Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Physician-reported disease activity has a modest association with patient-reported outcomes (PROs) in systemic lupus erythematosus patients. The aim of this study is to evaluate the impact of patient-reported disease activity in other patient-reported outcomes.
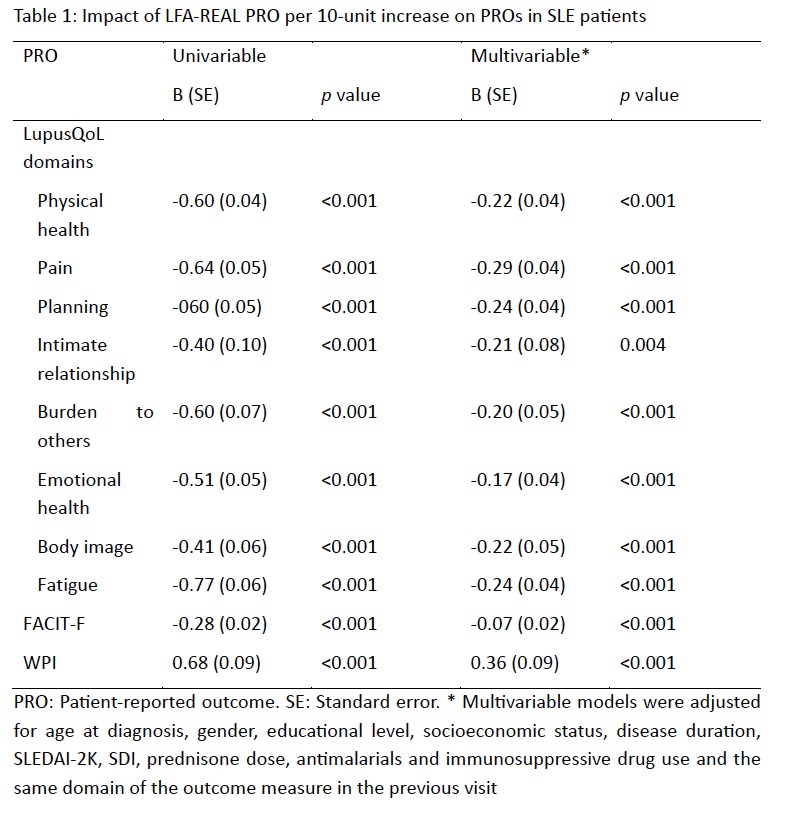
Methods: We evaluated patient-reported disease activity on SLE patients from the Almenara Lupus Cohort. Disease activity was assessed using the Lupus Foundation of America Rapid Evaluation of Activity in Lupus (LFA-REAL) PRO which ranges between 0 and 1200 (the higher the score is, the worse the activity is); health-related quality of life (HRQoL) was ascertained using the LupusQoL which ranges between 0 and 100 (the higher the score is, the better the HRQoL); fatigue was ascertained using the Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy – Fatigue (FACIT-F), which ranges between 0 and 52 (the higher score, the lower fatigue); and work productivity impairment was ascertained with the work productivity and activity impairment (WPAI) which ranges between 0 and 100 (the higher score, the higher disability). Generalized estimating equations were performed for each domain of the LupusQoL, the FACIT-F and the WPAI and the LFA-REAL PRO measured at the previous visit; multivariable models were adjusted for possible confounders (age at diagnosis, gender, educational level, socioeconomic status, disease duration, SLEDAI-2K, SDI, prednisone dose, antimalarials and immunosuppressive drug use and the same domain of the outcome variable)measured at the same visit as the LFA-REAL PRO. B was reported per 10 units increase of the LFA-REAL PRO.
Results: A total of 311 patients and 1116 visits were included. Of them, 289 (91.5%) were women, mean age at diagnosis was 34.6 (13.6) years. Mean (SD) LFA-REAL PRO at baseline was 240.9 (182.1). LFA-REAL PRO predicted a worse PRO in all domains of the LupusQoL, the FACIT-F and the WPAI, even after adjustment by possible confounders (table 1).
Conclusion: A higher patient-reported disease activity predicted a worse HRQoL and fatigue as well as a higher work productivity impairment in SLE patients, even after adjustment for possible confounders. Patient-reported disease activity should be included in the evaluation of SLE patients on a regular basis.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ugarte-Gil M, Gamboa-Cardenas R, Pimentel-Quiroz V, Reategui C, Elera Fitzcarrald C, García-Hirsh S, Alfaro-Lozano J, Pastor-Asurza C, Rodriguez-Bellido Z, Perich-Campos R, Alarcon G. Impact of the Lupus Foundation of America Rapid Evaluation of Activity in Lupus (LFA-REAL) Patient Reported Outcome (PRO) in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients from the Almenara Lupus Cohort [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-the-lupus-foundation-of-america-rapid-evaluation-of-activity-in-lupus-lfa-real-patient-reported-outcome-pro-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-patients-from-the-almenara-lupus-cohort/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-the-lupus-foundation-of-america-rapid-evaluation-of-activity-in-lupus-lfa-real-patient-reported-outcome-pro-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-patients-from-the-almenara-lupus-cohort/