Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: Methotrexate (MTX) is an anchor drug for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Appropriate effective and/or tolerable doses of weekly pulse MTX therapy vary widely among RA patients, especially in different countries. MTX is intracellularly converted to polyglutamate compounds (MTX-PGs) being active forms by several transporters and enzymes. Although genetic polymorphisms of enzymes such as dihydrofolate reductase and methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase have been studied in patients with malignant lymphoma, relationships between the genetic conditions of these enzymes and intracellular MTX-PGs or also clinical responses in RA patients were not cleared yet. We then investigated genetic polymorphisms of solute carrier family 19 member 1 (SLC19A1), a transporter protein of MTX into cells, and gamma-glutamyl hydrolase (GGH), an enzyme that has the capacity to cleave gamma-glutamyl bonds from MTX-PGs.
Methods: Two hundred and seventy-three RA patients (Mean±SD; 58.3±9.8 y.o.) undergoing stable oral doses of weekly pulse MTX (8.9±2.6 mg/week) for at least more than 3 months were inclued in this study. MTX-PGs concentration in red blood cells (RBCs) was measured by TDX analyzer (Abbott, IL) after extraction and purification from RBCs. The polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism assay was applied to determine the genotypes of SLC19A1 and GGH.
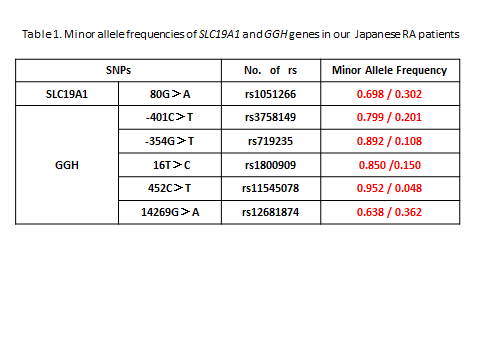
Results: Mean concentration of MTX-PGs in RBCs of 273 patients was 108±12 nmol/L. Mean concentration in the patient group receiving different doses of MTX was increased in a dose-dependent manner, however, individual MTX-PGs concentration was widely distributed among patients. MTX-PGs concentration was then devided by weekly MTX dose to exclude the influence of doses. The adjusted MTX-PGs values revealed a tendency of constant levels among the different dose groups. Results of minor allele frequencies of SLC19A1 and GGH in our Japanese RA patients were shown in the Table. Adjusted MTX-PGs (11.70±6.70 nmol/L/mg) in patients with at least either one of 3 GGH variants (-401C>T, -354G>T, or 16T>C) was significantly (p<0.03) increased, when compared to that (9.88±6.24 nmol/L/mg) in patients with wild types of these genes. Adjusted MTX-PGs in patients with other SLC19A1 and/or GGH gene variants was not changed from that in patients with wild types of these genes.
Conclusion: GGH may play an important role in regulation of the intracelluler MTX-PGs. Since intracellular MTX-PGs level is known as a surrogate marker of the efficacies and/or adverse responses of MTX, measurement of the GGH polymorphisms may predict clinical responses to MTX therapy.
Disclosure:
T. Yamamoto,
None;
M. Kawazoe,
None;
E. Shindo,
None;
N. Fujio,
None;
K. Shikano,
None;
K. Kitahara,
None;
S. Muraoka,
None;
M. Kaburaki,
None;
N. Tanaka,
None;
K. Kaneko,
None;
N. Kusunoki,
None;
Y. Kusunoki,
None;
K. Takagi,
None;
T. Hasunuma,
None;
H. Endo,
None;
S. Kawai,
Pfizer Inc,
2,
Pfizer Inc,
5,
Santen Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.,
2,
Santen Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.,
5.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/intracellular-concentration-of-methotrexate-is-influenced-by-polymorphisms-of-gamma-glutamyl-hydrolase-gene-in-japanese-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/