Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: Methotrexate (MTX) is the most widely used disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Despite of its efficacy, the continuous use of MTX is often accompanied by several adverse effects, especially in high-dosage MTX. We developed the multifunctional nanoparticle (MNP; Poly(DL-lactic-co-glycolic acid)-Au half-shell coated nanoparticles) containing 0.2mg/kg of MTX. Upon near-infrared (NIR) irradiation, these MNP can enhance the drug release and generate heat by Au half-shells. This study aimed to investigate the therapeutic efficacy of MNP containing MTX in a murine model of arthritis.
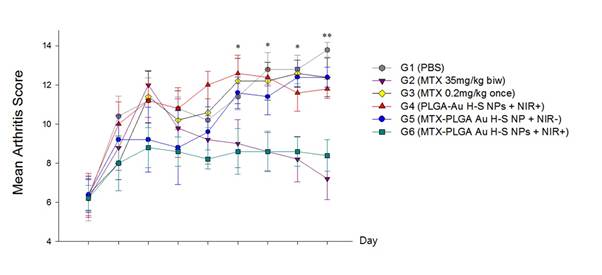
Methods: Collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) was induced in male DBA/1J mice by immunization with bovine type II collagen. Thirty CIA mice were divided into 6 groups (untreated, conventional MTX (35 mg/kg x 8 times intraperitoneal), MTX 0.2mg/kg once intravenous (IV), MTX-unloaded MNP IV with NIR, MTX-loaded MNP IV, and MTX-loaded MNP IV with NIR). The clinical scores and hind paw thickness were evaluated. Histopathologic assessment of joint sections was performed. The serum levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
Results: Treatment of MTX-loaded MNP with NIR significantly alleviated the severity of the arthritis, based on the reduced hind paw swelling and clinical scores, compared with untreated CIA mice. The treatment efficacy of MTX-loaded MNP with NIR group was comparable to that of conventional MTX-treated group. However, arthritis was not ameliorated in the mice treated with MTX 0.2mg/kg once or MTX-unloaded MNP with NIR. Treatment of MTX-loaded MNP without NIR showed partial treatment response only in an early treatment period. Histopathologic analyses and serum pro-inflammatory cytokines showed the similar pattern.
Conclusion: Treatment efficacy of MTX-loaded MNP with NIR was similar with conventional treatment in a much smaller dosage of MTX (about 1/1000 of MTX). Our results showed that this novel drug delivery system using MNP can be a new therapeutic tool for treatment of RA.
Disclosure:
Y. J. Ha,
None;
S. M. Lee,
None;
J. H. Lim,
None;
H. J. Kim,
None;
S. W. Lee,
None;
S. K. Lee,
None;
K. H. Yoo,
None;
Y. B. Park,
None.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/alleviation-of-collagen-induced-arthritis-by-multifunctional-nanoparticle-containing-methotrexate/