Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: The objective of this study was to investigate the effects of tocilizumab on serum cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients with an inadequate response to disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs).
Methods: We collected sera from tocilizumab study (CWP-TCZ301), a 24-weeks, randomized, double–blinded trial of tocilizumab in RA patients with an inadequate response to disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs). Serum cytokine levels (tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-a, interleukin (IL)-6, IL-17, IL-21, IL-23 and IL-33) were determined by luminex multiplex analysis at baseline and after treatment (4, 12 and 24 weeks). Therapeutic response was evaluated by American College of Rheumatology 20% improvement (ACR 20) in tocilizumab (n=47) and DMARDs group (n=48) after 24 weeks.
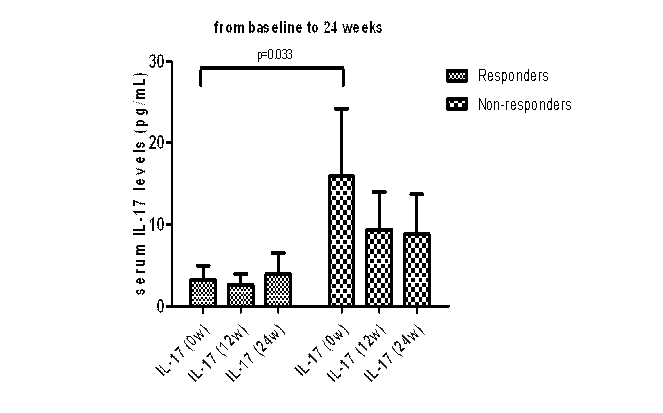
Results: Serum levels of IL-17, IL-21, IL-23 and IL-33 were significantly higher in RA patients than in healthy controls (all p<0.05). Early withdrawal patients from the study were excluded in the evaluation. In tocilizumab group, 29 patients were ACR 20 responders and 11 patients were non-responders after 24 weeks of treatment. Baseline serum levels of IL-17 were significantly lower in responders than in non-responders (mean ± SEM, 3.21 ± 1.74 pg/mL vs 15.89 ± 8.27 pg/mL, p<0.05). However IL-17 level did not significantly change during tocilizumab treatment irrespective of ACR 20 responsiveness. Levels of IL-21, IL-23 and IL-33 were not significantly different at baseline in responders and non-responders. However they were significantly decreased at 4, 12, 24 weeks in responders (p<0.005, respectively), but not in the non-responders. Levels of IL-6, TNF-a were not significantly different at baseline and did not significantly change during tocilizumab treatment. In DMARDs group, 8 patients were ACR 20 responders after 24 weeks of treatment. These patients’ baseline serum levels of IL-17 were significantly lower than those of DMARDs non-responders (n=35) (0.46 ± 0.46 pg/mL vs 4.40 ± 2.47 pg/mL, p=0.001). Levels of IL-21, IL-23 and IL-33 were not significantly different at baseline and did not significantly change during DMARDs treatment irrespective of ACR 20 responsiveness.
Conclusion: Baseline serum levels of IL-17 were lower in ACR 20 responders after tocilizumab therapy in RA. Serum levels of IL-21, IL-23 and IL-33 were significantly decreased during tocilizumab therapy in ACR 20 responders compared to non-responders.
Figure 1. After tocilizumab infusion, the change in serum cytokine levels in ACR 20 responders and non-responders from baseline to 24 weeks
Disclosure:
S. J. Lee,
None;
K. R. Kim,
None;
S. H. Joo,
None;
J. M. Lee,
None;
I. A. Choi,
None;
J. Y. Lee,
None;
H. J. Yoo,
None;
E. Y. Lee,
None;
E. B. Lee,
None;
W. Park,
None;
S. H. Park,
None;
S. C. Shim,
None;
D. H. Yoo,
None;
H. J. Baek,
None;
H. A. Kim,
None;
S. K. Lee,
None;
Y. J. Lee,
None;
Y. E. Park,
None;
H. S. Cha,
None;
Y. W. Song,
None.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effects-of-tocilizumab-on-serum-cytokines-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-with-an-inadequate-response-to-disease-modifying-antirheumatic-drugs/