Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 14, 2023
Title: (1913–1944) Miscellaneous Rheumatic & Inflammatory Diseases Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Patients with autoimmune or inflammatory diseases treated with immunosuppressants such as anti-CD20 are at increased risk for severe COVID-19 and have a high probability of insufficient response to vaccination. The monoclonal antibody combination tixagevimab/cilgavimab has received early access approval to reduce the frequency of symptomatic COVID-19 in immunocompromised patients at risk for severe COVID-19 and unresponsive to vaccination.We aim to evaluate the clinical efficacy of tixagevimab/cilgavimab in pre-exposure prophylaxis in patients with increased risk of severe COVID-19 in rheumatology.
Methods: In this multicenter observational study conducted between December 2021 and August 2022, we included patients with autoimmune or inflammatory diseases who received at least one intramuscular injection of tixagevimab/cilgavimab as pre-exposure prophylaxis in 3 French rheumatology units. Occurrence of COVID-19 was assessed during usual follow-up or by phone call. The endpoint was the incidence of COVID-19 and its severity.
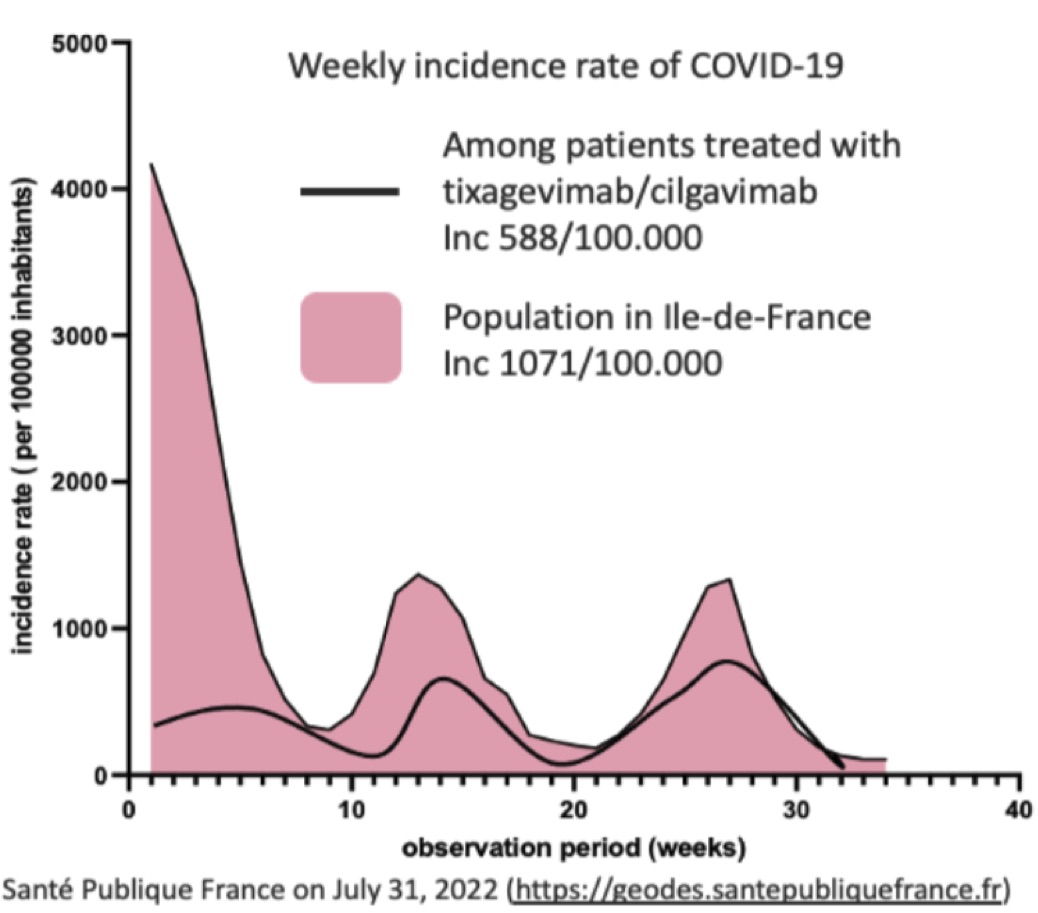
Results: Tixagevimab/cilgavimab was administered to 115 patients, median age 62 years (52-71), with chronic arthritis (n=53), connective tissue disease (n=38) or vasculitis (n=11). The main background immunosuppressants were rituximab (n=98), methotrexate (n=48), mycophenolate mofetil (n=19), cyclophosphamide (n=15), azathioprine (n=12), and corticosteroids (n=62, median dose 5 mg, CI95% 5-8). During a median follow-up of 128 days (93-173), COVID-19 occurred in 23/115 patients (20%) with Omicron identified for the 8 genotyped patients. During the study period, the average weekly incidence was 1071 per 100.000 inhabitants in Ile-de-France vs. 588 per 100.000 in our patients. Patients who received a 2-injections regimen had a lower risk of infection than patients with a single injection (16/49, 33%, vs. 5/64, 8%, p=0.0012). The COVID-19+ patients did not differ from uninfected patients in terms of age, comorbidities, type and duration of underlying disease, extra-articular organ involvement or background immunosuppressants. All COVID-19 cases were non-severe, there were no deaths. The tolerance of injections was excellent, with no side effects observed.
Conclusion: In a population with autoimmune or inflammatory diseases at increased risk of severe COVID-19 with a poor response to vaccination, pre-exposure prophylaxis by tixagevimab/cilgavimab limited the risk of infection and the severity of COVID-19. This study supports the use of COVID-19 serological tests in this patient population in order to detect those who do not respond adequately to vaccination since pre-exposure treatments and/or early treatments are available.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
THOMAS M, MASSON M, Seror R, Bitoun S, DUPUY H, ESTIBALIZ L, Richez C, ALLANORE Y, AVOUAC J. Pre-exposure Prophylaxis with Tixegvimab/cilgavimab Is Effective in Limiting the Risk and Severity of COVID-19 in Patients with Auto Immune or Inflammatory Diseases at Increased Risk of Severe COVID-19 [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/pre-exposure-prophylaxis-with-tixegvimab-cilgavimab-is-effective-in-limiting-the-risk-and-severity-of-covid-19-in-patients-with-auto-immune-or-inflammatory-diseases-at-increased-risk-of-severe-covid-1/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/pre-exposure-prophylaxis-with-tixegvimab-cilgavimab-is-effective-in-limiting-the-risk-and-severity-of-covid-19-in-patients-with-auto-immune-or-inflammatory-diseases-at-increased-risk-of-severe-covid-1/