Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Approximately half of the patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) present with axial disease. Previously, it was reported that PsA-patients with axial involvement present a higher cardiovascular risk compared with those without the axial disease. Additionally, it has been reported that axial disease is higher in patients with axial spondyloarthropathies, and carotid plaque (CP) identified by ultrasound than in patients without CP. The objective was to compare the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Metrology Index (BASMI) between PsA-patients with and without CP.
Methods: A cross-sectional and comparative study that included PsA patients aged 30 to 75 years old who fulfilled the 2006 Classification Criteria for PsA. Patients with previous cardiovascular atherosclerotic disease were excluded. B-mode carotid ultrasound was performed on all patients by a board-certified radiologist blinded to clinical information. Carotid plaque (CP) was defined as a carotid intima–media thickness (cIMT) ≥1.2 mm or a focal narrowing ≥0.5 mm of the surrounding lumen, and an increased cIMT was defined as a value ≥0.8 mm. Axial disease activity was measured using the BASMI in all patients.
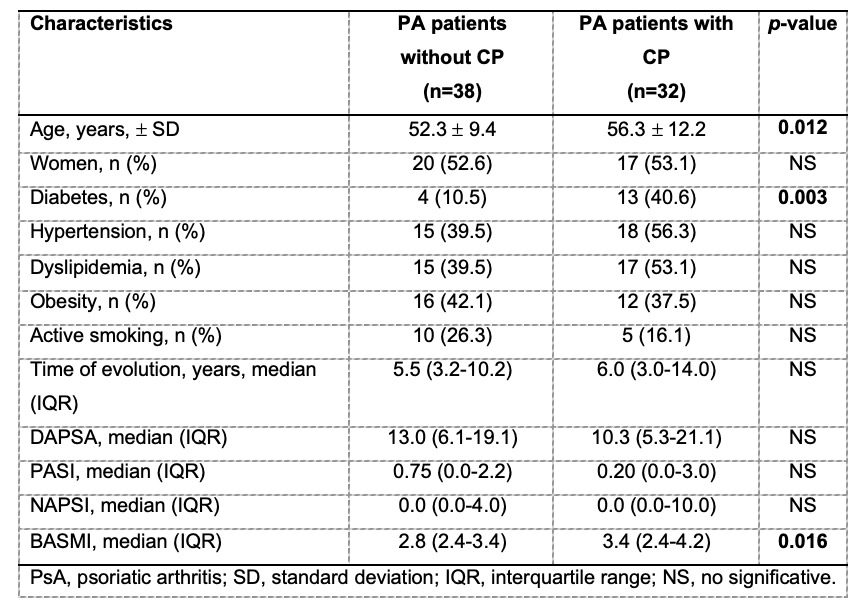
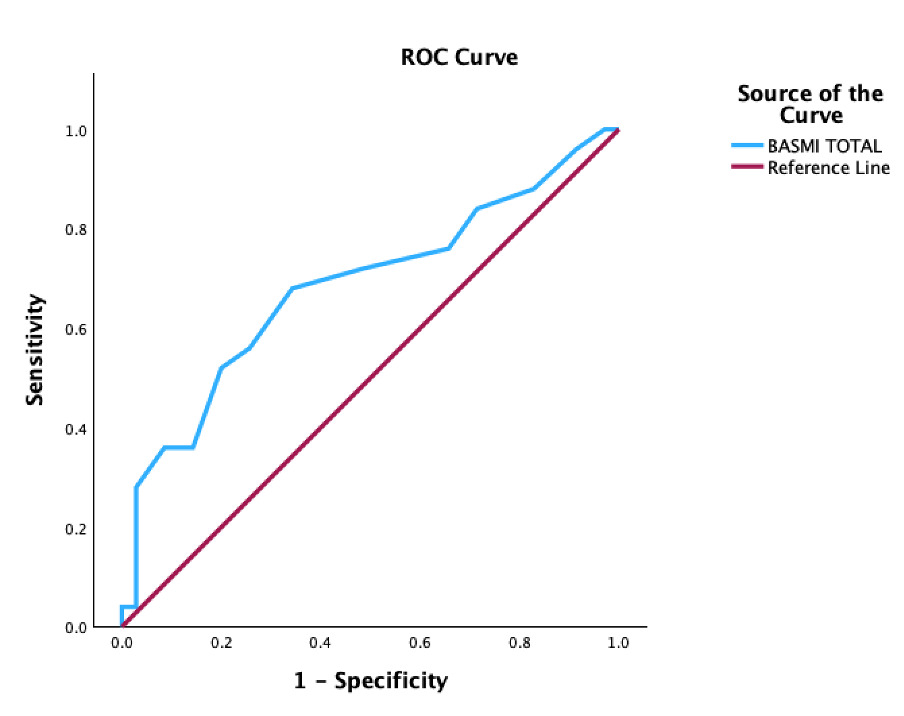
Results: A total of 70 patients with PsA were included, the mean age was 55 ± 11.47, the disease evolution of PsA was 7.95 ± 7.08 years, and the mean BASMI of all patients included was 3.09 ± 0.99. The prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus was higher in patients with PsA and CP (10.5% vs 40.6%, p=0.003). There was no difference between the prevalence of obesity and other cardiovascular risk factors, including smoking, obesity, hypertension, and dyslipidemia. BASMI was higher in PsA patients with CP in comparison to those patients without CP (3.4 vs 2.8, p=0.016). In a subanalysis, the Youden Index between CP and BASMI was assessed to determine the best cut-off point to identify CP, which resulted in a cut-off point of a BASMI of 2.9 with a sensitivity of 68% and a specificity of 65.7% (CI 0.541 – 0.826, p=0.012), Figure 1.
Conclusion: Patients with PsA and CP present higher axial disease activity compared to PsA patients without CP. A BASMI of 2.9 or higher may identify patients who would benefit from non-invasive screening for subclinical atherosclerosis.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Arvizu-Rivera R, Gonzalez-Gonzalez V, Galarza-Delgado D, Colunga I, Azpiri-López J, Beltran V, Arias Peralta A, Cardenas-De la Garza J. Axial Disease Activity in Psoriatic Arthritis Is Higher in Patients with Carotid Plaque [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/axial-disease-activity-in-psoriatic-arthritis-is-higher-in-patients-with-carotid-plaque/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/axial-disease-activity-in-psoriatic-arthritis-is-higher-in-patients-with-carotid-plaque/