Session Information
Date: Thursday, March 30, 2023
Title: Poster Breakout 1 - Lupus: Genetics, Epigenetics, & Social Determinants
Session Type: Breakout Session
Session Time: 5:10PM-5:40PM
Background/Purpose: Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic, systemic autoimmune disorder. The pathogenesis of SLE is not fully understood, but twin/sibling high concordance rate suggests a genetic component triggered by stochastic environmental events. Childhood-onset SLE (cSLE) patients have an extreme phenotype, with early age of diagnosis and more severe disease relative to adult-onset SLE. Therefore, cSLE are an ideal population in which to study genetic contributors to disease. Historically, rare variant analyses have focused on a single gene shared by multiple patients in unrelated families. This approach does not consider that rare variants in people may cluster in genes that participate in similar biological processes. Therefore we aim to identify rare, enriched variants in genes of the same biological pathways that may contribute to the pathogenesis of SLE by applying pathway analysis to whole genome sequencing data of a diverse cSLE cohort.
Methods: SLE subjects met at least 4 of 11 revised American College of Rheumatology classification SLE criteria with disease onset prior to age 18. Whole blood samples collected from 81 subjects and 111 parents underwent whole genome sequencing (Table 1). Rare (minor allele frequency cutoff of 0.01), nonsynonymous variants in coding exons present in cSLE patients were selected, resulting in 483 variants in 232 genes. We restricted to variants present in 2 or more cSLE patients and not present in unaffected parents, or variants that were present more often in the cSLE patients than parental controls, assessed by Fisher’s exact test (p < 0.05). The resulting gene list was sorted into Gene Ontolgoy: Biological Processes (GO:BP) using Metascape. The Cytoscape Enrichment Map App (Cytoscape v. 3.7) was then used to generate a network of pathways enriched for genes in which cSLE patients harbored rare variants.
Results: Of the 483 unique rare exonic variants, 239 variants were sorted into 133 GO:BP genesets. (Table 2) Enrichment map analysis to clustered them into 18 biologic pathways including RNA processing and apoptosis. (Figure 1) Some pathways (e.g. nucleic acid regulation) are well-established causes of monogenic SLE, while others have not previously been described in the SLE.
Conclusion: Rare, exotic variants were enriched in biologic pathways in cSLE patients compared to parental controls. Pathway-network analysis is a useful approach to identify biological pathways and specific genes that could contribute to SLE risk. Ongoing analysis of the specific variants identified in each pathway will allow us to prioritize key genes and pathways for further study. Additionally, assessing clinical genotype/phenotype correlations could contribute to advancing SLE past a broad clinical phenotype to a more precise molecular diagnosis.
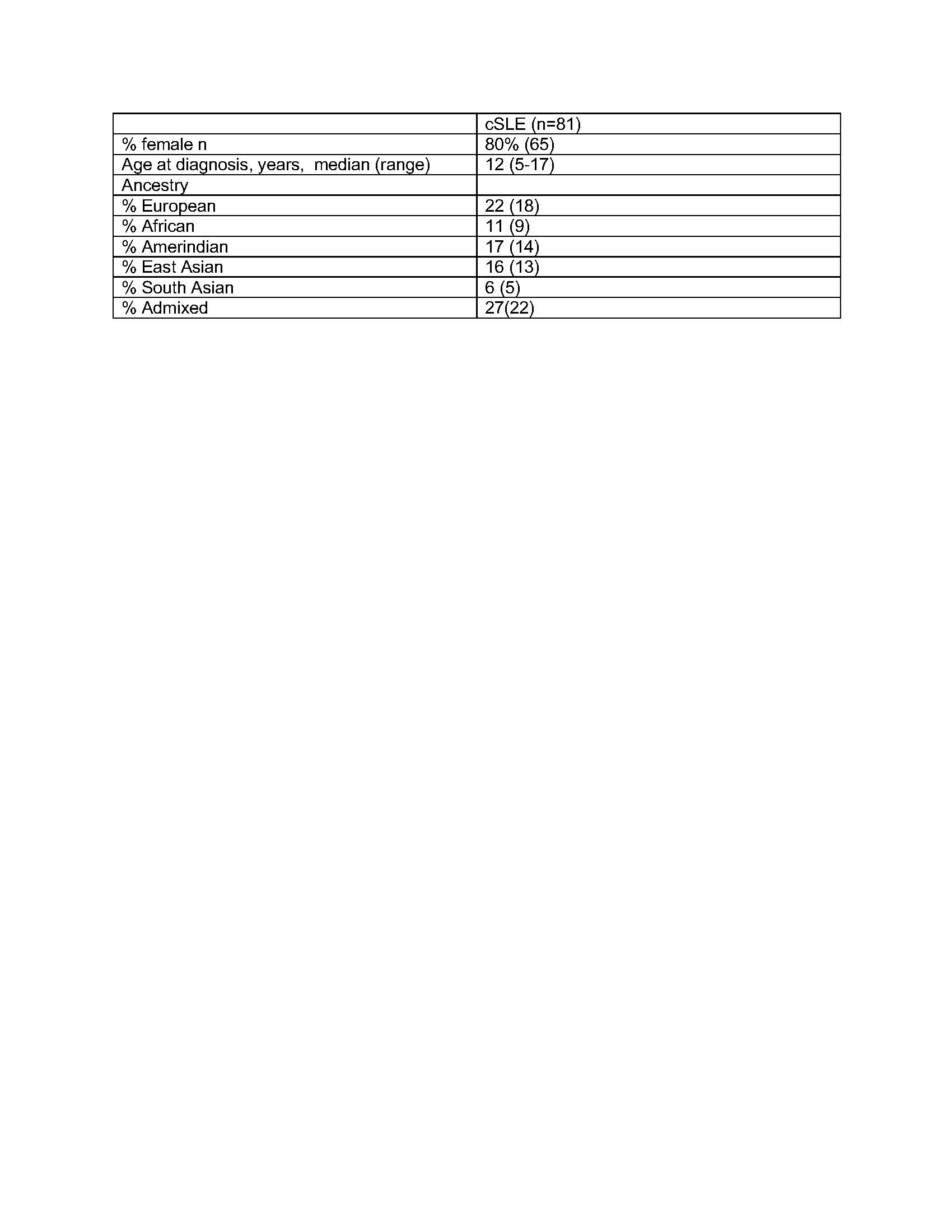 Table 1. Demographic data for the cSLE cohort
Table 1. Demographic data for the cSLE cohort
 Figure 1. Biologic Pathways Eniched in Rare Coding Variants in cSLE patients. Each red circle is a geneset, represented as a node. The deeper the color of the node, the more the gene set is enriched in rare variants.
Figure 1. Biologic Pathways Eniched in Rare Coding Variants in cSLE patients. Each red circle is a geneset, represented as a node. The deeper the color of the node, the more the gene set is enriched in rare variants.
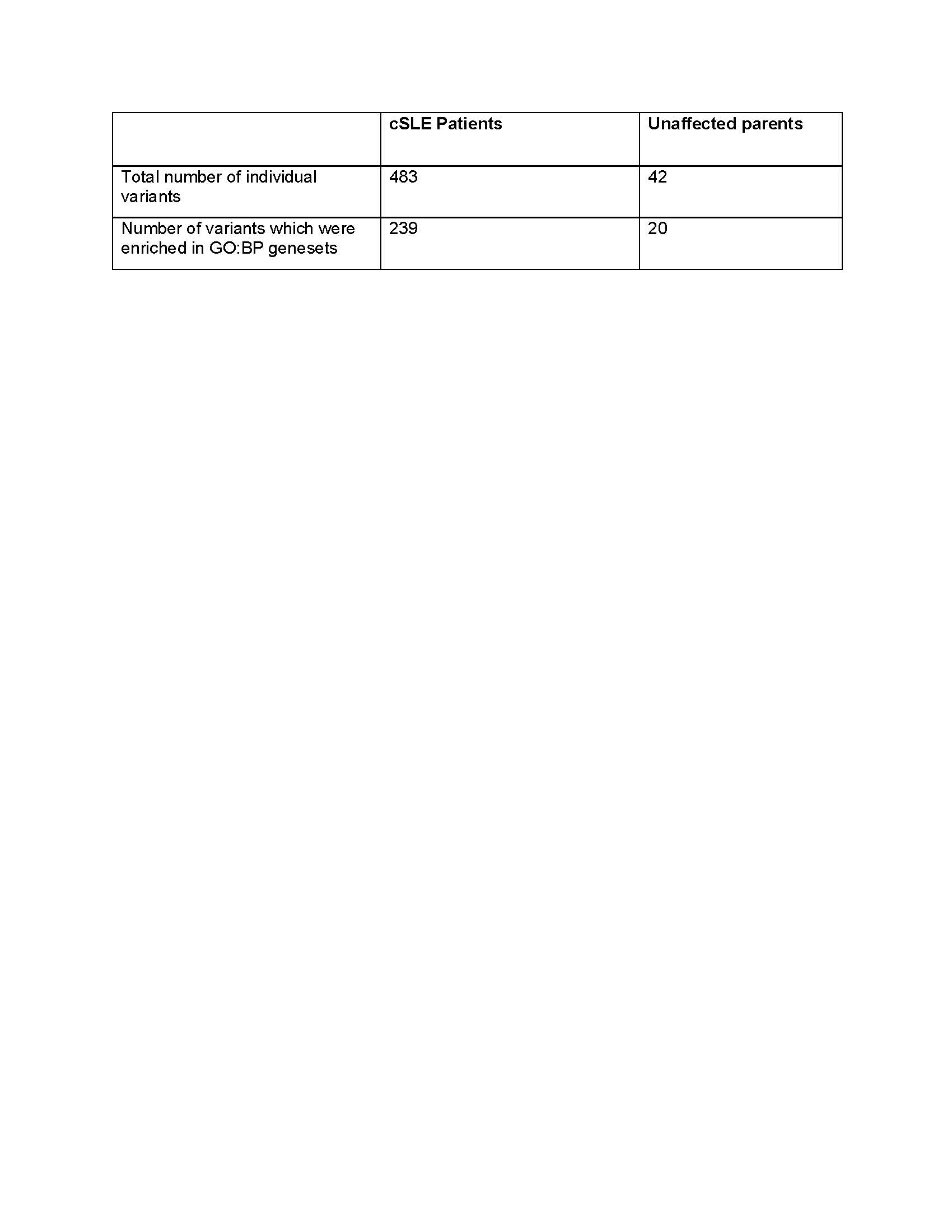 Table 2. Comparison of number rare variants in coding regions between cSLE patients and unaffected parents.
Table 2. Comparison of number rare variants in coding regions between cSLE patients and unaffected parents.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Heitzman K, Franco L, Hiraki L, Silverman E, Scott C, Barrera-Vargas A, Deng Z, Kaplan M, Lewandowski L. Applying Pathway Analysis to Whole Genome Data to Identify Pathophysiologic Pathways in Childhood-onset Systemic Lupus Erythematosus [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 4). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/applying-pathway-analysis-to-whole-genome-data-to-identify-pathophysiologic-pathways-in-childhood-onset-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/. Accessed .« Back to 2023 Pediatric Rheumatology Symposium
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/applying-pathway-analysis-to-whole-genome-data-to-identify-pathophysiologic-pathways-in-childhood-onset-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/
