associated with Drug-free Remission [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/reactive-arthritis-transcriptomics-enriched-enterobacteriaceae-related-pathways-in-synovial-fluid-and-in-blood-is-associated-with-drug-free-remission/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/reactive-arthritis-transcriptomics-enriched-enterobacteriaceae-related-pathways-in-synovial-fluid-and-in-blood-is-associated-with-drug-free-remission/
