Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: (1554–1578) Vasculitis – Non-ANCA-Associated & Related Disorders Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Arthritis is positioned as one of the main symptoms in Behcet’s disease (BD), and it is a relatively frequent symptom that is observed in about 57% of patients in Japan. Arthritis associated with BD is considered to be important domain affecting the patient’s QOL same as oral ulcers. However, few reports have compared the clinical symptoms and QOL of BD patients with and without arthritis. This study aims to clarify the correlation between arthritis and other clinical manifestations of BD, which affect the patient’s QOL in Japanese patients with BD.
Methods: Sixty-six BD patients treated at Kagawa University Hospital for more than 6 months and who visited the hospital from January to October 2022 were included in this retrospective study. We divided these patients into with (arthritis group) or without arthritis (non-arthritis group), and evaluated clinical symptoms, disease activity, and patient quality of life. Patient’s global assessment(PGA), Evaluator’s global assessment (EGA) and Behcet’s disease current activity form (BDCAF) were used as indices of disease activity. Behcet’s disease quality of life scale (BDQOL) was used to assess patient QOL. Statistical analysis was performed using JMP® Pro 16.1.0 software (SAS Institute, Cary, NC, USA).
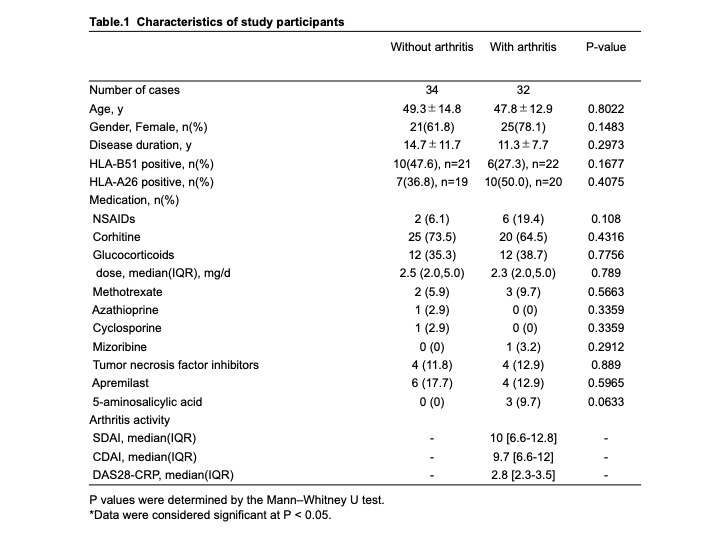
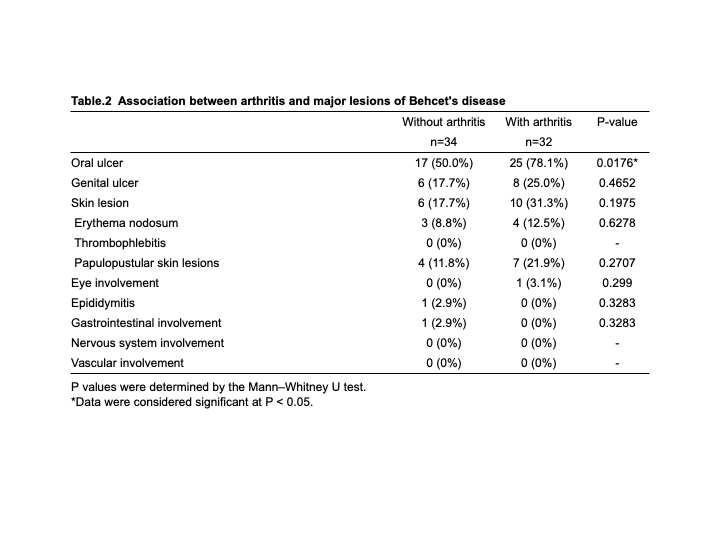
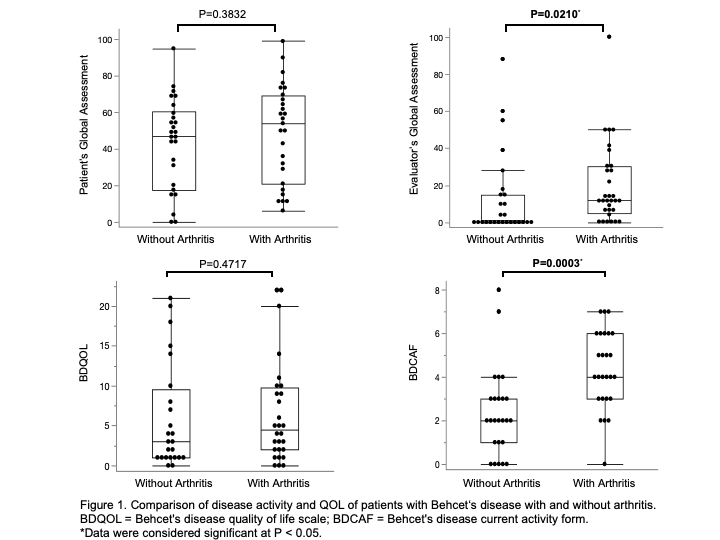
Results: Arthritis was observed in 48.5% of patients. No significant difference in patient characteristics was observed between two groups. Activity of arthritis in arthritis group evaluated by SDAI, CDAI and DAS-28CRP was low to moderate (Table 1). The frequency of oral ulcers were significantly higher in arthritis group than in non-arthritis group. Although skin lesions tended to be detected in arthritis group more than non-arthritis group, there was no significant difference between two groups. Among the skin domain, papulopustular lesion tended to be observed more frequently in arthritis group (Table 2). EGA and BDCAF were significantly higher in arthritis group. Although PGA and BDQOL were higher in arthritis group, the difference was not significant between two groups (Figure 1).
Conclusion: Japanese BD patients with arthritis tended to be complicated with mucocutaneous lesions. In addition, arthritis may affect overall disease activity and QOL in patients with BD, even if its activity is low to moderate. Because this study was a small, single-center, observational study, further research is needed to clarify the relationship between clinical feature and QOL in BD patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sugihara K, Wakiya R, Ushio Y, Nakashima S, Shimada H, Miyagi T, Chujo K, Kagawa R, Yamaguchi H, Kameda T, Dobashi H. Clinical Features and Quality of Life of Japanese Bechet’s Disease Patients with Arthritis: A Japanese Monocentric Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-features-and-quality-of-life-of-japanese-bechets-disease-patients-with-arthritis-a-japanese-monocentric-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-features-and-quality-of-life-of-japanese-bechets-disease-patients-with-arthritis-a-japanese-monocentric-study/