Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Rheumatoid arthritis is known to improve during pregnancy, and a flare of disease activity is observed after delivery (1). N-glycosylation of the constant region (Fc) of immunoglobulin (Ig) G has been associated with these observations (2). However, glycosylation of the antigen binding fragment (Fab) of IgG might also play a role. Fab glycosylation has been suggested to influence affinity to antigen, and antibody half-life (3, 4). Analysis of Fab glycosylation is challenging because of the hypervariable properties of IgG Fab. Here we describe a newly developed highly specific method for the analysis of Fab N-glycosylation.
Methods:
Sera were collected three times during pregnancy and three times after delivery from healthy individuals participating in a prospective cohort study on Pregnancy induced Amelioration of Rheumatoid Arthritis (PARA-study). IgG was affinity purified from the sera using IgG-Fc (Hu) beads. Using FabRICATOR® enzyme IgG was cleaved in two ½ Fc portions and a F(ab’)2 portion. Fc and F(ab’)2 were separated, and glycans were released followed by automated MALDI-TOF measurement to establish the levels as well as patterns of glycosylation.
Results:
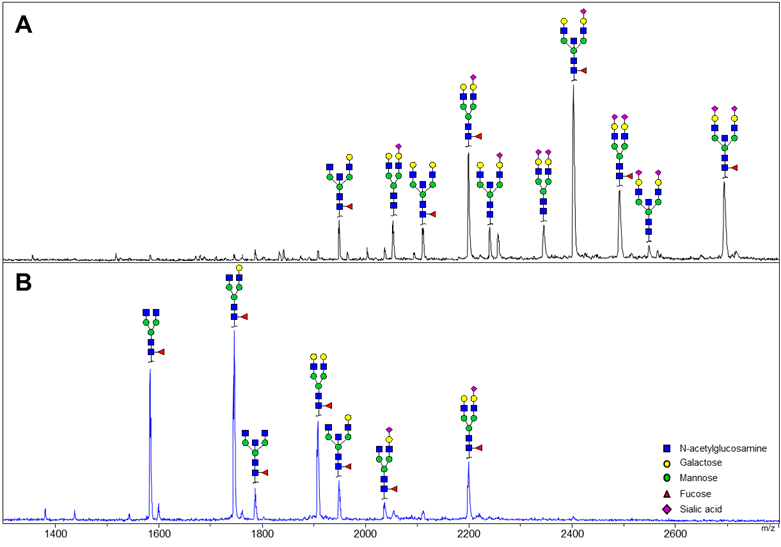
In healthy pregnant individuals Fc and Fab show distinct glycosylation patterns (Figure 1). Levels of galactosylation and sialylation are higher on Fab compared to Fc (±94% vs. ±60% and ±60% vs. ±15%, respectively). However, while major changes occur in these features on IgG Fc during pregnancy, the levels appear to be stable at the Fab portion. On the other hand, fucosylation and bisecting N-acetylglucosamine do not change drastically on the Fc portion with pregnancy, while pronounced lowered levels of both glycosylation features are observed during pregnancy in these individuals.
Conclusion:
Data obtained from serum of healthy pregnant individuals reveals differential glycosylation on Fab compared to Fc. Fab and Fc were found to show distinct glycosylation changes with pregnancy. In the near future we will apply this method to RA patient sera to identify whether Fc or Fab glycosylation could be a bigger effector in the improvement of RA during pregnancy.
Figure 1 Typical IgG Fab (A) and Fc (B) spectra showing distinguishable AA-labeled glycans
Acknowledgements
This research project is financed by the Dutch Arthritis Foundation.
References
3. Arnold JN, Wormald MR, Sim RB, Rudd PM, Dwek RA. Annu Rev Immunol 2007;25:21-50.
4. Huang L, Biolsi S, Bales KR, Kuchibhotla U. Anal Biochem 2006;349:197-207.
Disclosure:
A. Bondt,
None;
Y. Rombouts,
None;
M. H. J. Selman,
None;
R. J. Dolhain,
None;
M. Wuhrer,
None.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/high-throughput-immunoglobulin-g-fab-glycosylation-profiling-reveals-differential-glycosylation-on-fab-and-fc/