Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: The accurate interpretation of hand radiographs is critical in the diagnosis and management of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients. This project determined first, if the reading request and/or clinical history provided to the radiologist (RAD) improved the accuracy of the reported findings and second if the overall interpretation of the radiographs in the Veterans Affairs (VA) computerized patient record system (CPRS) was consistent with that of an expert reader (ER).
Methods: Bilateral hand and wrist radiographs of 302 RA patients enrolled in the Veterans Affairs Rheumatoid Arthritis (VARA) registry, a multi-center observational cohort, were assessed by an ER for the presence and/or absence of erosions (ERO) and/or joint space narrowing (JSN). RAD reports on these patients were evaluated by a blinded chart abstractor (CA) to determine if the CPRS report contained a clinical history for RA and if there was a specific request for the evaluation for ERO and/or JSN. The CA also specifically noted if a RAD reported the diagnosis of RA and/or an alternative diagnosis such as osteoarthritis (OA), mentioned ERO and/or JSN.
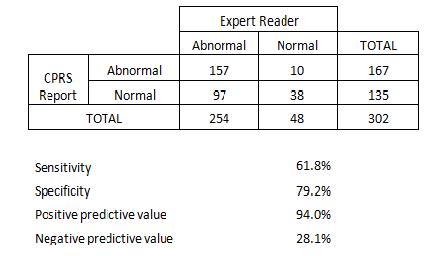
Results: The patients’ mean age was 64±11 years, 88% were male, RA disease duration was 13±11 years, and the majority was sero-positive for rheumatoid factor (84%) and anti-CCP (80%). As noted below, 157 were reported to have abnormal findings by both CPRS RAD and ER and 38 patients were reported normal by both CPRS RAD and ER. Ten patients were reported as abnormal by CPRS RAD but were reported normal by ER and 97 were reported abnormal by ER but normal by CPRS RAD (35% overall discordance). Of the 302 reports, 27 (8.9%) were given an alternative diagnosis by the CPRS RAD, the most common being OA and Calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease (CPPD). The sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive values were determined comparing the RAD to the ER as gold standard.
A notation of ‘RA’ and/or a specific request for an evaluation of ERO and/or JSN in the X-ray request did not improve the accuracy of the diagnosis and/or reporting of ERO and JSN. The only factors associated with higher likelihood of CPRS RAD reporting RA was joint swelling count (p<0.01) and C-reactive protein level (p<0.05).
Conclusion: The accuracy of RAD to identify patients with RA in comparison to the ER is not enhanced in reports that provided the RAD with a clinical history and specific directions to assess for ERO and JSN. While a positive RA diagnosis by the RAD in CPRS has a high potential to be correct, the absence of this diagnosis does not possess sufficient accuracy to exclude the diagnosis of RA.
Disclosure:
M. P. Martes,
None;
A. R. Erickson,
None;
T. R. Mikuls,
None;
G. W. Cannon,
None.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/low-accuracy-of-radiograph-reports-in-identifying-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-in-the-veterans-affairs-rheumatoid-arthritis-registry/