Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 13, 2022
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Ixekizumab (IXE), a monoclonal antibody that selectively targets interleukin IL-17A, has shown efficacy in patients with radiographic axial spondyloarthritis (r-axSpA). Spinal pain, in particular spinal pain at night (SP-N), is a major contributor to the patient burden of r-axSpA. Here we assess SP-N improvement in patients up to week (W) 52 and determine the association of SP-N improvement in patients treated with IXE with other patient-reported outcomes (PROs) at W16 and with reaching ASDAS LDA at W52.
Methods: The Phase III COAST-V (NCT02696785) trial investigated the efficacy of IXE in 341 patients with r-axSpA and were biological disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drug (bDMARD)-naïve. Patients were randomised to IXE every 2W (IXEQ2W), IXE every 4W (IXEQ4W), adalimumab (ADA) or placebo (PBO) up to W16. Only approved dose IXEQ4W data are presented here. SP-N was measured at each visit using a numeric rating scale (NRS) (0-10). A clinically relevant improvement in SP-N was defined as >2 point improvement from baseline. Differences in baseline variables between those achieving versus not achieving >2 improvement in SP-N were tested using Fisher’s exact test (binary variables) and analysis of variance (ANOVA; continuous variables). Associations of SP-N improvement with PROs (BASFI, Fatigue Severity NRS, Jenkins Sleep Evaluation Questionnaire (JSEQ), SF-36 PCS) at W16, and ASDAS LDA at W52 were tested using analysis of covariance (ANCOVA; continuous variables) and logistic regression (binary variables). Missing values were imputed using non-responder imputation (NRI), and modified baseline observation carried forward.
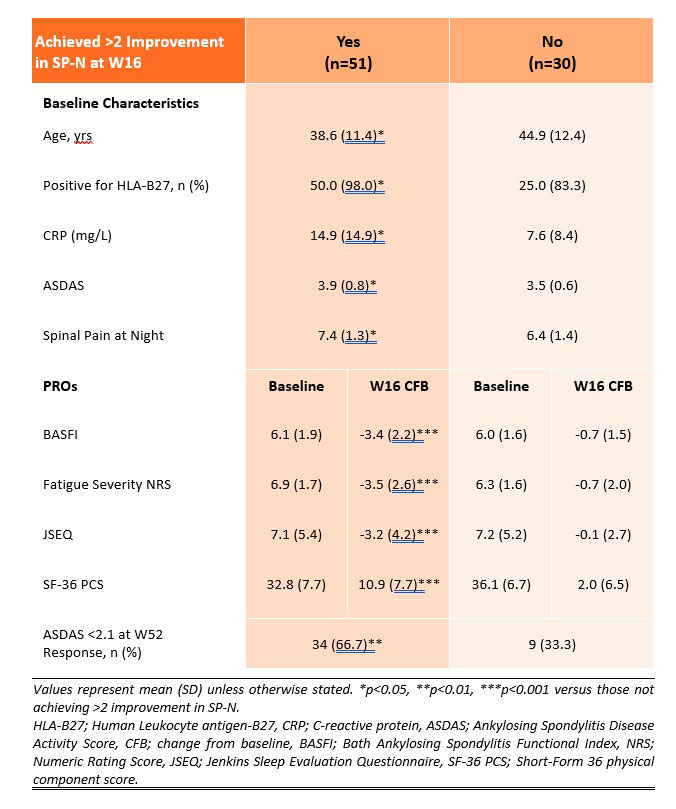
Results: A greater proportion of patients achieved >2 improvement in SP-N with IXE treatment compared to PBO at W16 (63.0% vs. 32.2%, p < 0.001) and improvement was sustained up to W52 (Figure 1). Of the 81 patients originally randomised to IXE, those achieving >2 improvement in SP-N (63%) at W16 were younger, more frequently positive for HLA-B27 and had higher disease activity at baseline compared to those that did not achieve >2 improvement (Table 1). Achieving >2 improvement in SP-N was associated with improvement in PROs including BASFI, Fatigue Severity, JSEQ and SF-36 PCS at W16 and with achieving ASDAS< 2.1 at W52 compared to those not achieving >2 improvement in SP-N (Table 1).
Conclusion: IXE improved SP-N for patients with r-axSpA not previously treated with bDMARDs. Improvements in SP-N were associated with improvements in disease activity, function, fatigue and quality of life.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ramiro S, Lukas C, Nissen M, Schymura Y, Ng K, Bradley A, Doridot G, Liu-Leage S, Chan A, WEI J. Efficacy and Improvement in Patient-Reported Outcomes at Weeks 16 and 52 in Ixekizumab Treated Biological Naïve Patients with Radiographic Axial Spondyloarthritis Achieving Clinically Important Pain at Night Reduction at Week 16: Results from COAST-V Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-improvement-in-patient-reported-outcomes-at-weeks-16-and-52-in-ixekizumab-treated-biological-naive-patients-with-radiographic-axial-spondyloarthritis-achieving-clinically-important-pain-a/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-improvement-in-patient-reported-outcomes-at-weeks-16-and-52-in-ixekizumab-treated-biological-naive-patients-with-radiographic-axial-spondyloarthritis-achieving-clinically-important-pain-a/