Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Fibromyalgia is a disorder of chronic widespread pain. There is huge burden of this entity in community but there is scarcity of quality studies regarding its prevalence. Fibromyalgia is seen much more commonly in women as compared to men. Study was aimed to assess prevalence of fibromyalgia in young and middle-aged women using American College of Rheumatology classification criteria for fibromyalgia 2010. This has been validated for community studies and does not require examination for tender points.
Methods: We identified one urban and one rural area in the vicinity of our community health centers in Western India. Sample size was calculated based on previous reports of prevalence between 4% to 6.5% and design of alpha of 0.05 with power of 85%. House to house survey was conducted in 563 households. Total 648 women between age of 18 to 60 years were interviewed for presence or absence of any chronic pain lasting for more than 3 months. Those having chronic pain were screened as per ACR 2010 fibromyalgia criteria including widespread pain index (WPI), symptom severity score. They were also interviewed about their patterns of sleep. Data about social demographics and comorbidities with previous surgeries were also recorded.
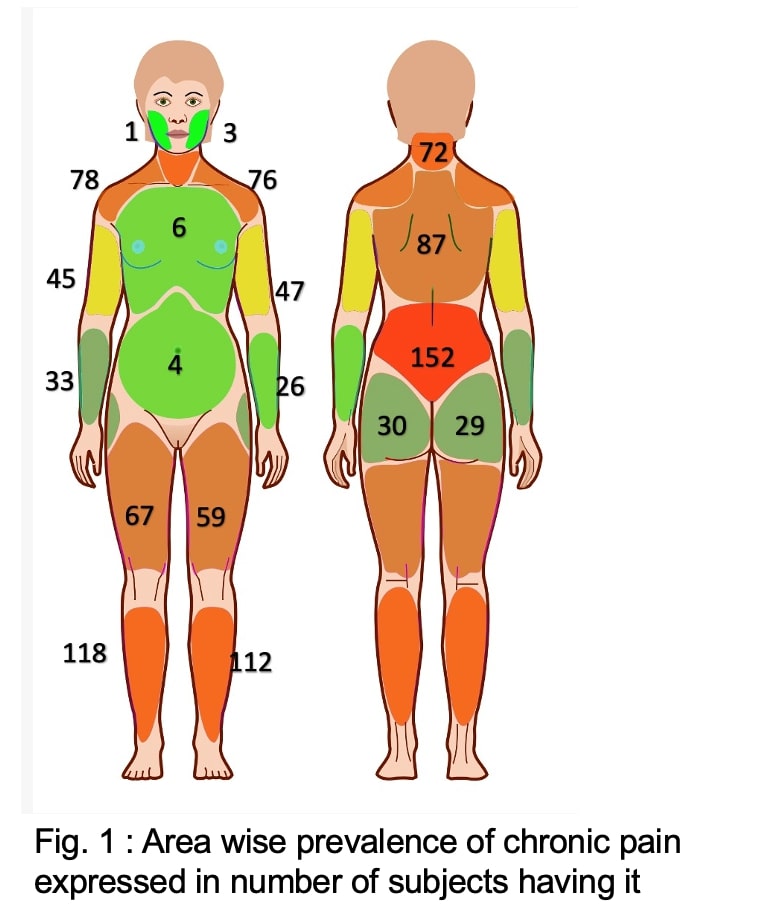
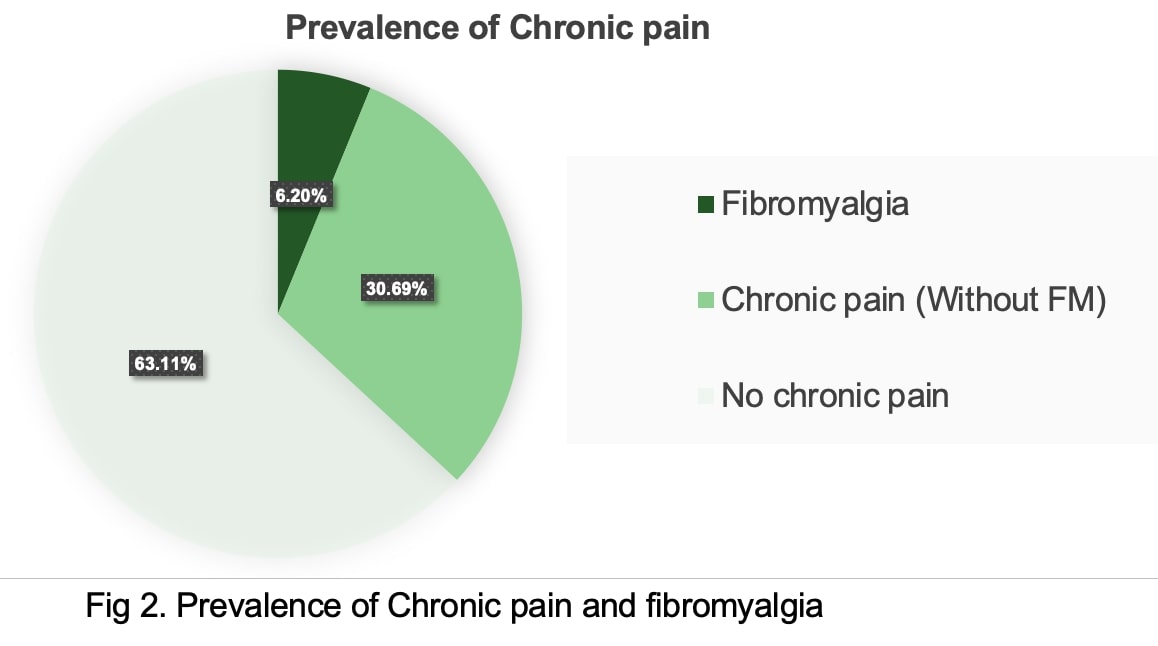
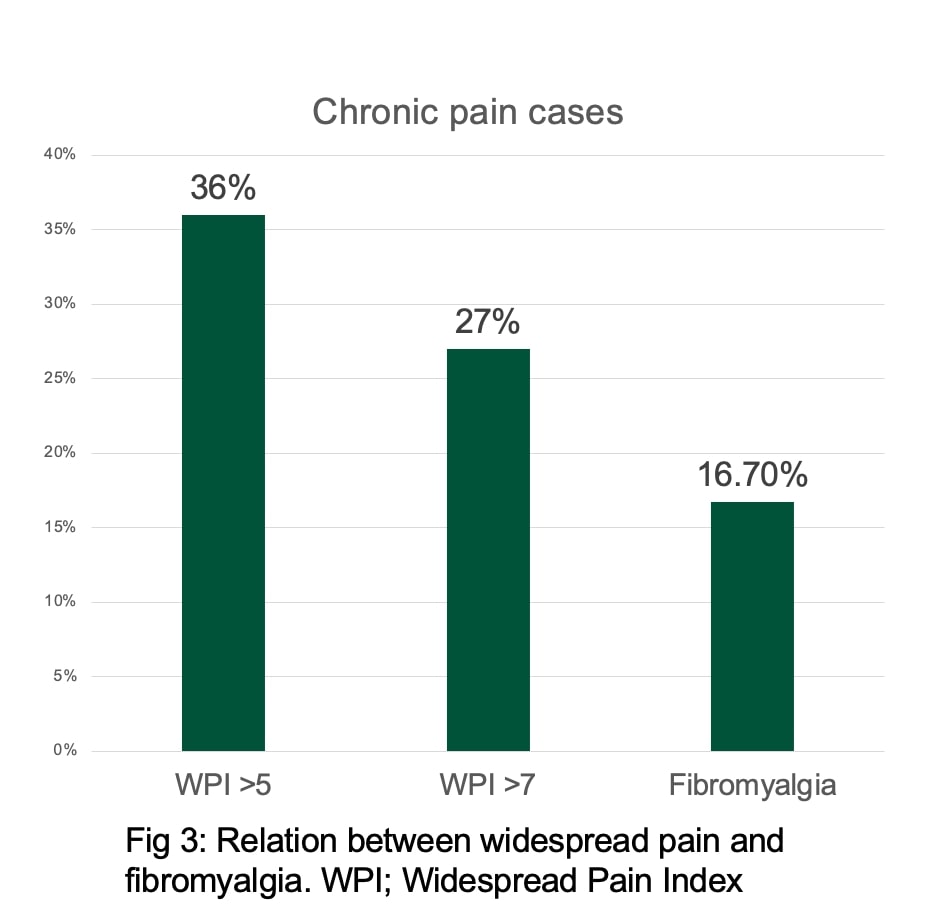
Results: Mean age of participants was 37.38±11.2 years. Out of total 648 participants 273 (42%) were from urban area others were from rural setting. One third of women (33.4%) had some form of chronic pain. Forty (6.17%) were found to have fibromyalgia. Among those having chronic pain, 78 (36%) had WPI more than 5, 58 (27%) had WPI more than 7 while 40(16.7%) satisfied the criteria for fibromyalgia. There was no significant difference in prevalence of fibromyalgia between rural and urban settings. Those having fibromyalgia had significantly lower annual family income (0.18±0.13 vs 0.24±0.24 million INR, p< 0.001), higher age (44.41±10.27 vs 36.05±11.35 year, p< 0.001) and higher body weight (62.02±11.65 vs 56.25±10.56 Kg).
Conclusion: Present study shows prevalence of fibromyalgia to be 6.17% in women of western India in age group of 18 to 60 years. Only half of those having widespread pain in community satisfied the criteria for fibromyalgia. There was association of fibromyalgia with lower income, higher body weight and sleep disturbances.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gupta V, Mishra D, Singh S, Chowhan V, Thorat S, Krishna K, Kansurkar S. Community Based Study of Prevalence and Social Factors for Chronic Pain and Fibromyalgia in Women from Western India [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/community-based-study-of-prevalence-and-social-factors-for-chronic-pain-and-fibromyalgia-in-women-from-western-india/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/community-based-study-of-prevalence-and-social-factors-for-chronic-pain-and-fibromyalgia-in-women-from-western-india/