Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose:
Tocilizumab, at a registered dose of 8mg/kg, has proven to be effective in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Clinical trial data show that a large proportion of patients achieve low disease activity on a lower than registered starting dose.1 A lower dose might reduce dose-dependent side effects and costs. We investigated the feasibility of dose reduction to 4 mg/kg in patients who reached low disease activity at a registered dose of 8 mg/kg.
Methods:
According to the local treatment protocol, rheumatoid arthritis patients start with tocilizumab 8mg/kg every 4 weeks. After about 6 months, the dose is reduced to 4 mg/kg if patients have low disease activity (DAS28<3.2 and/or judgement of rheumatologist). In case of loss of disease control (DAS28>3.2 and/or judgement rheumatologist), the dose could be increased again to 8mg/kg. In this retrospective study, baseline patient-, disease- and treatment characteristics were collected as well as data on disease activity before and 3 and 6 months after dose reduction and when applicable 3 and 6 months after dose escalation.
Results:
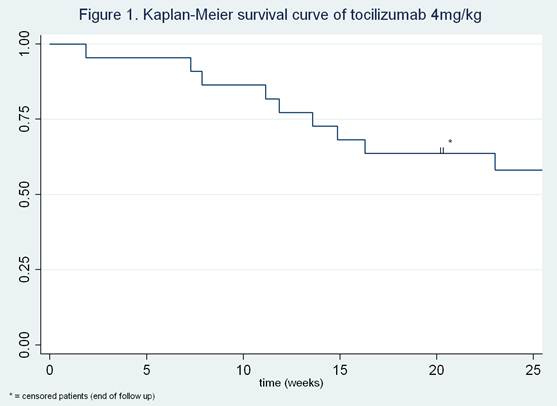
In 22 patients tocilizumab dose was reduced because of low disease activity (table 1). After 3 and 6 months follow up, 77% (95% CI 54-91) and 55% (95% CI 32-76) of patients still had low disease activity, respectively (figure 1). Seven out of 9 flares after dose reduction (78%), occurred within the first 16 weeks. The mean DAS28 at time of dose reduction was 2.3 (SD 0.9). The DAS28 at 3 and 6 months was somewhat higher than baseline, 2.7 (SD 1.2) and 2.5 (SD 1.0) respectively. All patients who experienced worsening of disease activity after dose reduction regained low disease activity after dose escalation.
Conclusion:
In this proof of principle study, dose reduction of tocilizumab to 4 mg/kg seems feasible in the majority of rheumatoid arthritis patients who had achieved low disease activity at a 8 mg/kg dose. Dose escalation after flare was effective in all patients.
Reference list:
1. Kremer JM, et al. Arthritis Rheum 2011;63(3):609-21.
Table 1. Baseline characteristics (start tocilizumab 8 mg/kg)
|
|
n = 22 |
|
Age, years (SD) |
61 (12) |
|
Woman, n (%) |
20 (91) |
|
Disease duration, years median [p25-p75] |
10 [5-17] |
|
Rheumatoid factor positive, n (%) |
14 (64) |
|
Anti-CCP positive, n (%) |
14/19 (74) |
|
Erosive disease, n (%) |
13 (59) |
|
DAS28 before start tocilizumab (SD) |
4.9 (0.9) |
|
Previous DMARDs, n median [p25-p75] |
3 [2-5] |
|
Previous biologicals n, median [p25-p75] |
3 [2-5] |
|
Concomitant DMARD, n (%) |
9 (41) |
|
Concomitant corticosteroid, n (%) |
14 (64) |
anti-CCP= anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide; DAS28 = 28 joints disease activity score;
DMARD = disease-modifying antirheumatic drug
Disclosure:
N. van Herwaarden,
None;
S. Herfkens-Hol,
None;
A. van der Maas,
None;
B. J. F. van Den Bemt,
None;
R. F. van Vollenhoven,
Abbott Immunology Pharmaceuticals,
2,
BMS,
2,
GSK,
2,
MSD,
2,
Pfizer Inc,
2,
Roche Pharmaceuticals,
2,
UCB,
2,
Abbott Immunology Pharmaceuticals,
5,
BMS,
5,
GSK,
5,
MSD,
5,
Pfizer Inc,
5,
Roche Pharmaceuticals,
5,
UCB,
5;
J. W. J. Bijlsma,
Abbott Immunology Pharmaceuticals,
5,
Roche Pharmaceuticals,
5,
BMS,
5,
UCB,
5,
Pfizer Inc,
5,
Merck Pharmaceuticals,
2,
Pfizer Inc,
2,
UCB,
2,
BMS,
2,
Roche Pharmaceuticals,
2,
Abbott Immunology Pharmaceuticals,
2;
A. A. den Broeder,
None.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/dose-reduction-of-tocilizumab-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-with-low-disease-activity-is-feasible/