Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: In the phase 3 DISCOVER (D)-1 and D-2 studies, guselkumab (GUS) significantly improved joint symptoms, skin disease, enthesitis, dactylitis, physical function, and quality of life at Week (W)24 in patients (pts) with psoriatic arthritis (PsA).1,2 Clinical responses across these disease domains were maintained or increased with GUS at W52,3,4 regardless of baseline (BL) pt demographics, disease characteristics, or conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (csDMARD) use.5 Durable efficacy with GUS through W100 across multiple disease domains was observed.6 This study assessed both BL predictors of, and by BL pt subgroups, GUS efficacy across PsA disease domains through W100 of D-2.
Methods: Biologic-naïve pts with active PsA despite standard therapies in D-2 (swollen joint count [SJC] ≥5 & tender joint count [TJC] ≥5, C-reactive protein [CRP] ≥0.6 mg/dL) were randomized 1:1:1 to GUS 100 mg every 4 weeks (Q4W); GUS 100 mg at W0, W4, then Q8W; or placebo (PBO).2 GUS effects on joint, skin, enthesitis, dactylitis, spinal pain, and disease severity endpoints (change in Disease Activity in PsA [DAPSA], SJC, and TJC scores; Psoriasis [PsO] Area Severity Index [PASI] score [among pts with BL IGA ≥2 and body surface area [BSA] with PsO ≥3%]; Leeds enthesitis index [LEI] score; dactylitis score; spinal pain score; and PsA Disease Activity Score [PASDAS], respectively) at W100 were evaluated for GUS-randomized pts. A multivariate linear model adjusting for BL pt characteristics assessed associations between BL predictors and changes in DAPSA, PASI, and LEI scores from BL to W100, and least squares mean changes and 95% confidence intervals in all continuous endpoints from BL to W100 within subgroups of pts defined by BL sex, body mass index, PsA duration, SJC, TJC, CRP, %BSA, PASI score, and csDMARD use.
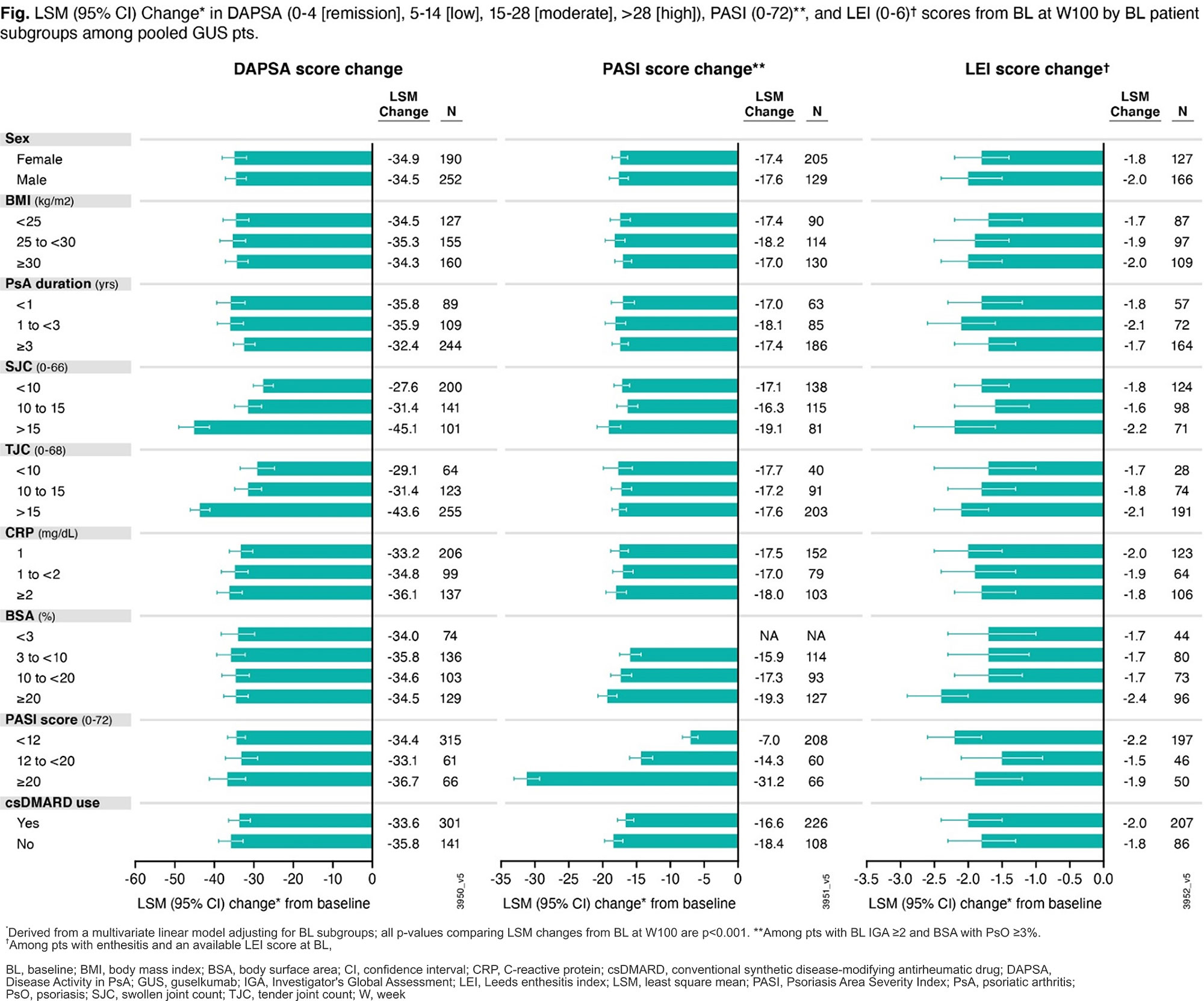
Results: 442 (90%) GUS-randomized pts completed study treatment through W100.6 Among the BL predictors of long-term GUS efficacy assessed, only PsA duration (p=0.032), SJC (p< 0.001), and TJC (p< 0.001) were significant predictors of long-term (BL to W100) DAPSA score change; %BSA (p=0.002), PASI score (p< 0.001), SJC (p=0.008), and csDMARD use (p=0.014) were significant predictors of long-term PASI score change; and none significantly predicted long-term LEI score change among pooled GUS pts (Fig). However, statistically significant improvements from BL to W100 in DAPSA, PASI, and LEI scores were observed across all BL strata in pooled GUS Q4W+Q8W pts (Fig, all p< 0.001) and within each dosing group. Similar improvements were observed for other continuous endpoints assessed (change in PASDAS, SJC, TJC, spinal pain, and dactylitis score).
Conclusion: GUS significantly improved PsA signs and symptoms through W100 across all BL pt subgroups including pts with highly active disease regardless of dosing regimen.
References:
1. Deodhar A et al. Lancet 2020; 395:1115-25
2. Mease PJ et al. Lancet 2020; 395;1126-36
3. Ritchlin CT et al. RMD Open 2021;7(1):e001457
4. McInnes IB et al. Arthritis Rheumatol 2021; 73:604-16
5. Ritchlin CT et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2021; 80:1291-2
6. McInnes IB et al. Arthritis Rheumatol 2021; doi: 10.1002/art.42010
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
McInnes I, Tesser J, Schiopu E, Merola J, Chakravarty S, Rampakakis E, Shiff N, Kollmeier A, Xu X, Shawi M, Lavie F, Bird P, Mease P. Consistent Long-Term Guselkumab Efficacy Across Psoriatic Arthritis Domains Irrespective of Baseline Patient Characteristics [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/consistent-long-term-guselkumab-efficacy-across-psoriatic-arthritis-domains-irrespective-of-baseline-patient-characteristics/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/consistent-long-term-guselkumab-efficacy-across-psoriatic-arthritis-domains-irrespective-of-baseline-patient-characteristics/