Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Improvement in both joint and skin manifestations is an important goal in the treatment of psoriatic arthritis (PsA). This study describes durability of 50% improvement in the modified American College of Rheumatology (mACR50) over 24 months and associated factors of response among patients (pts) with PsA initiating biological/targeted synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (b/tsDMARDs) in the CorEvitas PsA/Spondyloarthritis Registry – a prospective, non‑interventional North American research registry.
Methods: Pts who initiated b/tsDMARDs (March 2013–February 2022) and achieved mACR50 at 6 (±3) months post-initiation were followed until the first occurrence of loss of treatment response (defined as earliest occurrence of b/tsDMARD discontinuation, non-biologic addition, or loss of mACR50), last study visit, or 24 months post-achievement. The mACR50 response measure, which did not require laboratory results, was validated to have high correlation with ACR50 in the CorEvitas registry.1
Pt and clinical characteristics, including disease activity and pt-reported outcomes (PROs), were assessed at treatment initiation (index) and time of mACR50 achievement. Percent (95% confidence interval [CI]) maintaining treatment response at 6, 12, 18, and 24 months along with median time to loss of response were reported. Unadjusted proportional hazards regression models for interval-censored outcomes were used to identify predictors of mACR50 response durability. A multivariable‑adjusted regression model was used to calculate hazard ratios (HRs) to evaluate associations between pt characteristics and loss of response over follow-up.
Results: The analysis included 189 b/tsDMARD initiations. Mean (standard deviation [SD]) age was 53.0 (13.3) years. Overall, 52% of pts were female, 89% were white, 86% were overweight/obese, 58% pts were biologic‑naïve. Mean (SD) PsA disease duration was 5.9 (7.6) years, with 8.1 (9.3) years since symptom onset.
At mACR50 achievement, improvements in disease activity and PROs were observed. However, 8% of mACR50 achievers still had moderate/high disease activity according to the Clinical Disease Activity Index for Psoriatic Arthritis (cDAPSA) and 20% had not reached Minimal Disease Activity.
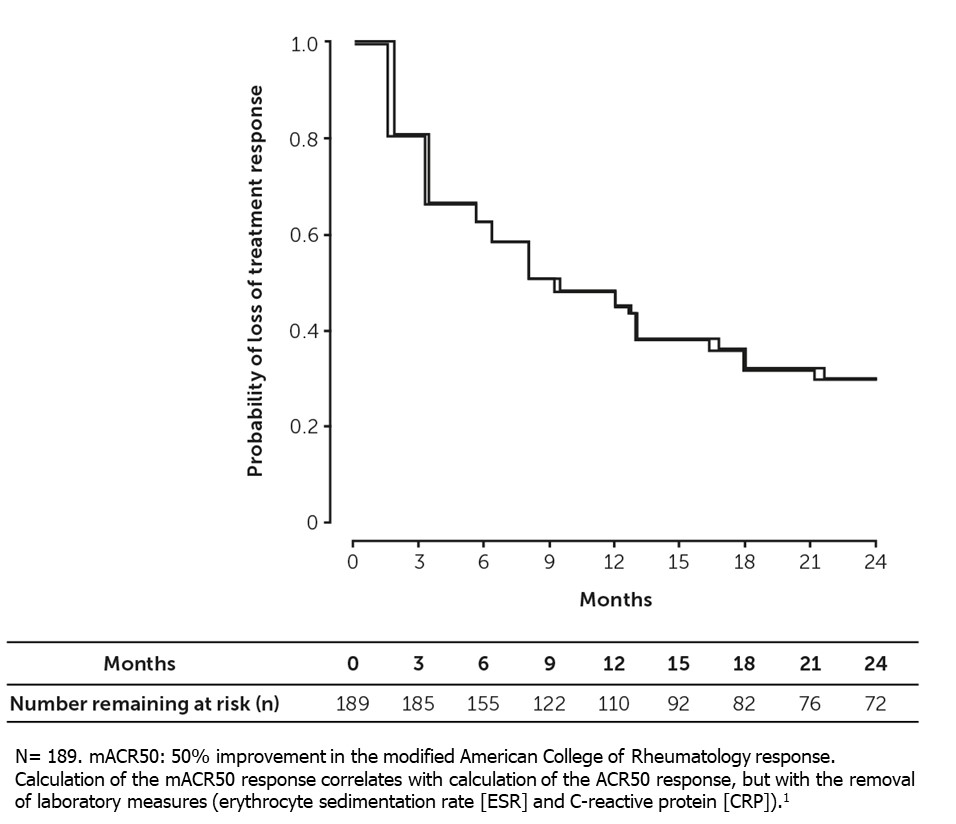
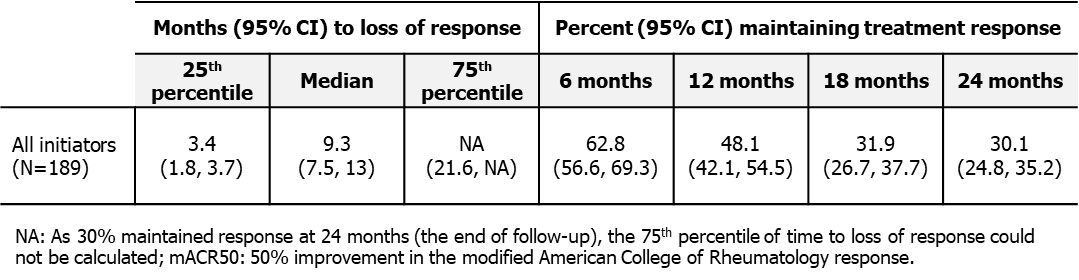
Over the 24-month follow-up, 37% (95% CI: 31%, 43%) lost response at 6 months, 52% (95% CI: 45%, 58%) at 12 months, and 70% (95% CI: 65%, 75%) at 24 months (Figure 1, Table 1). Median time for loss of mACR50 was 9.3 months (95% CI: 7.5, 13.0).
Multivariable-adjusted analysis showed that higher EuroQol-5D (EQ-5D) score at achievement of mACR50 (0.1 unit increase, HR=0.8 [95% CI: 0.67, 0.96]) and having a college education (HR=0.5 [95% CI: 0.30, 0.83]) were associated with lower risk of initial mACR50 loss (Table 2).
Conclusion: Among pts with PsA who achieved mACR50 after b/tsDMARD initiation, approximately one third lost treatment response at 6 months, and two thirds lost treatment response at 18- and 24-months post-achievement. A higher EQ-5D score, denoting greater health status, was associated with longer durability of mACR50, following the initial response.
References:
1. Greenberg JD et al. Rheumatol 2009;48:686–90.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ogdie A, Song C, Middaugh N, Marchese M, Eliot M, Beaty S, Low R, Mease P. Durability of Response Among Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA) Using Biological or Targeted Synthetic Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs in the CorEvitas PsA/Spondyloarthritis Registry [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/durability-of-response-among-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-psa-using-biological-or-targeted-synthetic-disease-modifying-antirheumatic-drugs-in-the-corevitas-psa-spondyloarthritis-registry/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/durability-of-response-among-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-psa-using-biological-or-targeted-synthetic-disease-modifying-antirheumatic-drugs-in-the-corevitas-psa-spondyloarthritis-registry/