Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: The shared epitope (SE) may play a functional role in RA via Th17/interleukin (IL)-17 polarization (Holoshitz et al. FEBS Lett 2011;585:3619-26). Two phase 2 studies of secukinumab in RA suggested that HLA-DRB1*04 allelic group and the SE could be candidate biomarkers for treatment with secukinumab. In this study, validation in an independent cohort was sought for candidate markers of response.
Methods: In a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, patients with RA (2010 criteria), TJC ≥ 6, SJC ≥ 6, CRP > 10 mg/L, who were biologic-naive and DMARD incomplete responders or DMARD naive, were randomized 2:1 to secukinumab 6×10 mg/kg i.v. or placebo every other week (wk). Associations of treatment effect of secukinumab vs. placebo with HLA-DRB1*04 (primary endpoint), HLA-DRB1*SE and protein markers RF and anti-CCP were assessed at wk 12 in 96 evaluable patients, using change from baseline in DAS28-CRP by ANCOVA, or ACR20 response by logistic regression.
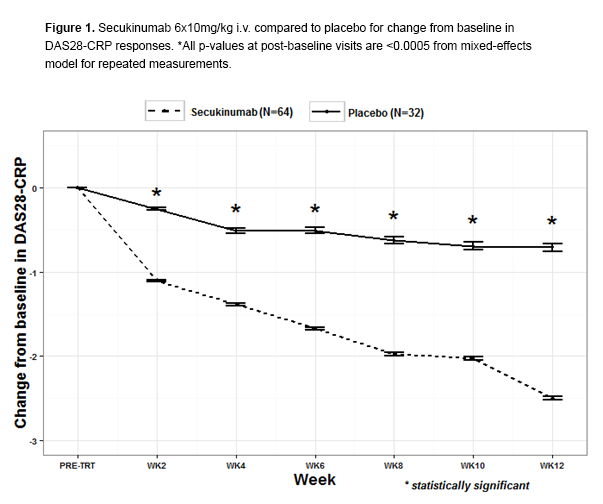
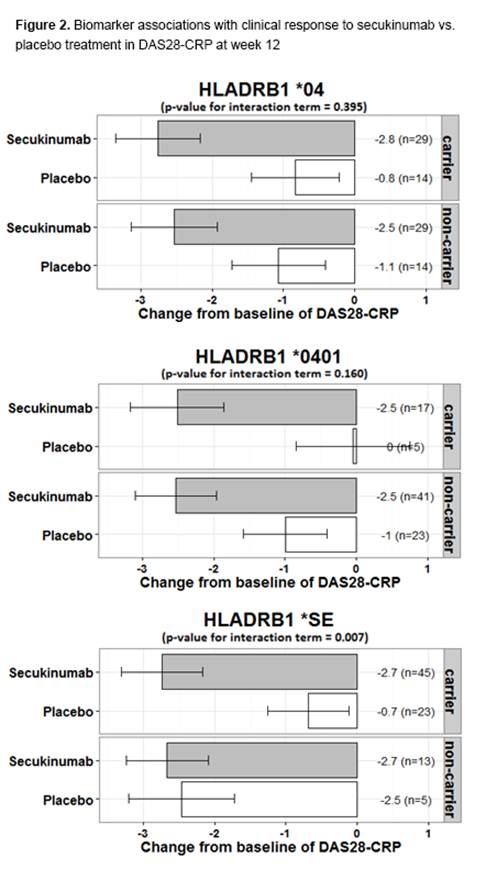
Results: At baseline, 46 (72%) on secukinumab and 23 (72%) on placebo were taking concomitant DMARDs; 16% were RF/anti-CCP negative. Frequency of HLA-DRB1*SE and *04 was 72% and 47%, respectively. ACR20 responses at wk 12 were 87.9% for secukinumab compared to 25.0% for placebo. Change from baseline in DAS28-CRP differed significantly as early as wk 2 and continued through wk 12 (Fig 1). For change from baseline in DAS28-CRP, HLA-DRB1*SE status demonstrated a significant association with response to secukinumab vs. placebo (p=0.007), but the HLA-DRB1*04 allelic group and HLA-DRB1*0401 did not (Fig 2). Among protein markers, RF but not anti-CCP was significantly associated with both DAS28-CRP (RF p=0.022, anti-CCP p=0.124) and ACR20 response (RF p=0.013, anti-CCP p=0.228). The small number of HLA-DRB1*SE non-carriers within the CCP/RF-positive subcohort precluded assessment of associations in this subgroup. Two SAEs were reported, necrotizing vasculitis and ovarian adenoma, both leading to early secukinumab discontinuation.
Conclusion: Secukinumab was associated with improvements in efficacy outcomes compared with placebo. HLA-DRB1*SE was associated with response to secukinumab vs. placebo. However, these associations are driven by lack of placebo response in carriers vs. non-carriers. Notable differences in genetic ancestry and disease activity suggest potential confounder effects. Additional studies with enhanced power are needed to confirm contributions of SE and other markers to anti-IL-17A responsiveness.
Disclosure:
G. Burmester,
Novartis Pharma AG,
5;
P. Durez,
Pfizer, BMS,
8;
G. Shestakova,
None;
Y. Li,
Novartis Pharma AG,
1,
Novartis Pharma AG,
3;
A. Wang,
Novartis Pharma AG,
1,
Novartis Pharma AG,
3;
S. Lewitzky,
NIBR,
1,
NIBR,
3;
I. Koroleva,
Novartis Pharma AG; NIBR,
1,
Novartis Pharma AG; NIBR,
3;
D. Lee,
Novartis Pharma AG,
1,
Novartis Pharma AG,
3;
W. Hueber,
Novartis Pharma AG,
1,
Novartis Pharma AG,
3.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-of-hla-drb1-alleles-with-clinical-responses-to-the-anti-interleukin%e2%88%9217a-monoclonal-antibody-secukinumab-in-a-cohort-of-patients-with-active-rheumatoid-arthritis-an-explorato/