Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: In the Phase 3 DISCOVER (D)-1 and -2 studies, guselkumab (GUS; IL-23p19-subunit inhibitor) 100 mg every 4 weeks (Q4W) or Q8W significantly improved joint and skin symptoms in active PsA patients (pts). In D2, GUS-treated pts had lower rates of radiographic progression (RP) vs placebo (PBO) at W24, with durable suppression of RP through 2 years.1,2 Assessing the impact of GUS on joint disease activity (DA)/progression using an instrument suitable for routine care may facilitate disease monitoring in this setting. The clinical DA Index for PsA (cDAPSA), a version of DAPSA omitting CRP, performs similarly to DAPSA.3 These post hoc analyses describe the transition between cDAPSA DA states through W52 in GUS- vs PBO-treated PsA pts (pooled D1+D2) and evaluate the association between earlier clinical improvement in joint DA and long-term RP through 2 years in D2.
Methods: D1 (31% TNF inhibitor [TNFi]-experienced) & D2 (biologic-naïve) enrolled adults with active PsA despite conventional synthetic csDMARDs. Pts were randomized 1:1:1 to GUS 100 mg Q4W; GUS 100 mg at W0, W4, then Q8W; or PBO→GUS 100 mg Q4W at W24. Pts with moderate ( >13 to ≤27) or high ( >27) levels of joint DA (ModDA/HDA; cDAPSA >13) at baseline (BL) were included. cDAPSA low DA/remission (LDA/REM; ≤13) rates through W52 were determined using nonresponder imputation for missing data; rates through W24 were compared between GUS vs PBO with logistic regression adjusting for prior TNFi and BL csDMARD use and cDAPSA. Among GUS-randomized pts (RP evaluated) in D2, a predictive model (mixed linear) assessed associations between W8 improvement in DA (shift from cDAPSA ModDA/HDA→LDA/REM) and changes in total PsA-modified van der Heijde-Sharp [vdH-S] score through W100, after adjusting for known BL determinants of RP (vdH-S score, age, gender, CRP).
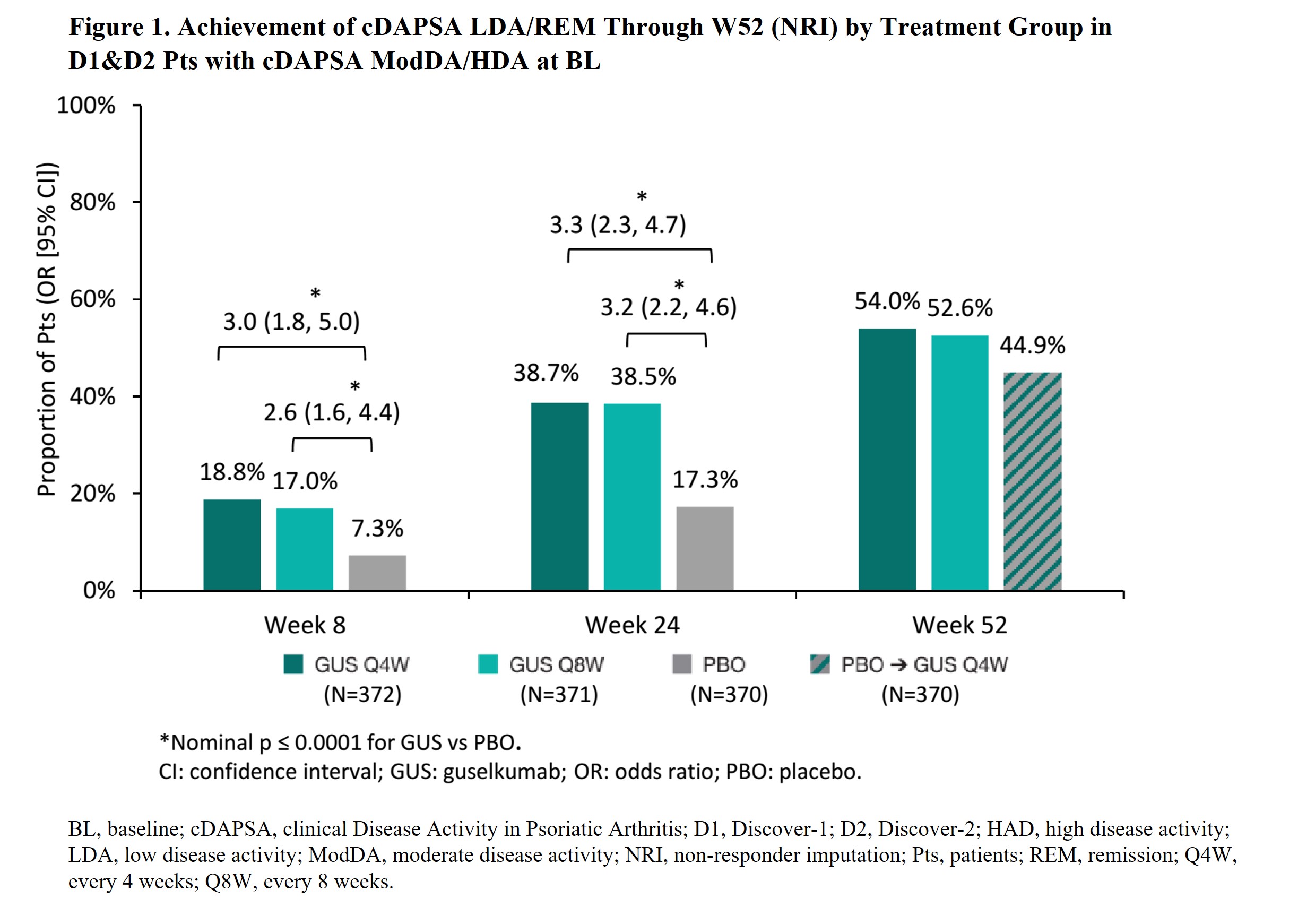
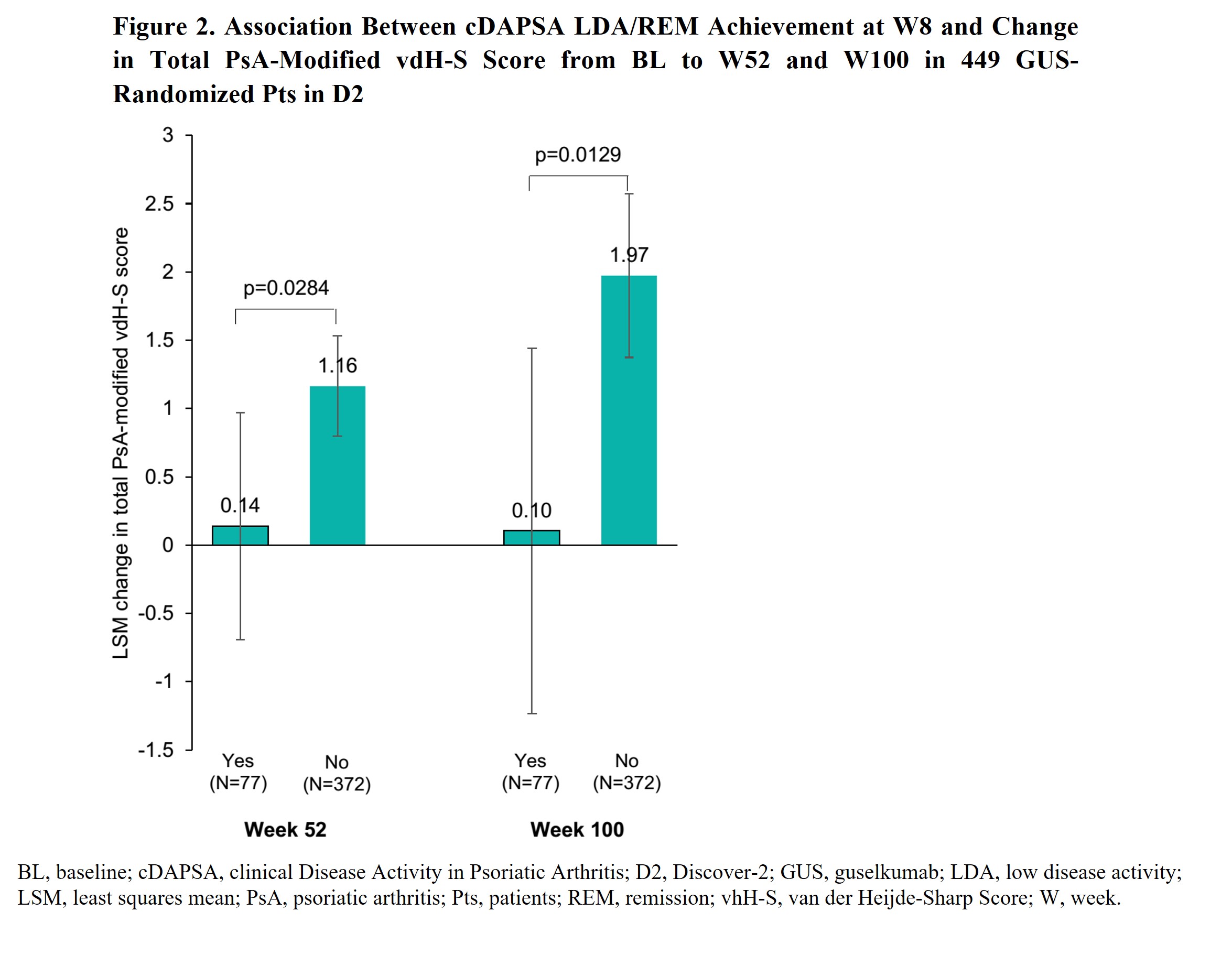
Results: Of 1120 D1&2 pts, 947 (84.6%: cDAPSA HAD) and 166 (14.8%: ModDA) were evaluated. W8 cDAPSA LDA/REM rates were significantly higher in GUS Q4W/Q8W pts vs PBO (18.8%/17%; vs 7.3%; p≤0.0001); corresponding W8 odds ratios (OR) vs PBO were enhanced by W24 (ORQ4W=3.0→3.3; ORQ8W=2.6→3.2). Response rates increased through W52 of GUS Q4W and Q8W (Fig 1). Among GUS-randomized D2 pts, achievement of cDAPSA LDA/REM at W8 associated with significantly lower rates of RP through W100. The effect of W8 cDAPSA LDA/REM on future RP strengthened over time among achievers vs non-achievers (least square means difference at W52= ‑1.03 [p=0.03] and W100= ‑1.87 [p=0.01]; Fig 2).
Conclusion: Among PsA pts with ModDA/HDA, GUS was associated with significantly greater rates of cDAPSA LDA/REM achievement vs PBO at W8 (after 2 doses). Response rates increased over time, with nearly 40% and >50% of GUS-randomized pts achieving cDAPSA LDA/REM at Weeks 24 and 52, respectively. Earlier improvements in joint DA (W8 cDAPSA LDA/REM) among biologic-naïve GUS-treated pts associated with significantly lower RP rates through 2 years. Results highlight the potential utility of cDAPSA in routine care to monitor short-and long-term improvements in joint DA among GUS-treated PsA pts.
1. Mease P. Lancet 2020;395:1126
2. McInnes I. Arthritis Rheumatol 2022;74:475
3. Schoels M. Ann Rheum Dis 2016;75:811
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mease P, Gottlieb A, McInnes I, Shiff N, Thomas T, Rampakakis E, Nantel F, Lavie F, Rahman P. Effects of Guselkumab on cDAPSA Disease Activity State and Its Association with Long-Term Radiographic Progression in a Cohort of Patients with Moderately-Highly Active Psoriatic Arthritis: Post Hoc Analyses of Phase 3 Randomized Controlled Studies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effects-of-guselkumab-on-cdapsa-disease-activity-state-and-its-association-with-long-term-radiographic-progression-in-a-cohort-of-patients-with-moderately-highly-active-psoriatic-arthritis-post-hoc-a/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effects-of-guselkumab-on-cdapsa-disease-activity-state-and-its-association-with-long-term-radiographic-progression-in-a-cohort-of-patients-with-moderately-highly-active-psoriatic-arthritis-post-hoc-a/