Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Treatment with Tixagevimab/Cilgavimab 150/150 mg was authorized by the FDA on 12/8/21 under an Emergency Use Authorization as pre-exposure prophylaxis against COVID-19 infection. The dose was increased to 300/300 mg on 2/25/22. True efficacy of protection from breakthrough COVID-19 infection in immunosuppressed patients with rheumatic disorders, especially against emerging Omicron subvariants, is not well-established. A European study reported a breakthrough rate of 4.4% in a heterogeneous group of immunocompromised patients receiving tixagevimab/cilgavimab 150/150 with median followup of 63 days. A recent US cohort of 43 rheumatic patients receiving rituximab showed a 4.32% breakthrough rate after an average of 100 days. Real world data reflecting the recommended 6-month dosing interval in rheumatic patients remains lacking.
Methods: Longitudinal study of rheumatic patients initially dosed with tixagevimab/cilgavimab contacted at 6 months for redosing and questioned regarding interval COVID-19 infection with confirmation by manual chart review as well as retrospective chart review of patients who had not achieved a 6-month interval from last dose for rate of breakthrough COVID-19 infection.
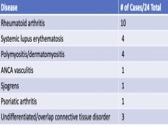
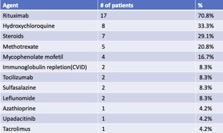
Results: 157 patients received Tixagevimab/Cilgavimab from 1/16/22– 8/31/22 with average follow up of 154 days. Disease distribution is reported in Table 1 and treatment regimens in Table 2. Due to limited resources, initial allocation was given to patients on B cell depleting therapy. After 2/22, all patients meeting FDA guidelines were offered monoclonal prophylaxis.
No serious adverse events occurred. There were 24 cases (15.3%) of breakthrough acute COVID-19 infection following Tixagevimab/Cilgavimab administration. There was an average of 99.5 days (ranging from 5-195 days) between the last dose and the date of breakthrough infection. These patients were predominantly female (87.5%), Caucasian (87.5%), averaging 60.5 years old (ranging 20-81 years). All patients were fully vaccinated against COVID-19, and 4 had a prior COVID-19 infection. Three patients received doses of 150/150 mg without makeup doses and 21 received 300/300 mg doses. Sixteen (66.6%) received post-exposure oral antiviral therapy. Most patients experienced mild to moderate symptoms but two patients, who both received the 300/300 mg dose, required hospitalization. 37.6 % receiving tixagevimab/cilgavimab were on rituximab and of these, 29% experienced symptomatic breakthrough COVID-19 infection. There were no deaths.
Conclusion: Following treatment with Tixagevimab/Cilgavimab, 15.3% of fully vaccinated rheumatic patients experienced symptomatic breakthrough COVID-19 infection during a period when Omicron subvariants were dominant, peaking in our region with a weekly incidence of 522 cases/100K population. Treatment with rituximab was a common risk factor in 70.8% of these breakthrough cases with ~ 1/3 of rituximab treated patients receiving monoclonal prophylaxis experiencing symptomatic mild to moderate infections. These breakthrough rates are significantly higher than previously reported. Ongoing evaluation of best practices for repeat dosing and intervals of Tixagevimab/Cilgavimab is needed.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Podgorski C, Parks D. Breakthrough Acute COVID-19 Infection During the US Omicron Surge Following Administration of Tixagevimab/Cilgavimab in Immunocompromised Patients with Rheumatologic Disorders [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/breakthrough-acute-covid-19-infection-during-the-us-omicron-surge-following-administration-of-tixagevimab-cilgavimab-in-immunocompromised-patients-with-rheumatologic-disorders/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/breakthrough-acute-covid-19-infection-during-the-us-omicron-surge-following-administration-of-tixagevimab-cilgavimab-in-immunocompromised-patients-with-rheumatologic-disorders/