Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: Down-regulation of MAP kinase pathway has been recognized in T cells from patients with SLE that results in hypo-methylation of DNA. RasGRP1 is an intracellular signaling protein highly expressed in T cells and activates the Ras signaling pathway downstream of TCR engagement. RasGRP1 deficient mice develop late-onset lymphoproliferative autoimmune syndrome. Previously we reported that defective (alternatively spliced) RasGRP1 transcripts correlate with lower levels of RasGRP1 protein in SLE T cells (Yasuda S et.al. J Immunol 2007). Splicing factor 2 / Alternative Splicing factor (SF2/ASF) is a member of the serine arginine family of splicing proteins that binds pre-mRNA to regulate alternative splicing. For instance, SF2/ASF binds to the 3’UTR of CD3 zeta and enables normal splicing of this signaling protein. (Moulton V et.al. J Biol Chem. 2010). The purpose of this study is to determine the relationship between aberrant splicing of RasGRP1 and SF2/ASF expression in SLE T cells.
Methods: Forty-five SLE patients and eighteen healthy subjects were included in this study. T cells were collected from peripheral blood of each subject and RNA was isolated. Expression levels of SF2/ASF, normally spliced RasGRP1 and DNMT1 transcripts were assessed by real time quantitative PCR. RNA electrophoretic mobility shift assays (EMSA) and immunoprecipitations (IP) were performed to confirm the direct binding of SF2 to RasGRP1 pre-mRNA. RasGRP1 exon11 RNA oligonucleotides end-labeled with biotin and recombinant SF2/ASF phosphate mimic were used in these experiments.
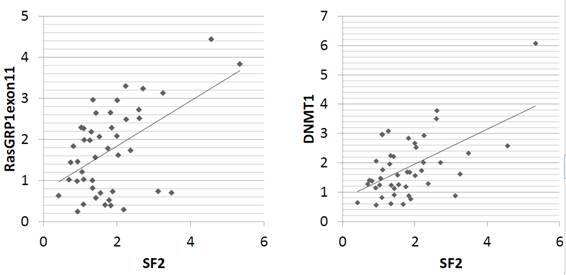
Results: Expression levels of SF2/ASF transcripts were significantly lower in SLE patients compared with healthy subjects (p=0.001, t-test). In patients with SLE, expression levels of SF2/ASF correlated with those of normally spliced RasGRP1 and DNMT1 (r=0.517, p=0.023 [RasGRP1]; r=0.557, p=0.013 [DNMT1], Figure). EMSA and IP studies suggested that SF2/ASF binds directly to RasGRP1 exon 11 RNA.
Conclusion: SF2/ASF binds to RasGRP1 mRNA and controls its expression. Low SF2/ASF levels in SLE T cells correlate with the expression levels of RasGRP1 and DNMT1. We propose that SF2/ASF regulates the alternative splicing of important genes in SLE T cells including RasGRP1 and CD3 zeta.
Disclosure:
T. Kurita,
None;
S. Yasuda,
None;
V. R. Moulton,
None;
M. Kono,
None;
H. Koide,
None;
K. Oku,
None;
T. Bohgaki,
None;
O. Amengual,
None;
T. Horita,
None;
G. C. Tsokos,
None;
T. Atsumi,
None.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/decreased-levels-of-splicing-factor-2-alternative-splicing-factor-sf2asf-correlate-with-lower-transcript-levels-of-the-rasgrp1-normal-isoform-in-lupus-t-cells/