Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose:
A key question is whether biologic agents can be stopped but clinical benefit maintained for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients (pts) in remission or low disease activity (LDA). Potential benefits include lower costs, reduced safety concerns, and conforming with pt preference. To date, this has been addressed in a few clinical trials, using heterogeneous methods (1). We sought to determine the time course for persistent clinical benefit among RA pts in LDA (CDAI ≤ 10) who discontinued their first TNF Inhibitor (TNFi).
Methods:
We assessed RA pts from the CORRONA registry. End of Benefit (EOB) was defined as: a) having CDAI>10 at any followup b) initiation of another biologic or DMARD, or c) adding or increasing prednisone. Pts with no EOB event were censored at their last recorded CORRONA visit. Kaplan-Meier method was used to estimate median time to EOB and proportion remaining ‘with benefit’ at 6 month intervals from 6 to 36 months after drug discontinuation. Cox proportional hazard models were assessed to identify factors related to EOB. Factors that were significant at the 20% level in univariable modeling were evaluated in a multivariable models, adjusting for age, gender, race, smoking, and BMI.
Results:
Among 35,656 RA pts, we identified 717 who had: a) discontinued their 1st TNFi while in CORRONA, b) did not add another biologic or DMARD, c) were in LDA at the time TNFi discontinuation, and d) had ≥ 1 followup visit: 301 of these pts had initiated their first TNFi while in CORRONA. At discontinuation, pts had median RA duration of 8 yrs, mean CDAI of 4.3 ± 0.11. 41.8% used TNFi as monotherapy. 601/717 (83.8%) patients had an EOB event and 116 (16.8%) were censored. Kaplan-Meier estimates for the proportion of patients remaining with benefit (percentage, 95%CI) were: 6 mos – 98.7 (97.6-99.3), 12 mos – 73.4 (70.0-76.5), 18 mos – 55.6 (52.8-59.2), 24 mos 42.2 (38.6-46.0), 36 mos 27.6 (24.2-31.0)(Figure). Time course was similar among the 301 pts initiating their 1st TNFi within CORRONA.
Figure 1: Kaplan-Meier Curve for Time to End of Benefit (in months) 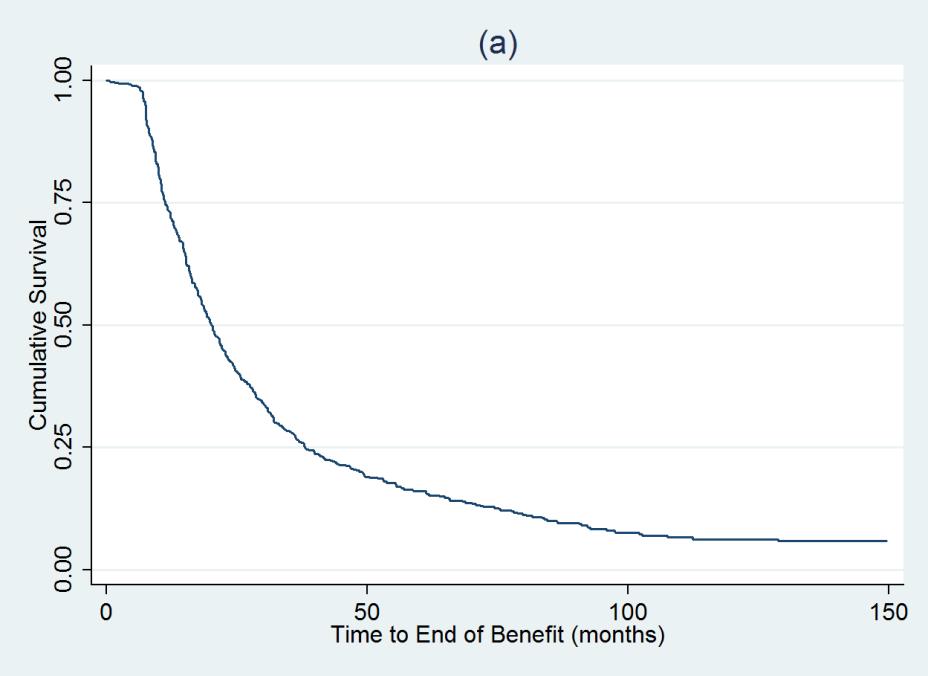
Factors predictive of EOB in univariate analysis included higher CDAI, pt pain score, and HAQ at discontinuation, as well as smoking, higher BMI, and positive RF/ACPA. In multivariate analysis, the 1st 3 factors remained significant with a HR for EOB with CDAI of 1.28 (1.08-1.5 95%CI). Among pts initiating their 1st TNFi within CORRONA, slower responders (time to LDA while on TNF>4 months) did worse than faster responders (HR 1.54 [1.17-2.04 CI]). Of note, RA disease duration did not affect time to EOB.
Conclusion:
These data show that discontinuation of a first course of TNFi may be associated with persistent benefit, and that patient characteristics at TNFi discontinuation may help predict persistent benefit.
Reference:
1. Yoshida K et al. Ann Rheum Dis Epub 30 May 2013
Disclosure:
A. Kavanaugh,
AbbVie, Inc.,
2,
Amgen,
2,
Janssen Pharmaceutica Product, L.P.,
2,
UCB,
2;
S. J. Lee,
None;
D. H. Solomon,
Amgen, Lilly, CORRONA,
2,
UpToDate,
7,
Pfizer, Novartis, Lilly, BMS,
6;
J. D. Greenberg,
Corrona Inc.,
1,
Corrona, Inc,
5,
AstraZeneca,
5,
Novartis Pharmaceutical Corporation,
5,
Pfizer Inc,
5;
J. M. Kremer,
Corrona, Inc,
1,
Corrona Inc.,
3;
L. Soto,
None;
C. J. Etzel,
Corrona Inc.,
3;
G. W. Reed,
Corrona, Inc,
3.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/discontinuation-of-tumor-necrosis-factor-inhibitors-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-in-low-disease-activity-persistent-benefits/
