Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Sex differences have been reported in pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, and treatment responses in several rheumatic diseases, including psoriatic arthritis (PsA).1 Although PsA is equally prevalent in male and female patients, it is important to understand sex-specific outcomes related to physician assessment of disease activity and patient-reported outcomes (PROs).1Previous research also suggests there may be a differential response to therapy with TNF or IL-17 inhibition in male and female patients. Deucravacitinib is a first-in-class, oral, selective, allosteric inhibitor of tyrosine kinase 2 approved in multiple countries for adults with plaque psoriasis.2,3 Here, we further characterize the effect of deucravacitinib on PsA disease activity by sex as derived from physician assessments and PROs.
Methods: Patients with PsA (N=203) were randomized 1:1:1 to placebo, deucravacitinib 6 mg once daily (QD), or deucravacitinib 12 mg QD in this phase 2 study. Outcomes were reported descriptively by sex. Composite changes in PsA disease activity were assessed by the achievement of ACR 20/50/70 and Minimal Disease Activity (MDA) and by mean changes in Psoriatic Arthritis Disease Activity scores. Mean change from baseline scores were calculated for physician assessments of specific disease domains including both Tender and Swollen Joint Counts, Leeds Enthesitis Index, and Leeds Dactylitis Index. Mean change from baseline scores were calculated for PROs included HAQ Disability Index (HAQ-DI), Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System (PROMIS)-Fatigue, and Subject Global Assessment of Pain (Pain).
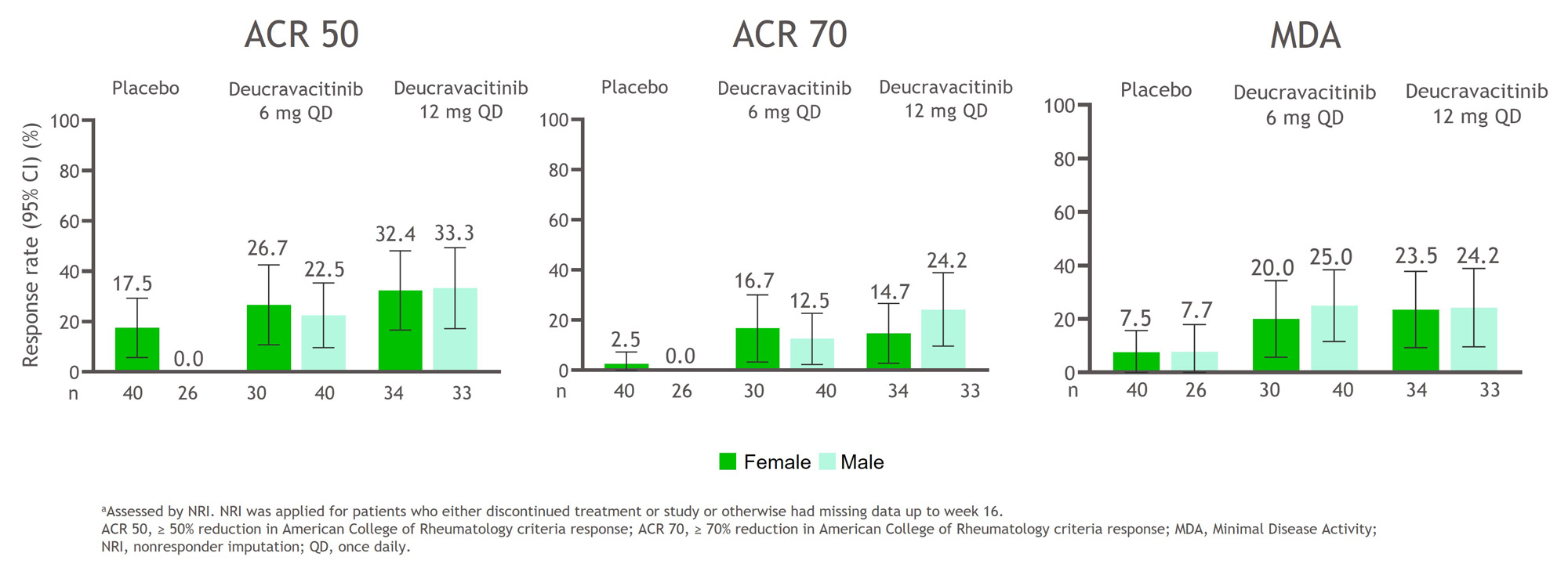
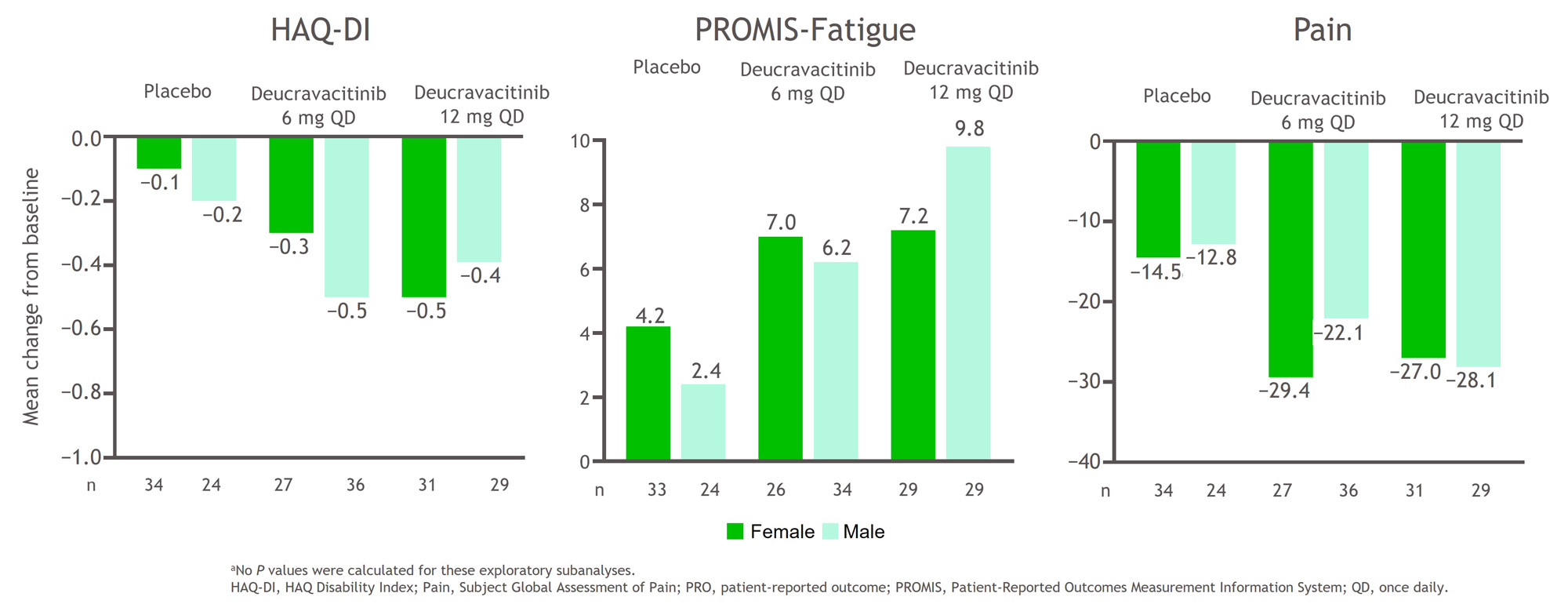
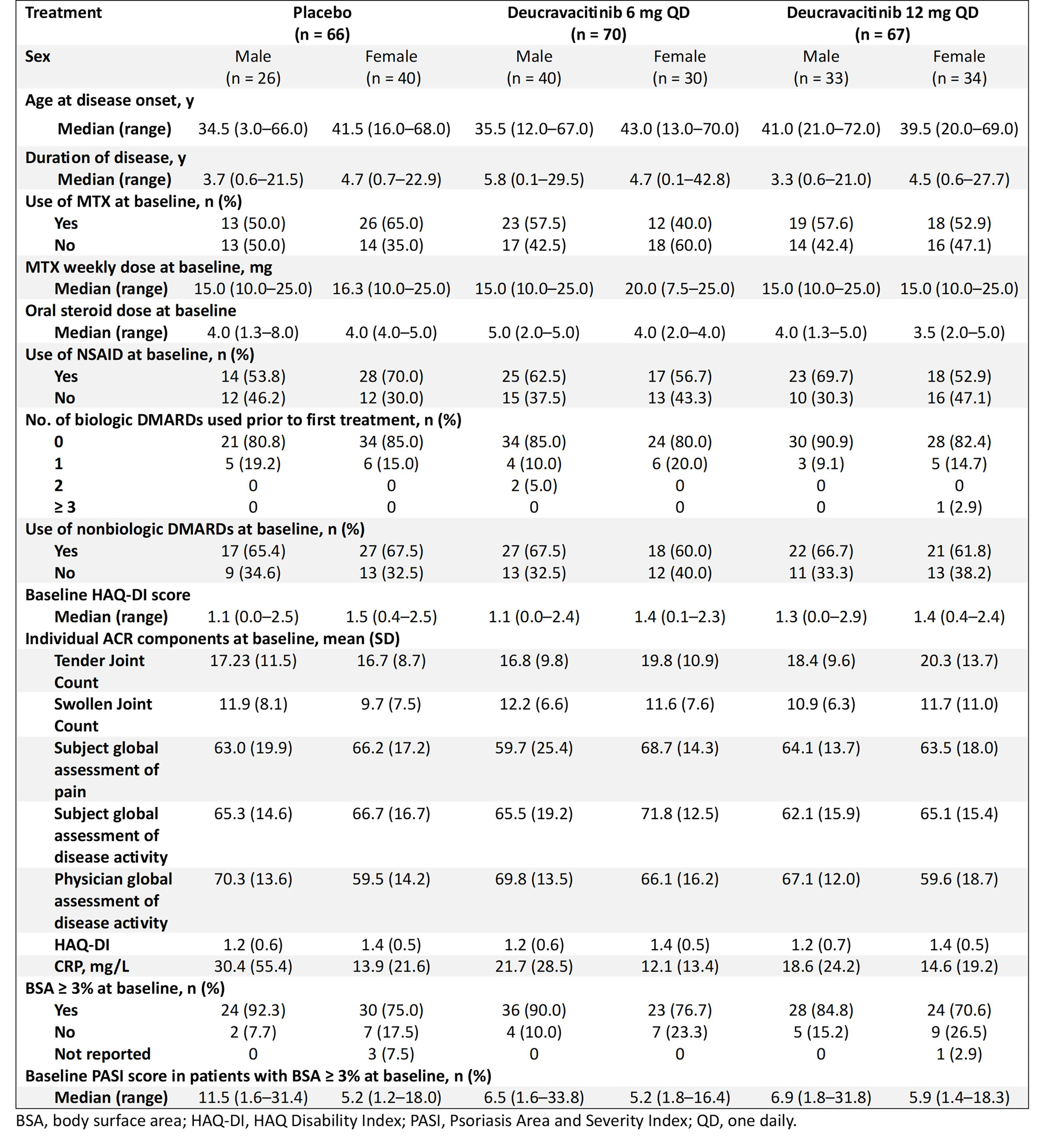
Results: Baseline characteristics were balanced between sexes and are shown in the Table. A higher percentage of patients of both sexes treated with deucravacitinib achieved ACR 50, ACR 70, and MDA responses at week 16 compared with placebo (Figure 1). In addition, a greater mean change from baseline HAQ-DI, PROMIS-Fatigue, and Pain scores occurred in patients treated with deucravacitinib compared with placebo among both sexes (Figure 2). Treatment-associated responses were generally similar between sexes in disease activity assessments and PROs.
Conclusion: Patients treated with deucravacitinib more frequently achieved reductions in disease activity measures and had greater changes from baseline scores for PROs compared with patients who received placebo. Deucravacitinib has comparable effects on PsA disease activity and PROs for the instruments assessed after 16 weeks of treatment in male and female patients.
References:
1. Coates L, et al. J Rheumatol 2023; 50:488–496.
2. Armstrong A, et al. J Am Acad Dermatol 2023;88:29–39.
3. Strober B, et al. J Am Acad Dermatol 2023;88:40–51.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Eder L, Ogdie A, Banerjee S, Nowak M, Lehman T, Mease P. Sex and Treatment-associated Outcomes in Patients with Active Psoriatic Arthritis Treated with Deucravacitinib, an Oral, Selective, Allosteric Tyrosine Kinase 2 Inhibitor, in a Phase 2 Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/sex-and-treatment-associated-outcomes-in-patients-with-active-psoriatic-arthritis-treated-with-deucravacitinib-an-oral-selective-allosteric-tyrosine-kinase-2-inhibitor-in-a-phase-2-trial/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/sex-and-treatment-associated-outcomes-in-patients-with-active-psoriatic-arthritis-treated-with-deucravacitinib-an-oral-selective-allosteric-tyrosine-kinase-2-inhibitor-in-a-phase-2-trial/