Background/Purpose:
Biologic agents, newly developed medications targeting for inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-alpha or IL-6, have been drastically improving the disease course of JIA who were resistant to conventional therapy. However, there are very few studies examined whether the biologic agents had also improved the quality of life (QOL) of patients. Focusing on their both physical and psychological condition, therefore, we examined QOL of JIA patients treated with biologic agents.
Methods:
Nation-wide survey was conducted for 8-18 years old JIA patients treated with biologic agents. To the family members of the JIA patients, both PedsQL™ Generic Core Scales¹⁾ evaluating for QOL and questionnaires evaluating for medical condition were handed from medical doctors who had registered the patient for the Governmental Medical Support Program for Chronic Pediatric Diseases in Japan. Statistical analysis was performed by Spearman rank correlation coefficient or Kruskal-Wallis test by using SPSS ver.19.
Results:
A total of 201 JIA patients (77 boys and 124 girls) were involved in the study. The biologic agent was initiated at mean 3 years from onset. Functional daily activities of JIA patients were classified from Class 1 to Class 4 according to the Steinbrocker’s functional class health assessment questionnaire score²⁾.
The incidence of patient who had no difficulty in daily activities (Class 1) increased from 25 % to 75 % after mean 3 years of biologic therapy. On the contrary, the incidence of patients with Class 3 difficulty in daily activities decreased from 34 % to 3 % during the treatment period.
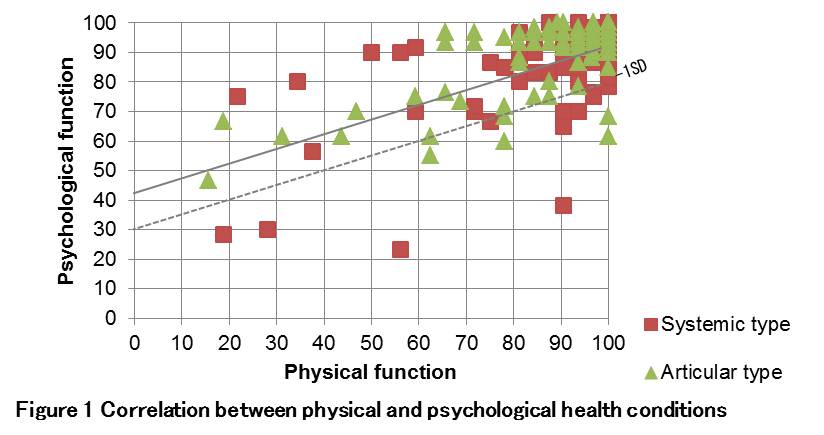 PedsQL™ Generic Core Scalesindicate that total psychological health score statistically correlated with total physical health score in JIA patients treated with biologic agents (P=0.559, p<0.001)(Figure 1).
PedsQL™ Generic Core Scalesindicate that total psychological health score statistically correlated with total physical health score in JIA patients treated with biologic agents (P=0.559, p<0.001)(Figure 1).
However, there were some JIA patients whose psychological health score were relatively low for their physical health score as seen in figure 1 (below -1SD correlation line).
In such patients with relatively lower psychological health score, there were more patients who were systemic onset, treated with tocilizumab that forces to frequent refer to the hospital (every 2week), and, as the result, frequently absent from school.
Conclusion:
In JIA patients treated with biologic agents, the psychological health condition improved in accordance with their physical health condition. However, we should aware that there are still patients who need psychological health support even if their physical function has improved, especially in systemic JIA patients treated with tocilizumab.
References:
1) Kobayashi K, et al. Pediatr Int 2010, 52: 80-8.
2) Steinbrocker O, et al. JAMA1949;140:659–62.
Disclosure:
Y. Osako,
None;
Y. Nonaka,
None;
H. Akaike,
None;
T. Kubota,
None;
T. Yamatou,
None;
T. Nagakura,
None;
J. Yasumura,
None;
H. Imanaka,
None;
S. Takei,
Caugai, Eisai, Takeda, Bristol-Myers,
2,
Chugai, Eisai, Takeda, Abbvie, Astellas, Teijin, Novartis, Pfizer, Asahi Kasei,
8.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/psychological-condition-of-jia-patients-treated-with-biologic-agents-a-nation-wide-survey-in-japan/
