Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
José Félix Restrepo1, Inmaculada del Rincón1, Roy W Haas1, Daniel F Battafarano2, Agustín Escalante1 University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio1; San Antonio Military Medical Center, San Antonio, Texas2
Background/Purpose: Interstitial lung disease (ILD) is associated with significant morbidity and mortality in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Diagnosis requires imaging studies or invasive procedures that are costly and may entail risk. Because of this, diagnostic procedures are only performed on patients who display symptoms or sign of the disease. A strategy to identify patients at high risk would help target those who would benefit from a diagnostic intervention. The objective of the present study is to develop an index for the identification of RA patients at high risk of ILD.
Patients and Methods: We studied patients with RA recruited from rheumatology practices. We assessed each patient for the following variables: Age, sex, joint tenderness and swelling, rales on auscultation, subcutaneous nodules, disease severity, use of methotrexate and current prednisone use, smoking status, rheumatoid factor , antibodies against cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti- CCP), and ESR. ILD was diagnosed using chest X-ray, CT scan, and/or lung biopsy. We divided the study sample into two equivalent groups using a random procedure. We used the first group as the development sample. We performed a stepwise logistic regression model using the above variables as predictors. Using the results of the model we developed an index, which we then tested in the second group, or validation sample.
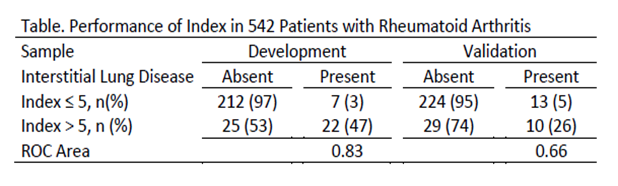
Results: The sample included 779 patients, of whom 69 had ILD, 147 had other pulmonary diseases and 563 had no lung diseases. We conducted the current analysis on 542 patients (52 with ILD, 490 without ILD) who had all the variables for the index. The variables and score in the index were as follow: male sex=2 ; ESR (mm/hr.) ≤ 30=0, 31-60=1,61-100=2,>100=3; anti- CCP ≤20=0, 21-60=1, 61-150=2, >150=3; rales present=2. The Index is the sum of the score for each variable. The maximum value is 10. The performance of the index in identifying patients with ILD in the development and validation sample is shown in Table.
Conclusion: This novel index may be used to identify RA patients at increased risk of ILD. Patients with a score higher than 5 may benefit from additional diagnostic testing to detect ILD, while those with 5 or less are unlikely to have ILD.
Disclosure: Nothing to disclose.
Disclosure:
J. F. Restrepo,
None;
I. Del Rincon,
None;
R. W. Haas,
None;
D. F. Battafarano,
None;
A. Escalante,
None.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-novel-index-to-identify-interstitial-lung-disease-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients/