Session Information
Date: Monday, November 14, 2022
Title: SLE – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster III: Outcomes
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Infections are significant causes of mortality in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), and their prevention is essential. Although some previous reports have shown the efficacy of hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) in preventing infection, there is no such evidence in the Japanese population. Here we investigated the effect of HCQ on reducing infections in SLE patients in Japan using data from the Lupus Registry of Nationwide Institutions (LUNA) registry.
Methods: Patients older than 20 years and who met the 1997 ACR revised classification criteria were enrolled in the LUNA registry. We defined “severe infections” as infections that required inpatient treatment, and collected data on the type of infection, treatment, disease activity, and clinical and serological variables. To analyze the protective effect of the HCQ on infections using a generalized estimating equation (GEE) logistic regression model as primary endpoint, we converted all follow-up periods to person-years at each observation point. We defined the HCQ group as the period when the patient was taking HCQ both points before and after each annual observation period and the non-HCQ group as when the patient was not taking HCQ at both points. To analyze the survival time by log-rank test and perform a multivariate analysis of the association between the HCQ and the time until the first severe infection within the observation period, we defined the HCQ group as the patients who took HCQ for at least two observation points, and the non-HCQ group as those who did not take HCQ during the follow-up period. We used multiple imputation for missing data.
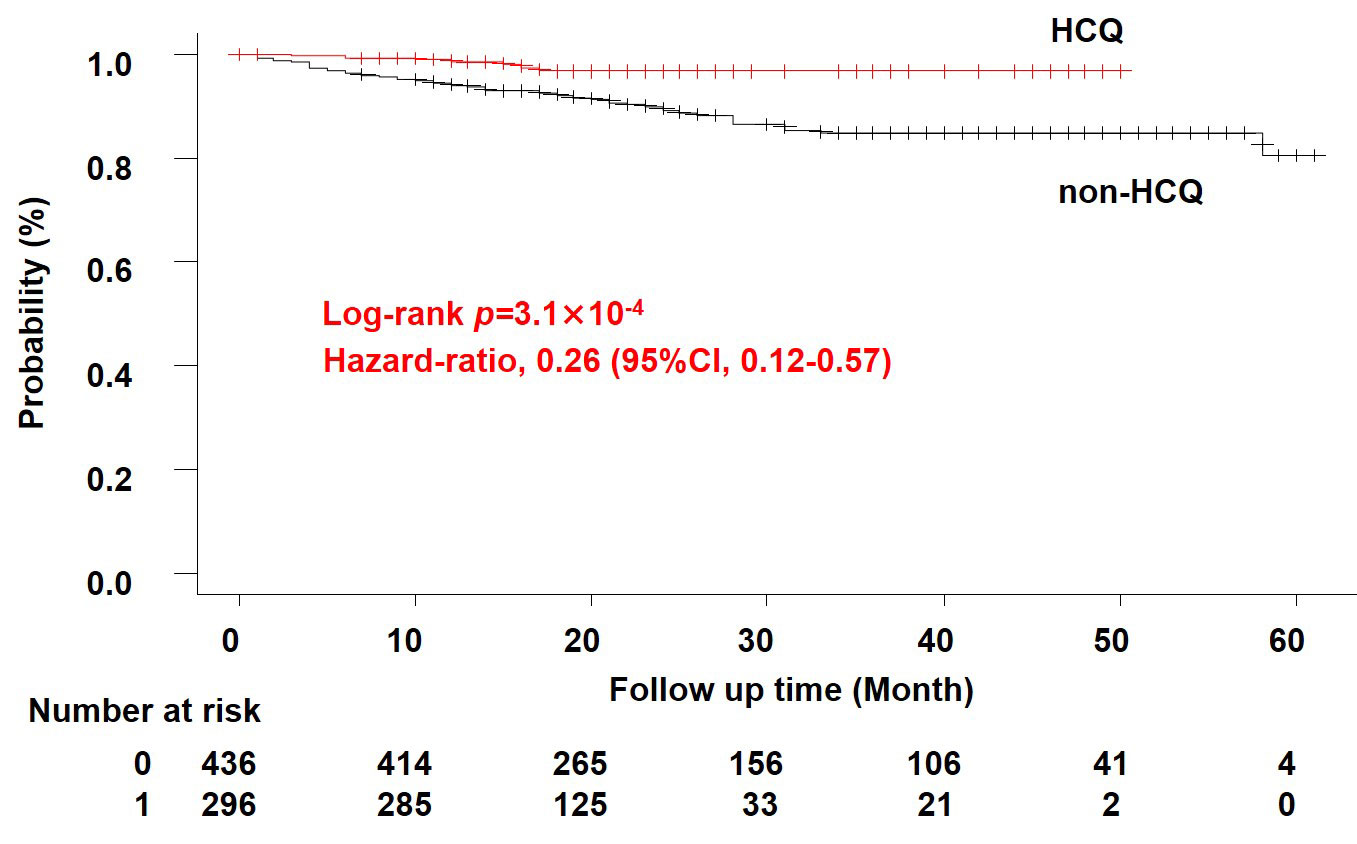
Results: A total of 925 patients were included in the study (median age 45 (IQR 35-57) years; female 88.1 %; the observation period 1-5 years). At enrollment, 267 patients were prescribed HCQ, while 656 were not. The median dose of glucocorticoid was 5.5 (IQR 4.0-9.0) mg/day and systemic lupus erythematosus disease activity index (SLEDAI) was 4 (IQR 2-8). A total of 110 severe infections were reported, with pulmonary infections the most common (29.1 %), followed by urinary tract infections (27.3 %) and skin and soft tissue infections (15.5 %). To examine the effect of HCQ and other factors on severe infections, we extracted 1,990 person-years. GEE analysis showed that severe infection was positively associated with the glucocorticoid dose (odds ratio [OR] 1.96 [95% confidence interval 1.38-2.81], p = 2.0×10-4), immunosuppressive drugs (OR 1.56 [1.03-2.38], p = 0.038), and the age at baseline (OR 1.04 [1,03-1.06], p = 1.5×10-7). HCQ tended to reduce the incidence of severe infections, although the difference was not statistically significant (OR 0.59 [0,33-1.06], p = 0.077). Survival time analysis showed that the HCQ group (n = 296) had a lower incidence of severe infection than the non-HCQ group (n = 436) (p = 3.1×10-4). Using a cox proportional hazards model, we found that age at baseline (hazard ratio [HR] 1.033 [1.014-1.052], p = 6.0×10-4) and HCQ (HR 0.32 [0.142-0.723], p = 6.0×10-3) were significantly associated with incidence rate.
Conclusion: This study demonstrated that HCQ could reduce the incidence of infection, which may improve the clinical course of SLE patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hidekawa C, Yoshimi R, Saigusa Y, Tamura J, Yajima N, Suzuki N, Kojitani N, Yoshioka Y, Sakurai N, Sugiyama Y, Kunishita Y, Kishimoto D, Higashitani K, Sato Y, Komiya T, Nagai H, Hamada N, Maeda A, Tsuchida N, Hirahara L, Soejima Y, Takase-Minegishi K, Kirino Y, Sada K, Miyawaki Y, Ichinose K, Ohno S, Kajiyama H, Sato S, Shimojima Y, Fujiwara M, Nakajima H. Association of Hydroxychloroquine with the Incidence of Infectious Disease in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Data from the LUNA Registry [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-of-hydroxychloroquine-with-the-incidence-of-infectious-disease-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-data-from-the-luna-registry/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-of-hydroxychloroquine-with-the-incidence-of-infectious-disease-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-data-from-the-luna-registry/