Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: (1345–1364) Reproductive Issues in Rheumatic Disorders Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Due to its multisystemic involvement, systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) can have a significant impact on patients’ quality of life (QoL). Sexual (dis)function is a key component of QoL but is often underappreciated. Little is known about sexual disfunction in SLE patients, a condition that primarily affects women during their fertile age.
We aimed at determining the prevalence of sexual dysfunction among women with SLE and predictors thereof.
Methods: We performed a cross-sectional multicenter study in which women (18-70 years-old) with a clinical diagnosis of SLE (according to their treating rheumatologist) were included. An anonymous online questionnaire was perfomed where data on demographics (e.g., age), symptoms of depression and anxiety [Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS)), health-related QoL (Short Form Health
Survey Index 36 Item (SF36)]) and sexual function [Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI) – a 19-item patient-report outcome that assesses female sexual function]) were collected. Data on clinical features [disease activity according to the Safety of Estrogens in Lupus National Assessment-SLE Disease Activity Index (SELENA-SLEDAI), organ involvement and evaluation of comorbidity (Charlson Comorbidity Index)] and on treatment status were collected from medical records. The main outcome was sexual dysfunction, defined as FSFI< 26.5 (validated cut-off). A multivariable logistic regression was perfomed to test the association of clinical and demographic characteristics with sexual dysfunction (present vs absent).
Results: In total, 194 female patients with SLE were included (mean age 44 years-old [standard deviation (SD) 11]). The mean SELENA-SLEDAI score was 1.7 (SD: 2.2), corresponding to low disease activity, and 94% of patients were on classical disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs. The mean value of HADS was 9 (0-21), for both depression and anxiety scores. Regarding SF36, the mental component had a mean value of 61 (0-100) and the physical one of 70 (0-100). Sexual disfunction was present in 128 (66%) patients.
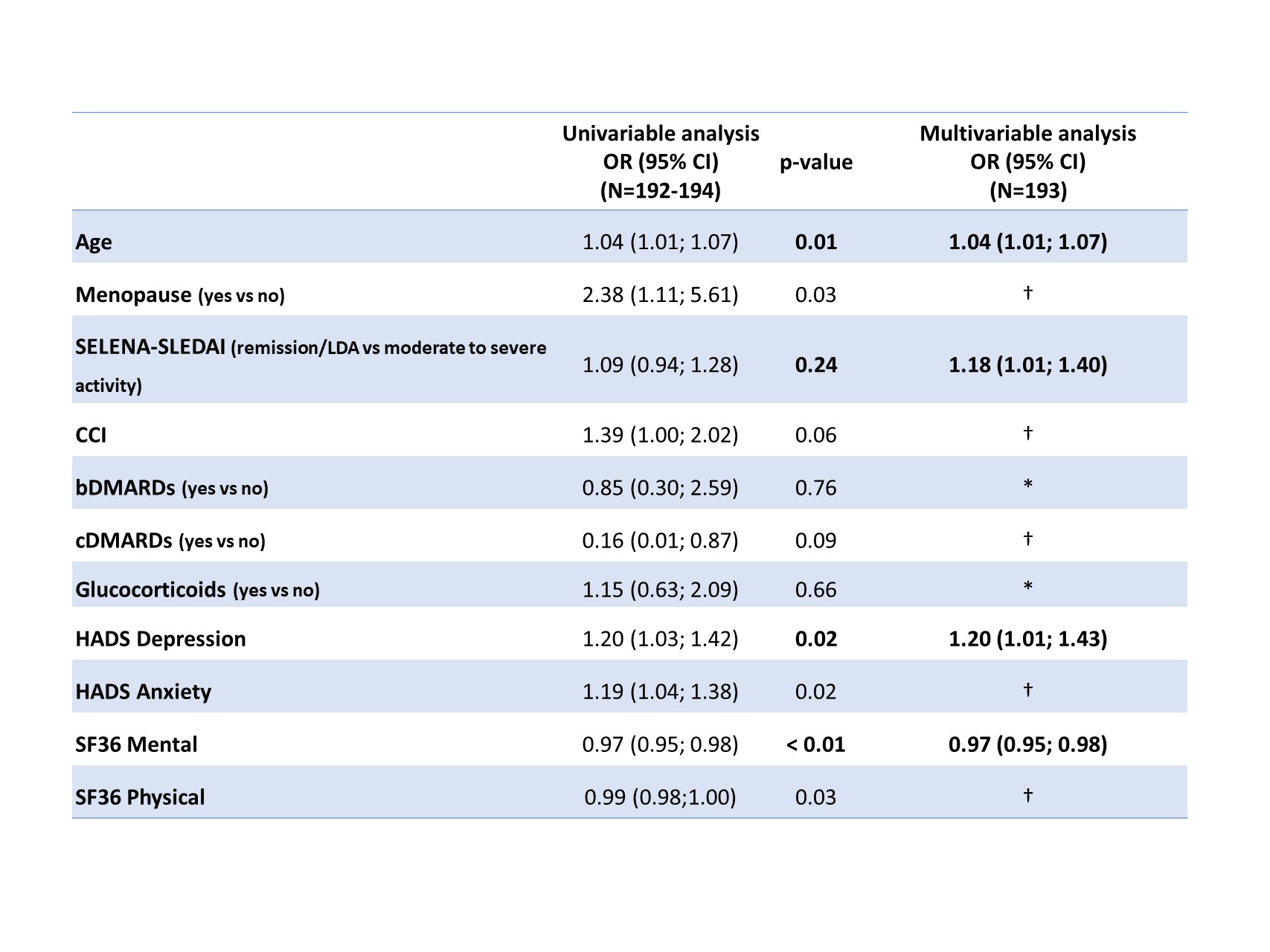
In the multivariable analysis (Table 1), older age (OR: 1.04; 95%CI: 1.01; 1.07), higher SELENA-SLEDAI (OR: 1.18; 95%CI: 1.01; 1.40), higher HADS depression score (OR: 1.20; 95%CI: 1.01; 1.43), as well as a lower (that is, worse) SF36 mental component score (OR: 0.97; 95%CI: 0.95; 0.98) were independently associated with sexual dysfunction.
Conclusion: Sexual disfunction is common in women with SLE and is influenced by both physical and mental health components. Clinicians should consider both for the optimal management of their patients in order to improve their sexual QoL.
SD, standard deviation; SELENA-SLEDAI, Safety of Estrogens in Lupus Erythematosus National Assessment (SELENA) – systemic lupus erythematosus disease activity index (SLEDAI); cDMARDs, classic disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs; bDMARDs, biologic disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs
* Not selected in the univariable model (p>0.25); † Not selected in the multivariable model (p>0.05); Safety of Estrogens in Lupus Erythematosus National Assessment (SELENA) – systemic lupus erythematosus disease activity index (SLEDAI); CCI, Charlson Comorbidity Index; bDMARDs, biologic disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs; cDMARDs, classic disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lourenco M, Torres R, Rodrigues-Manica S, Fraga V, Abreu A, Costa R, Ochôa Matos C, Mendes B, Samões B, Silva I, Pimentel-Santos F, Costa M, Branco J, Sepriano A. Sexual Dysfunction in Women with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Cross-Sectional Multicentre Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/sexual-dysfunction-in-women-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-a-cross-sectional-multicentre-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/sexual-dysfunction-in-women-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-a-cross-sectional-multicentre-study/