Session Information
Title: Epidemiology and Health Services Research III: Healthcare Costs and Mortality in Rheumatic Disease
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: In the treatment in the Rotterdam Early Arthritis Cohort (tREACH) trial we showed that treatment goals were attained faster and maintained with less treatment intensifications within the initial triple DMARD therapy (iTDT) groups as opposed to the initial methotrexate (MTX) mono-therapy (iMM) group. Medication costs are just 20-50% of the total costs. Furthermore the policy for covering prescribed drugs by health insurance companies and governments is more and more influenced by cost-effectiveness. Therefore, our aim is to investigate which initial treatment regimen has the lowest costs per Quality Adjusted Life Year (QALY)
Methods: The one-year data of the tREACH trial were used. Patients were included who had a high probability (> 70%) of progressing to persistent arthritis, based on the prediction model of Visser. The Visser algorithm and 2010 criteria for RA have similar discriminative abilities to identify patients at risk of persistent arthritis at 1 year. Patients were randomized into 3 induction therapy strategies: (A) iTDT ( MTX 25 mg/week + sulfasalazine 2 grams/day + hydroxychloroquine 400mg/day) with intramusculair glucocorticoids (GCs) (depomedrol 120mg), (B) iTDT with an oral GCs tapering scheme (starting 15 mg) and (C) iMM with oral GCs similar to B. We used a treat-to-target approach, with patients being examined every 3 months and treatment decisions based upon the original DAS thresholds for low disease activity. Data on QALYs, direct and indirect cost were used. Direct costs are the costs of treatment and medical consumption, whereas indirect costs are costs due to loss of productivity (i.e. sick leave and unemployment).
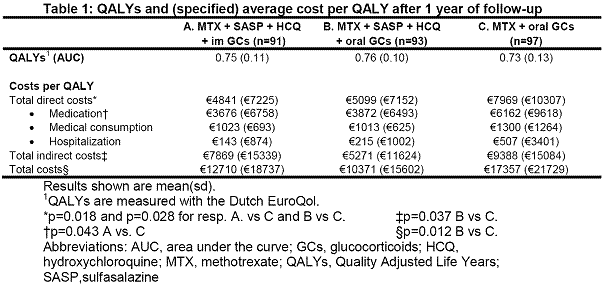
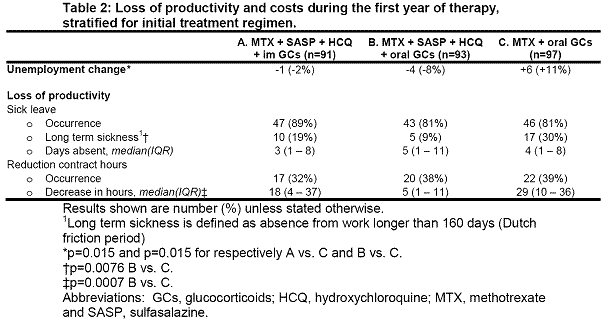
Results: A total of 281 patients were randomly assigned to strategy (A) (n=91), (B) (n=93) or (C) (n=97). Average QALYs (ideally 1) for treatment strategy A, B and C are given in table 1. Direct and indirect costs per QALY were higher in the iMM group compared with the iTDT groups (table 1). The difference in direct costs was due to ~40% more biological usage, from 3 months up to 1 year. Less unemployment, long-term sickness and reduction in contract hours caused the difference in indirect costs (table 2). Total costs per QALY differed significantly between treatment arm B and C (p=0.012, table 1).
Conclusion: iTDT had the lowest costs per QALY compared with iMM. Furthermore iTDT has significant better worker productivity. This underlines once again why iTDT instead of iMM is preferred as first choice in very early RA.
Disclosure:
P. H. P. de Jong,
None;
A. E. A. M. Weel,
None;
J. J. Luime,
None;
P. J. Barendregt,
None;
A. H. Gerards,
None;
P. A. van der Lubbe,
None;
M. H. de Jager,
None;
P. B. de Sonnaville,
None;
D. van Zeben,
None;
B. A. Grillet,
None;
J. M. W. Hazes,
None.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/better-cost-effectiveness-and-worker-productivity-in-triple-dmard-therapy-versus-methotrexate-monotherapy-in-early-rheumatoid-arthritis-cost-utility-analysis-of-the-treach-trial/